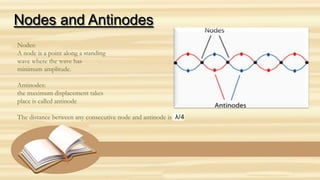
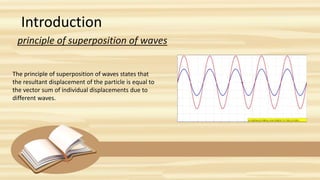
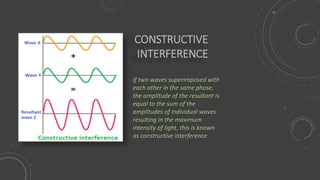
This document discusses the principle of superposition of waves and the formation of stationary waves. It defines superposition of waves as the vector sum of individual displacements from different waves. There are two types of interference - constructive and destructive - depending on whether the waves are in phase or out of phase. A stationary wave is formed when two progressive waves of the same amplitude and wavelength travel in opposite directions. The stationary wave has nodes where the amplitude is minimum and antinodes where it is maximum.

![Presented by : [SECTION M2] Yukesh Gautam
Sirson Sharma
Ujjwal Shah
Shreeyansh Poudel
Sarthak Rijal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspresentationyukesh-230204192705-a7d11c3a/85/physics-presentation-yukesh-pptx-2-320.jpg)





![from the principle of superposition,
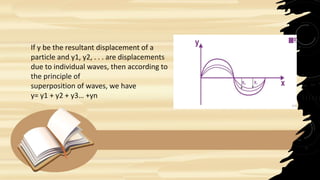
= y1 + y2
= a sin (ωt – kx) + a sin (ωt + kx)
= a [sin (ωt – kx) + a sin (ωt + kx)] Applying formula sinC+sinD
y = 2a cos kx. sinωt
y = A sinωt . . . (3)
Equation (3) represents a simple harmonic wave whose amplitude is A = 2a
cos kx. It is evident that, for different values of x, the amplitude will have
different values. Obviously, the frequency of stationary wave is equal to the
interfering waves i.e. there is no change in frequency.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspresentationyukesh-230204192705-a7d11c3a/85/physics-presentation-yukesh-pptx-12-320.jpg)