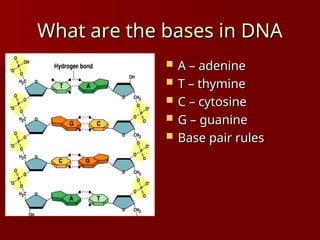
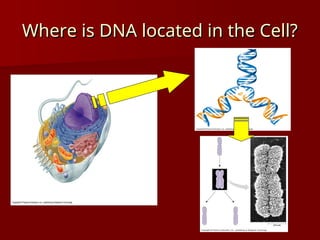
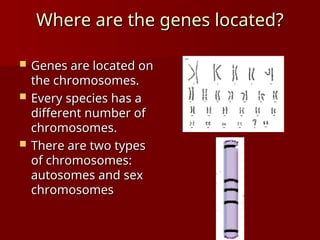
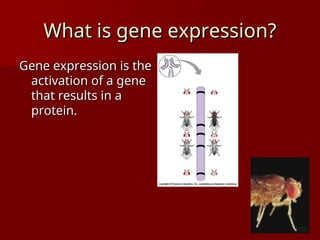
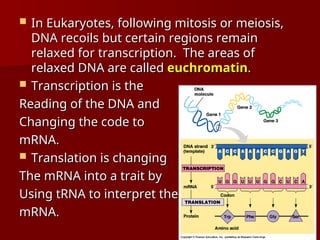
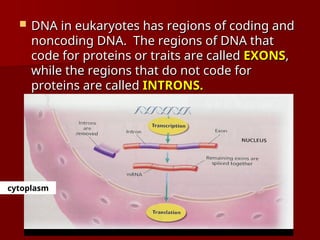
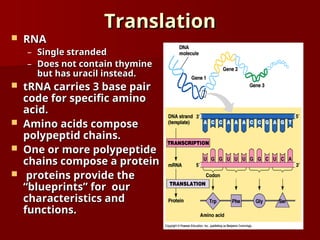
DNA is a double helix structure located in the nucleus that carries genetic information and consists of nucleotides, which include bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. Gene expression involves the activation of genes to produce proteins, with processes differing between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and is characterized by transcription and translation events. Eukaryotic DNA contains coding (exons) and noncoding (introns) regions, while prokaryotic processes occur in the cytoplasm.