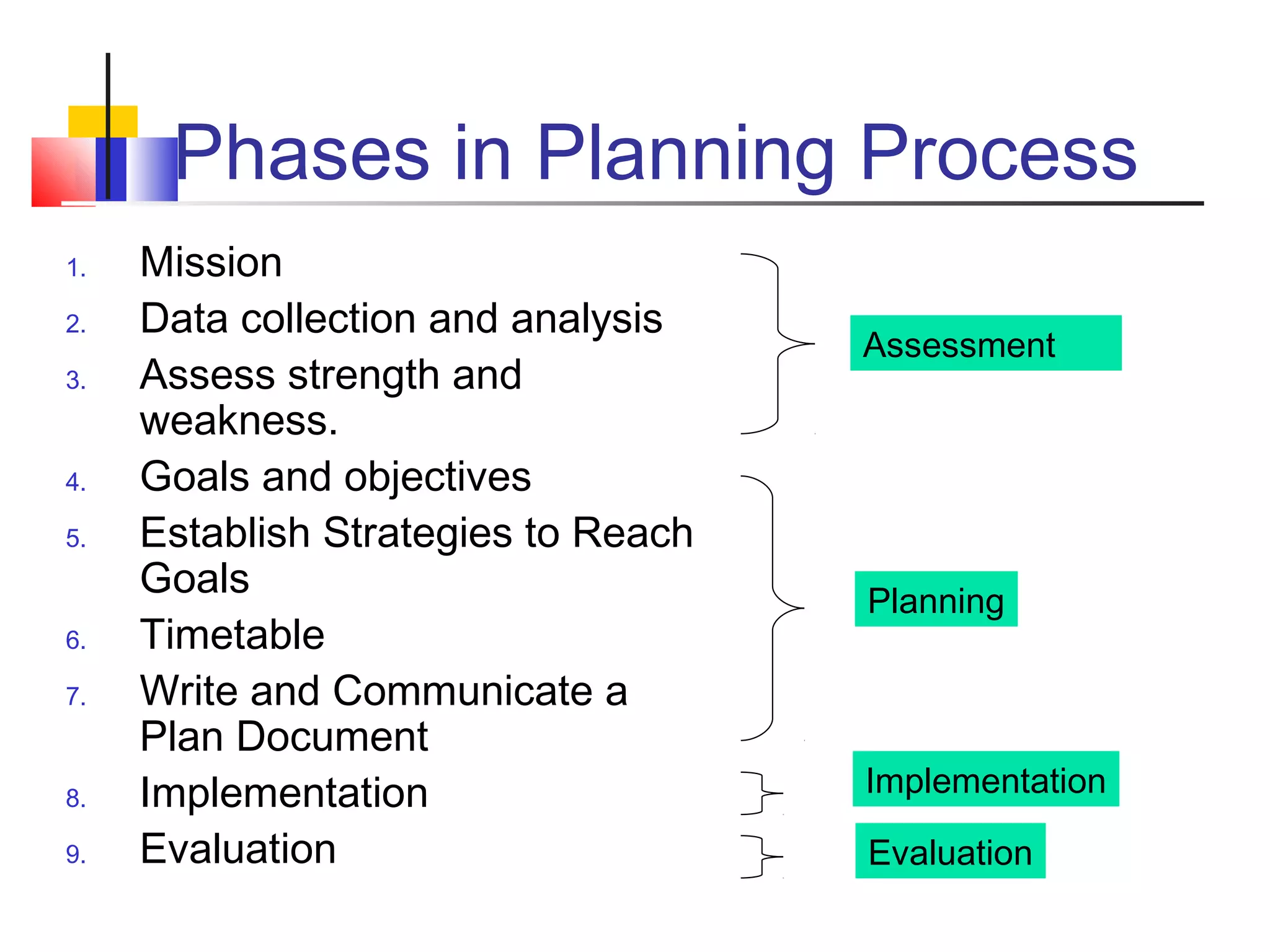
Planning is a core management function and continuous process that involves setting goals and objectives, developing strategies to achieve them, implementing the plan, reviewing outcomes, and providing feedback. The planning process includes collecting internal and external data, conducting a SWOT analysis, establishing goals and objectives aligned with the organization's mission, developing strategies and timelines, documenting the plan, implementing it, and evaluating results through formative and summative methods. Barriers to effective planning include lack of skills, focus on short-term operations over long-term vision, and inadequate support. Key elements of successful planning are involvement of stakeholders, establishing SMART objectives, building in accountability, and ongoing review and revision of the plan.