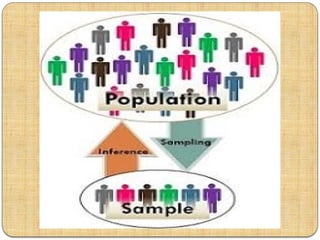
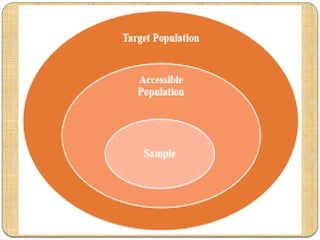
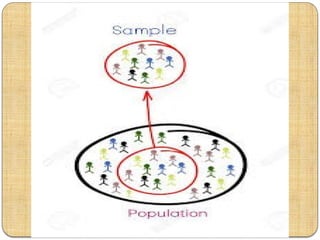
The document explains the concepts of population and sampling in research, distinguishing between target and accessible populations. It discusses the definition of a sample as a representative unit of the target population and outlines principles of sampling, including statistical regularity and optimization. Additionally, it highlights the differences between population and sample in terms of characteristics, data collection methods, and inference-making.