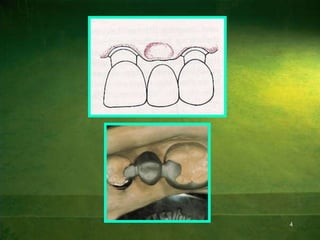
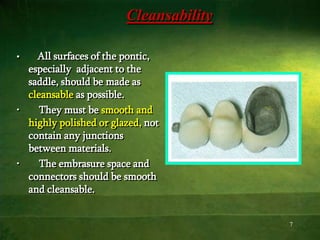
This document discusses the principles and considerations for pontic design in fixed partial dentures. It defines a pontic as an artificial tooth that replaces a missing tooth and restores function. The key factors in pontic design are biological considerations to maintain healthy tissue, esthetic considerations to replicate the natural tooth, and mechanical considerations for strength and durability. Different pontic designs are described based on their relationship to soft tissues and the materials used. The ideal pontic design depends on the location in the mouth and priorities of esthetics, function, and oral hygiene.