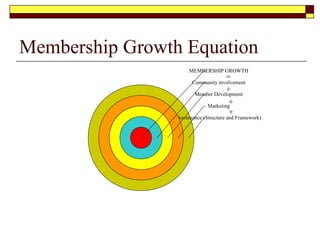
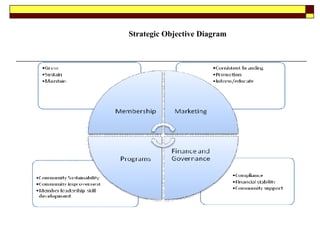
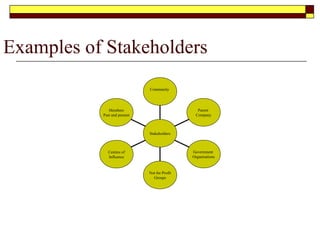
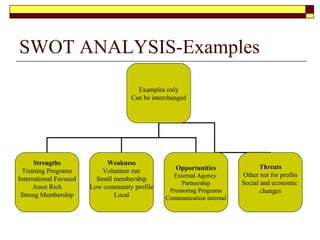
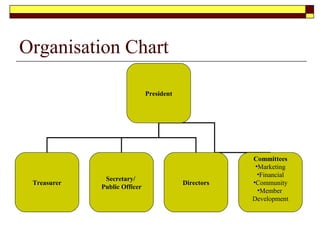
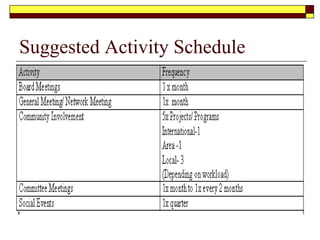
This document provides guidance on developing a strategic plan for a not-for-profit club. It outlines key components of an effective plan, including defining the vision, values, and mission. The plan should identify strategic objectives, stakeholders, and goals. It also describes conducting a SWOT analysis and developing an organizational chart, activity schedule, and membership involvement strategy. The final steps are consolidating individual action plans, communicating the completed plan to members, and providing resources to support the planning process.