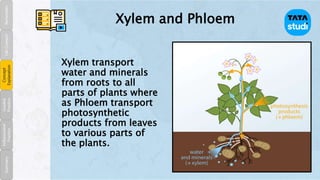
- The xylem and phloem tissues are responsible for transporting water, minerals, and food throughout plants.
- Xylem transports water and minerals from the roots to all parts of the plant. It is composed of dead cells with thick cell walls.
- Phloem transports photosynthetic products like sugar from leaves to all parts of the plant. It is composed of living cells with thin cell walls.
- Together, xylem and phloem allow plants to absorb and distribute nutrients and food throughout their systems.