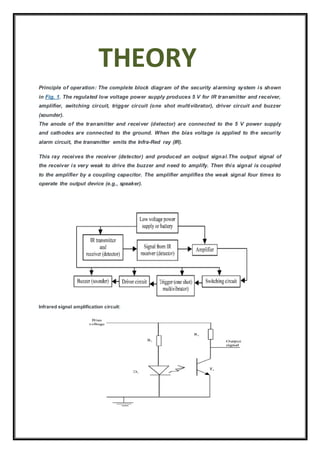
This certificate certifies that Akash Dixit and Yogesh Malik, students of class XII-B, successfully completed a physics investigatory project on an infrared sensor-based security system under the guidance of their teacher Mr. S.V. Singh during the 2016-2017 school year. The project involved building an infrared sensor security system and studying its working principles and ability to detect intruders.