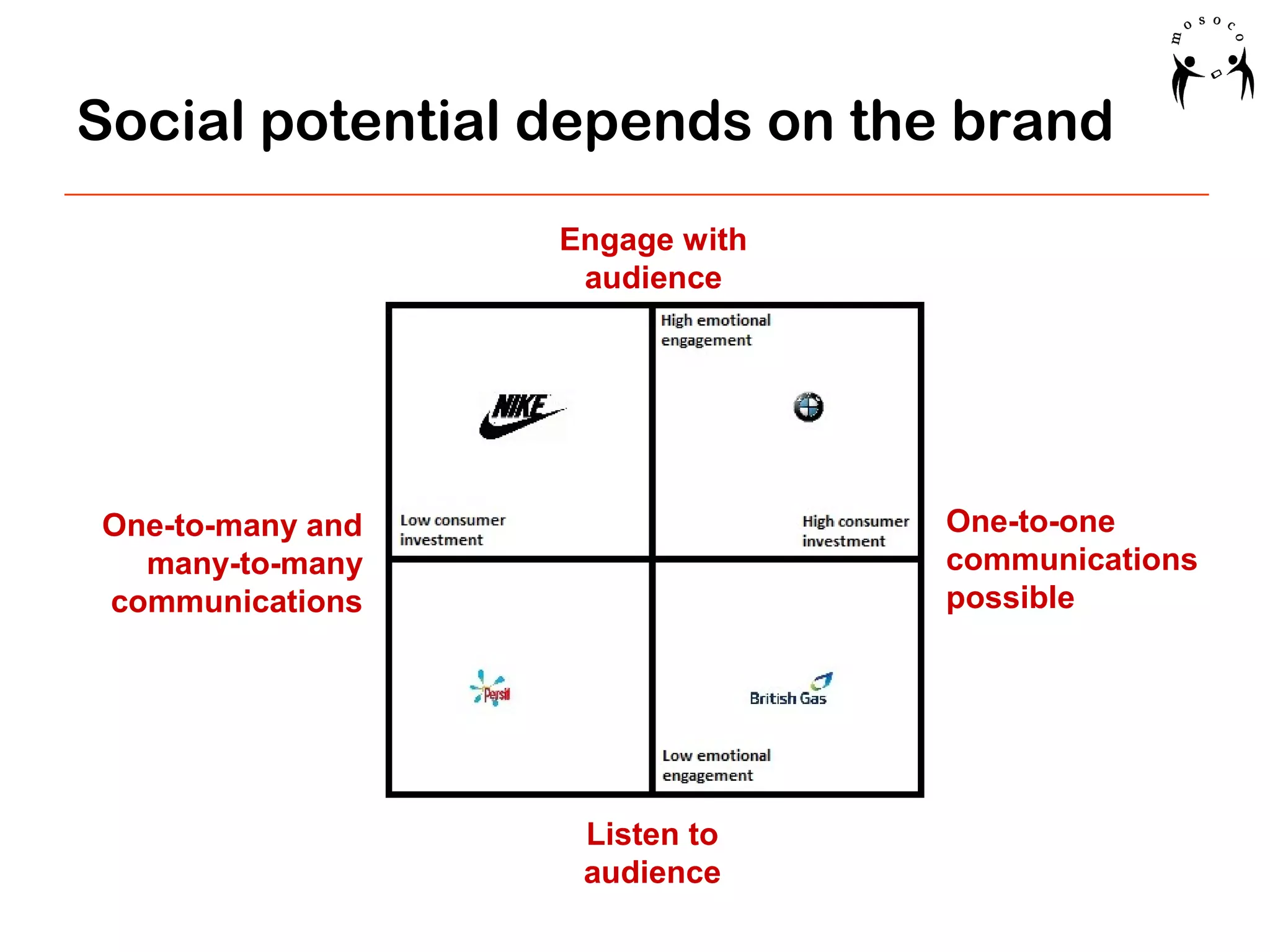
The document outlines strategies for planning successful social media marketing campaigns, emphasizing the importance of integrating marketing activities, audience engagement, and content creation. It details the distribution of effort across planning, content generation, and engagement, along with the significance of measuring ROI and understanding audience dynamics. Key elements include creating relevant content, leveraging influencer partnerships, and optimizing user experience across various platforms.