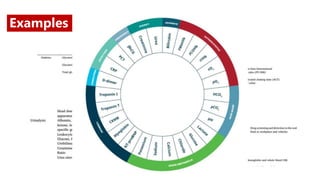
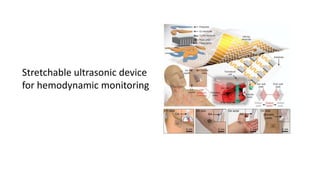
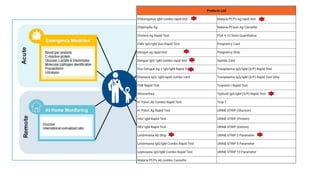
The document discusses the importance and advantages of point of care testing (POCT) in pediatric emergency medicine, emphasizing its role in improving patient care through rapid diagnosis and treatment decisions. It outlines various applications of POCT in managing diseases such as diabetes, sepsis, and COVID-19, along with its benefits in resource-limited settings. Additionally, it highlights the need for effective training and quality evaluation to ensure the proper use of POCT in healthcare environments.