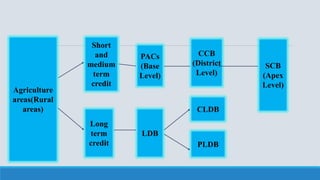
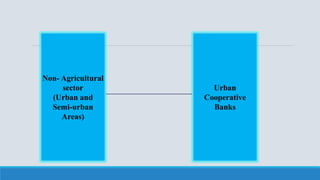
This document provides an overview of banking cooperatives, including their structure, features, objectives, importance, functions, principles, and products/services. It discusses how cooperative banks are owned and controlled democratically by their members. They aim to serve members' needs rather than maximize profits. The document also summarizes the structure of cooperative banking in India and provides examples of specific cooperative banks in India, including their history and objectives.