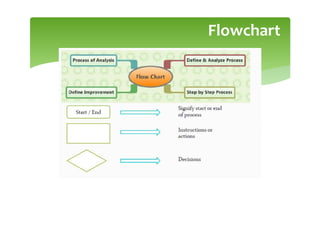
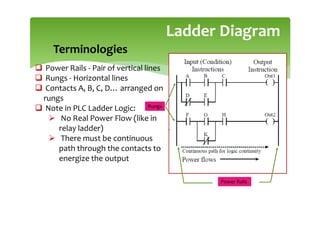
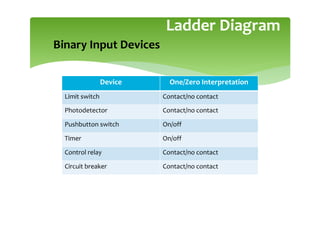
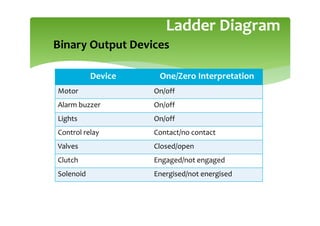
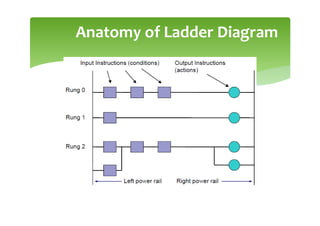
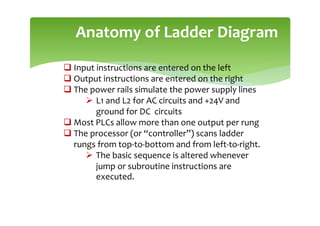
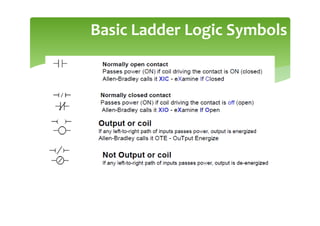
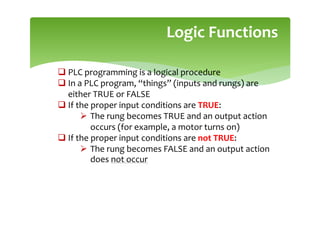
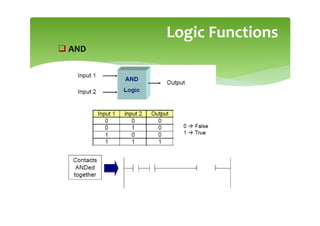
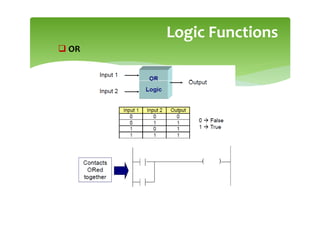
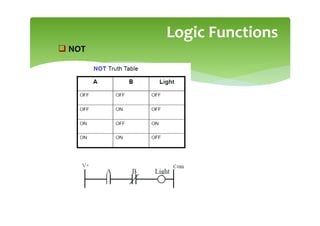
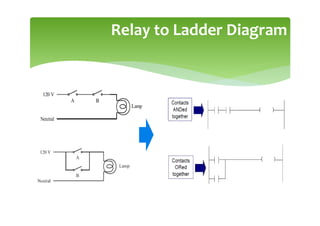
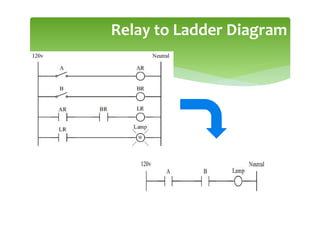
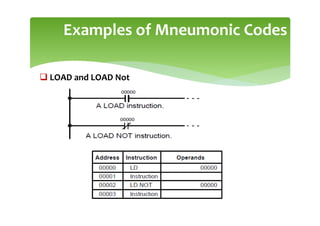
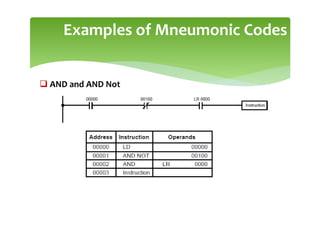
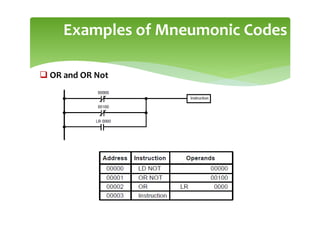
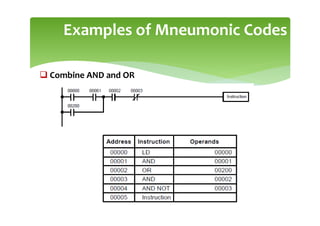
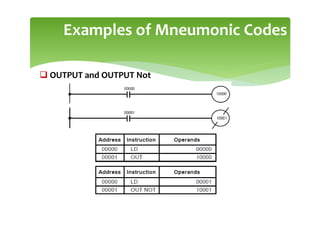
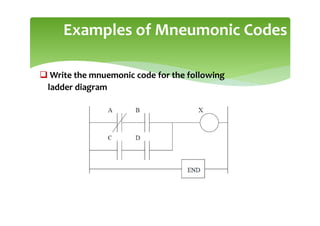
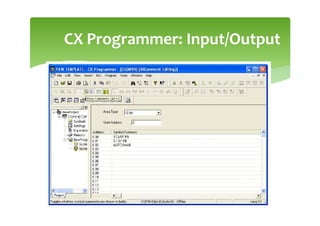
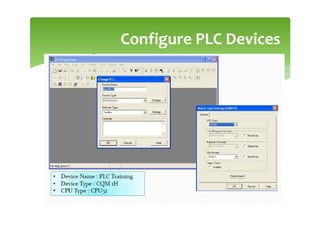
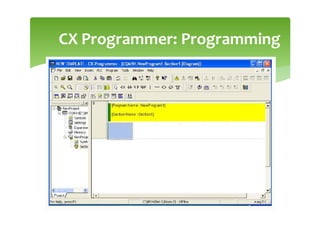
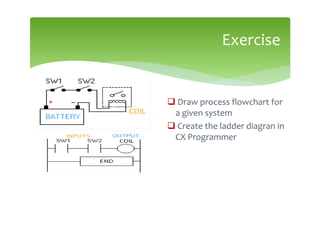
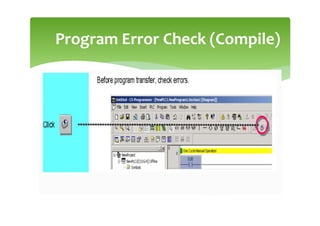
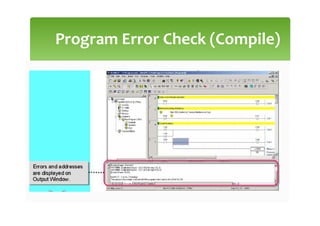
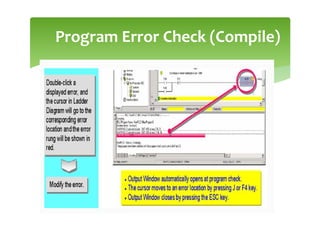
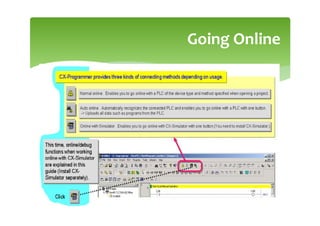
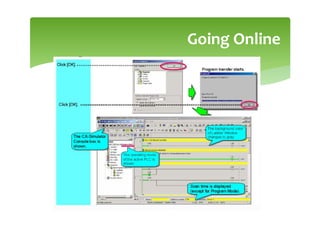
This document provides an overview of basic PLC programming concepts including ladder logic diagrams, logic functions like AND and OR, mnemonic codes, and the CX-Programmer software. Ladder diagrams are the primary programming language and are based on relay logic, with rungs and contacts. PLCs use binary input and output devices that are either on or off. CX-Programmer is Omron software that allows creating and editing ladder programs through a drag and drop interface.