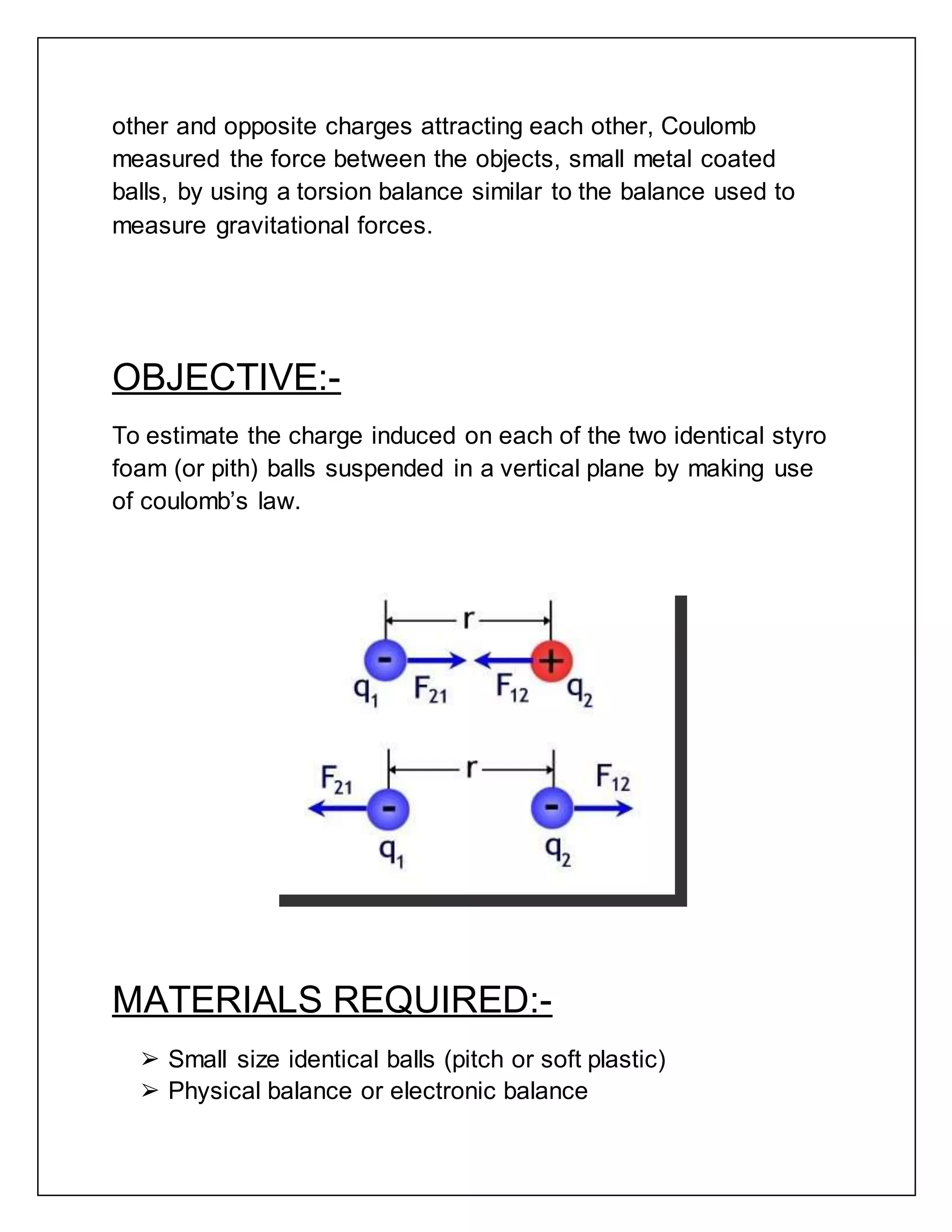
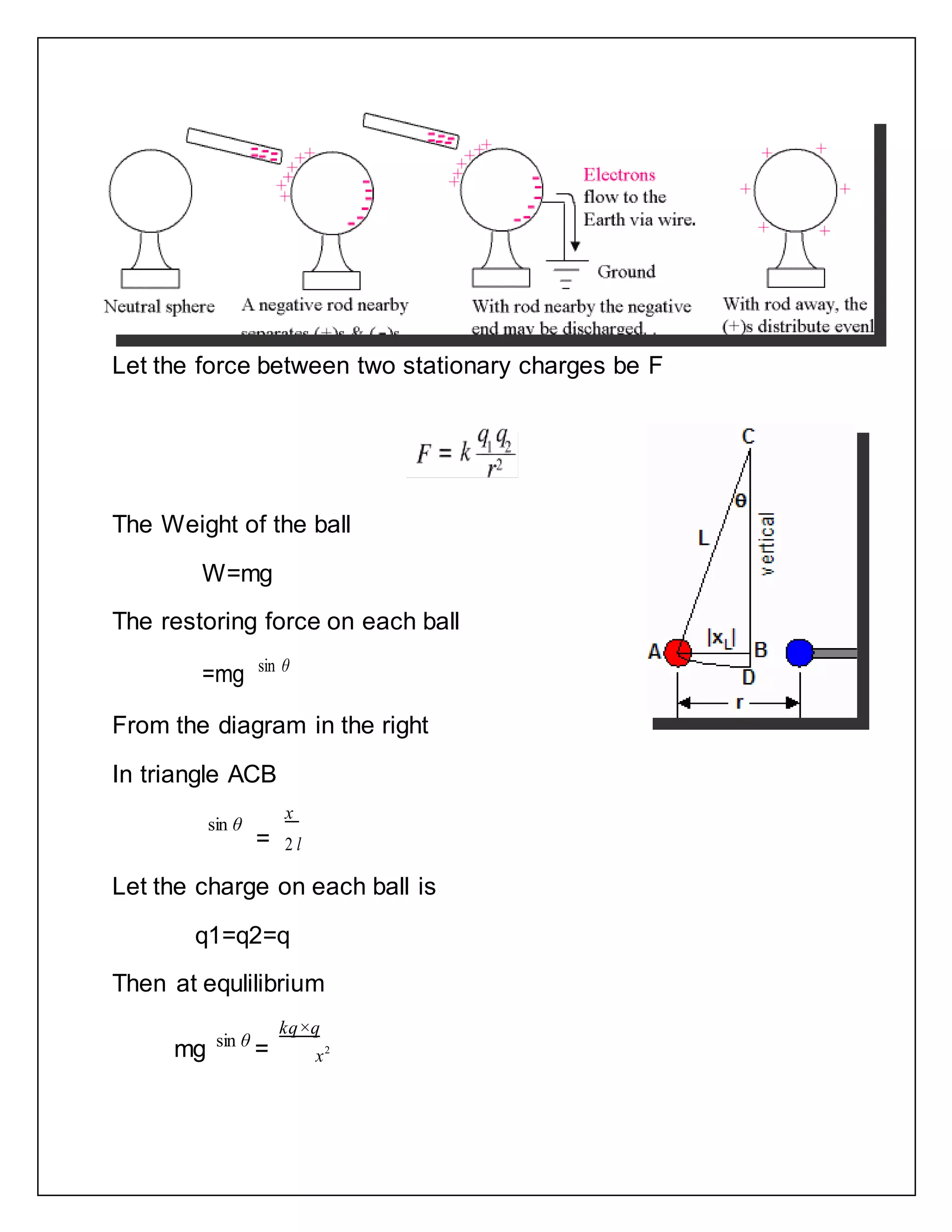
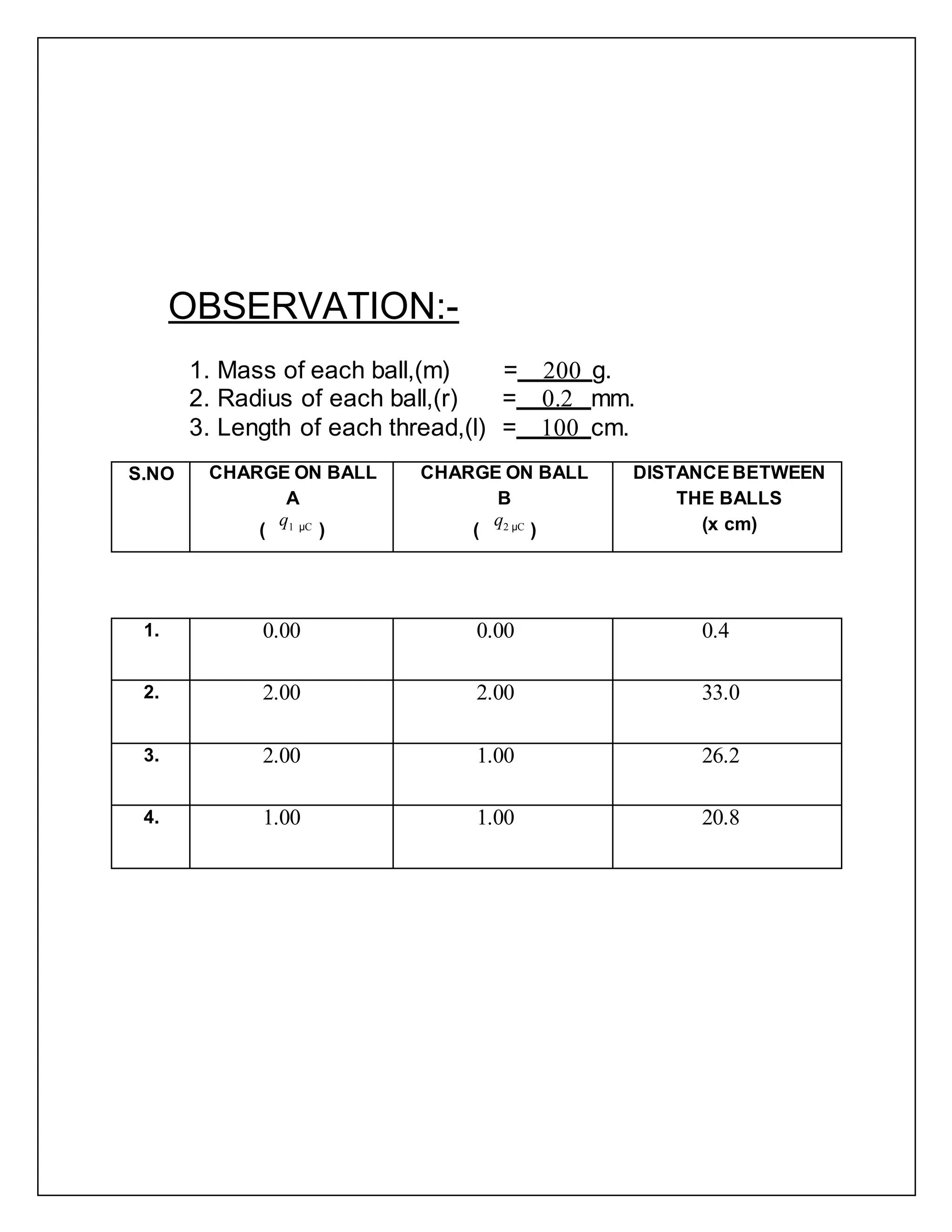
The document reports on a physics project to estimate the charge induced on two identical styrofoam balls suspended in a vertical plane using Coulomb's Law. It provides background on Coulomb's Law and the theory of electrostatics. It then describes the materials, procedure, observations, calculations, results, and sources of error for the experiment.