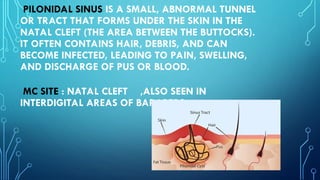
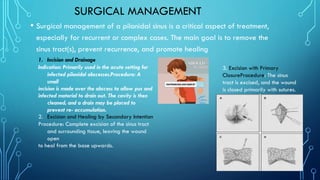
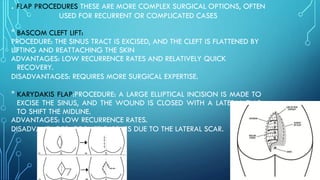
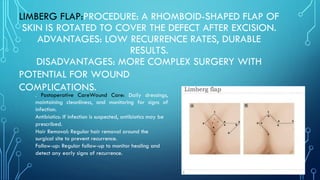
Pilonidal sinus is an abnormal tract under the skin in the natal cleft area, commonly caused by hair penetrating the skin and leading to infections. Surgical management is essential for recurrent cases, with procedures ranging from incision and drainage to more complex flap procedures like the Bascom cleft lift and Karydakis flap, aimed at removing the sinus tract and preventing recurrence. Postoperative care includes wound care, potential use of antibiotics, hair removal at the surgical site, and regular follow-ups to monitor healing.