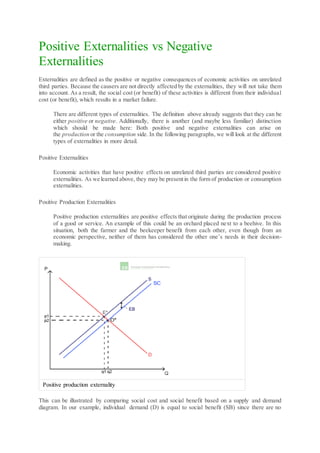
This document discusses positive and negative externalities, which are the positive or negative consequences of economic activities on unrelated third parties. It provides examples of how externalities can arise from production or consumption. Positive externalities result in an undersupply of beneficial goods, while negative externalities lead to an oversupply of harmful goods, causing market failures. The document illustrates these concepts using supply and demand diagrams to compare social costs and benefits to individual costs and benefits.