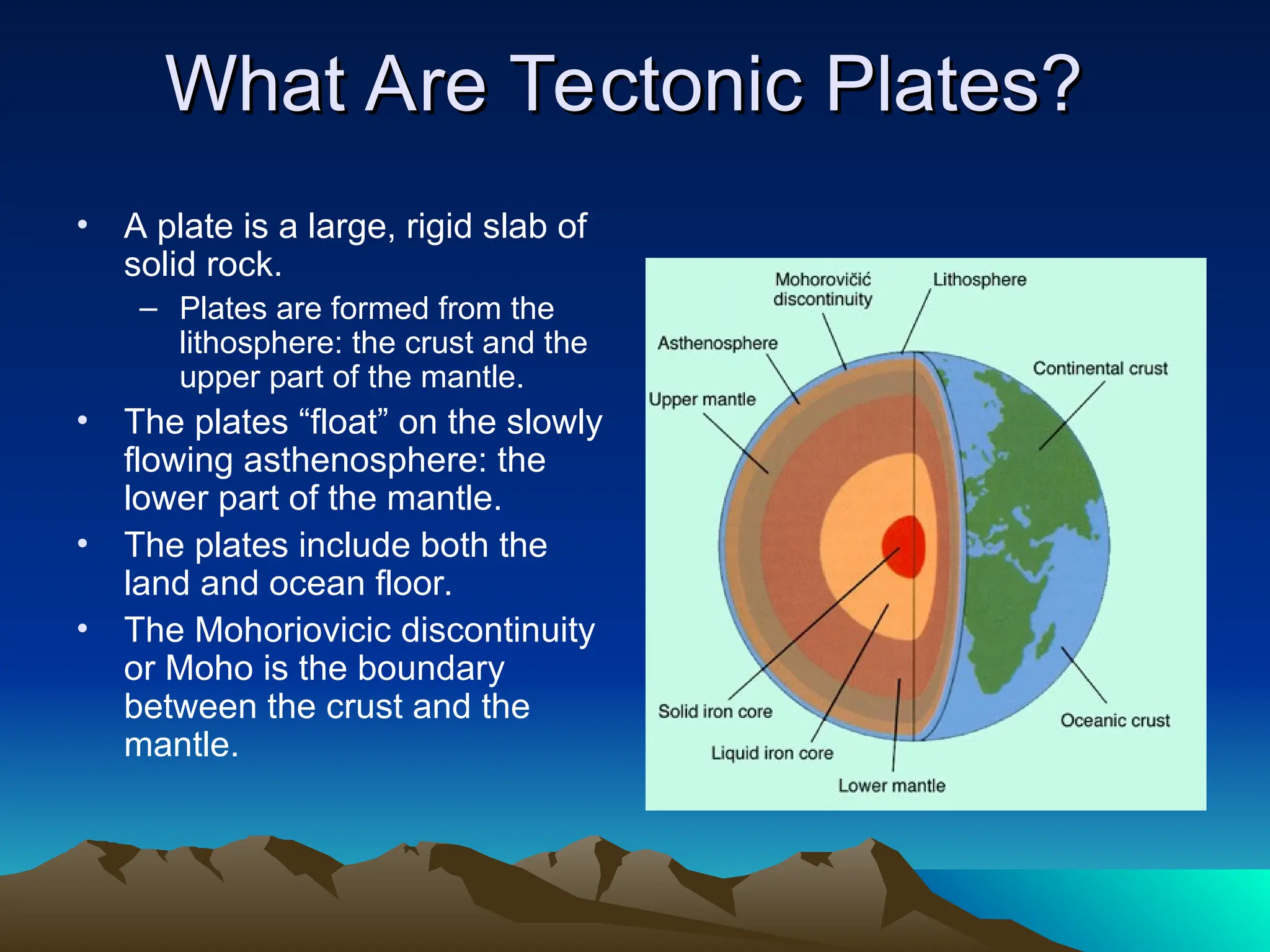
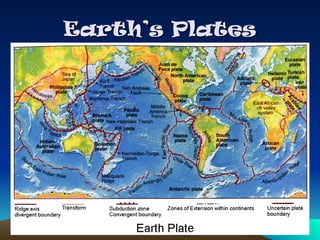
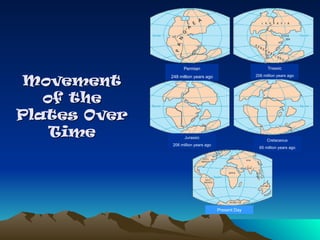
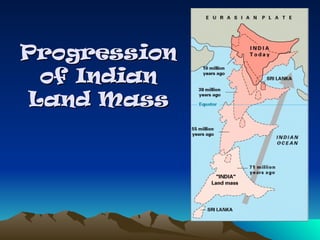
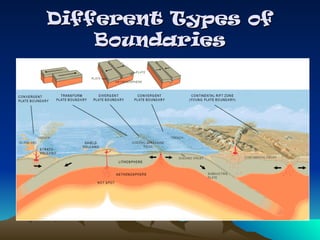
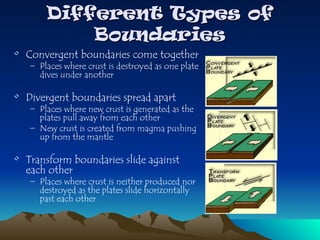
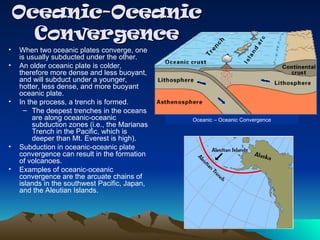
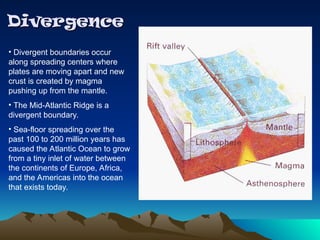
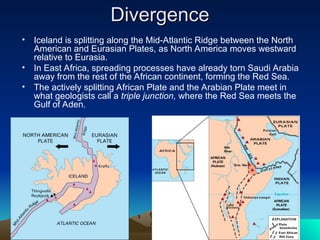
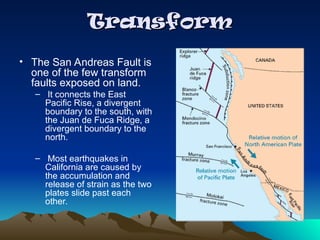
Tectonic plates are large, rigid slabs of solid rock that float on the asthenosphere and include both land and ocean floors. Their movement is driven by convection currents in the mantle, resulting in three types of boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform, each playing a role in geological activity such as earthquakes and the formation of mountains and trenches. Notable examples of tectonic interactions include the collision that formed the Himalayas and the divergent movement at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.