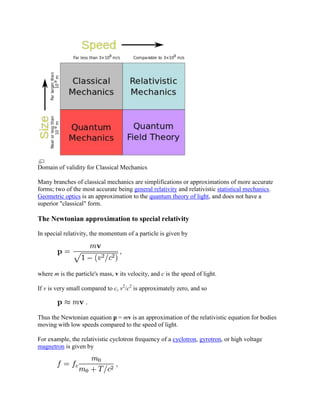
Classical mechanics is the branch of physics that describes the motion of macroscopic objects. It is based on Newton's laws of motion and law of universal gravitation. Classical mechanics provides accurate results for large objects moving at non-relativistic speeds. When dealing with very small objects or speeds approaching the speed of light, quantum mechanics and special relativity are required. Classical mechanics includes formulations like Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics that extend Newton's original work.
![Physics (from Ancient Greek: φύσις physis "nature") is a natural science that involves the study
of matter[1] and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy
and force.[2] More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand
how the universe behaves.[3][4][5]
Science (from Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes
knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.[1] In an older and
closely related meaning (found, for example, in Aristotle), "science" refers to the body of reliable
knowledge itself, of the type that can be logically and rationally explained (see History and philosophy
below).[2] Since classical antiquity science as a type of knowledge was closely linked to philosophy. In the
early modern era the words "science" and "philosophy" were sometimes used interchangeably in the
English language. By the 17th century, natural philosophy (which is today called "natural science") was
considered a separate branch of philosophy.[3] However, "science" continued to be used in a broad
sense denoting reliable knowledge about a topic, in the same way it is still used in modern terms such as
library science or political science.
The branches of science (which are also referred to as "sciences", "scientific fields", or "scientific
disciplines") are commonly divided into two major groups: natural sciences, which study natural
phenomena (including biological life), and social sciences, which study human behavior and societies.
These groupings are empirical sciences, which means the knowledge must be based on observable
phenomena and capable of being tested for its validity by other researchers working under the same
conditions.[1] There are also related disciplines that are grouped into interdisciplinary and applied
sciences, such as engineering and medicine. Within these categories are specialized scientific fields that
can include parts of other scientific disciplines but often possess their own terminology and expertise.[2]
PHYSICS
Physics is the science of matter and energy, and the movement and interactions between them
both.
The most popular branches of physics are:
mechanics
electromagnetism
heat and thermodynamics
atomic theory
relativity
astrophysics
theoretical physics
optics, geophysics
biophysics
particle physics
sound
light
atomic and molecular physics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/75/Physics-1-2048.jpg)
![nuclear physics
solid state physics
plasma physics
geophysics
biophysics
The two main branches are : 1) Classical Mechanics 2) Quantum MechanicsThis article is about the
physics sub-field. For the book written by Herbert Goldstein and others, see Classical Mechanics
(book).
Classical mechanics
History of classical mechanics
Timeline of classical mechanics
Branches[show]
Formulations[show]
Fundamental concepts[show]
Core topics[show]
Scientists[show]
v
t
e
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is
concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a
system of forces. The study of the motion of bodies is an ancient one, making classical
mechanics one of the oldest and largest subjects in science, engineering and technology.
Classical mechanics describes the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of
machinery, as well as astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies.
Besides this, many specializations within the subject deal with gases, liquids, solids, and other
specific sub-topics. Classical mechanics provides extremely accurate results as long as the
domain of study is restricted to large objects and the speeds involved do not approach the speed
of light. When the objects being dealt with become sufficiently small, it becomes necessary to](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-2-320.jpg)
![introduce the other major sub-field of mechanics, quantum mechanics, which reconciles the
macroscopic laws of physics with the atomic nature of matter and handles the wave–particle
duality of atoms and molecules. In the case of high velocity objects approaching the speed of
light, classical mechanics is enhanced by special relativity. General relativity unifies special
relativity with Newton's law of universal gravitation, allowing physicists to handle gravitation at
a deeper level.
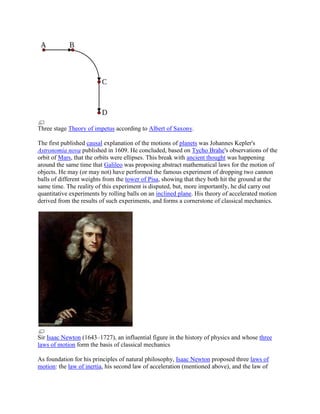
The term classical mechanics was coined in the early 20th century to describe the system of
physics begun by Isaac Newton and many contemporary 17th century natural philosophers,
building upon the earlier astronomical theories of Johannes Kepler, which in turn were based on
the precise observations of Tycho Brahe and the studies of terrestrial projectile motion of
Galileo. Since these aspects of physics were developed long before the emergence of quantum
physics and relativity, some sources exclude Einstein's theory of relativity from this category.
However, a number of modern sources do include relativistic mechanics, which in their view
represents classical mechanics in its most developed and most accurate form.[note 1]
The initial stage in the development of classical mechanics is often referred to as Newtonian
mechanics, and is associated with the physical concepts employed by and the mathematical
methods invented by Newton himself, in parallel with Leibniz, and others. This is further
described in the following sections. Later, more abstract and general methods were developed,
leading to reformulations of classical mechanics known as Lagrangian mechanics and
Hamiltonian mechanics. These advances were largely made in the 18th and 19th centuries, and
they extend substantially beyond Newton's work, particularly through their use of analytical
mechanics. Ultimately, the mathematics developed for these were central to the creation of
quantum mechanics.
Contents
1 History
2 Description of the theory
o 2.1 Position and its derivatives
2.1.1 Velocity and speed
2.1.2 Acceleration
2.1.3 Frames of reference
o 2.2 Forces; Newton's second law
o 2.3 Work and energy
o 2.4 Beyond Newton's laws
3 Limits of validity
o 3.1 The Newtonian approximation to special relativity
o 3.2 The classical approximation to quantum mechanics
4 Branches
5 See also
6 Notes
7 References
8 Further reading](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-3-320.jpg)
![9 External links
History
Main article: History of classical mechanics
See also: Timeline of classical mechanics
Classical Physics
Wave equation
History of physics
Founders[show]
Branches[show]
Scientists[show]
v
t
e
Some Greek philosophers of antiquity, among them Aristotle, founder of Aristotelian physics,
may have been the first to maintain the idea that "everything happens for a reason" and that
theoretical principles can assist in the understanding of nature. While to a modern reader, many
of these preserved ideas come forth as eminently reasonable, there is a conspicuous lack of both
mathematical theory and controlled experiment, as we know it. These both turned out to be
decisive factors in forming modern science, and they started out with classical mechanics.
The medieval "science of weights" (i.e., mechanics) owes much of its importance to the work of
Jordanus de Nemore. In the Elementa super demonstrationem ponderum, he introduces the
concept of "positional gravity" and the use of component forces.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-4-320.jpg)
![action and reaction; and hence laid the foundations for classical mechanics. Both Newton's
second and third laws were given proper scientific and mathematical treatment in Newton's
Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, which distinguishes them from earlier attempts at
explaining similar phenomena, which were either incomplete, incorrect, or given little accurate
mathematical expression. Newton also enunciated the principles of conservation of momentum
and angular momentum. In mechanics, Newton was also the first to provide the first correct
scientific and mathematical formulation of gravity in Newton's law of universal gravitation. The
combination of Newton's laws of motion and gravitation provide the fullest and most accurate
description of classical mechanics. He demonstrated that these laws apply to everyday objects as
well as to celestial objects. In particular, he obtained a theoretical explanation of Kepler's laws of
motion of the planets.
Newton previously invented the calculus, of mathematics, and used it to perform the
mathematical calculations. For acceptability, his book, the Principia, was formulated entirely in
terms of the long-established geometric methods, which were soon to be eclipsed by his calculus.
However it was Leibniz who developed the notation of the derivative and integral preferred[citation
needed]
today.
Hamilton's greatest contribution is perhaps the reformulation of Newtonian mechanics, now
called Hamiltonian mechanics.
Newton, and most of his contemporaries, with the notable exception of Huygens, worked on the
assumption that classical mechanics would be able to explain all phenomena, including light, in
the form of geometric optics. Even when discovering the so-called Newton's rings (a wave
interference phenomenon) his explanation remained with his own corpuscular theory of light.
After Newton, classical mechanics became a principal field of study in mathematics as well as
physics. After Newton there were several re-formulations which progressively allowed a solution
to be found to a far greater number of problems. The first notable re-formulation was in 1788 by
Joseph Louis Lagrange. Lagrangian mechanics was in turn re-formulated in 1833 by William
Rowan Hamilton.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-6-320.jpg)
![Some difficulties were discovered in the late 19th century that could only be resolved by more
modern physics. Some of these difficulties related to compatibility with electromagnetic theory,
and the famous Michelson–Morley experiment. The resolution of these problems led to the
special theory of relativity, often included in the term classical mechanics.
A second set of difficulties were related to thermodynamics. When combined with
thermodynamics, classical mechanics leads to the Gibbs paradox of classical statistical
mechanics, in which entropy is not a well-defined quantity. Black-body radiation was not
explained without the introduction of quanta. As experiments reached the atomic level, classical
mechanics failed to explain, even approximately, such basic things as the energy levels and sizes
of atoms and the photo-electric effect. The effort at resolving these problems led to the
development of quantum mechanics.
Since the end of the 20th century, the place of classical mechanics in physics has been no longer
that of an independent theory. Instead, classical mechanics is now considered to be an
approximate theory to the more general quantum mechanics. Emphasis has shifted to
understanding the fundamental forces of nature as in the Standard model and its more modern
extensions into a unified theory of everything.[1] Classical mechanics is a theory for the study of
the motion of non-quantum mechanical, low-energy particles in weak gravitational fields. In the
21st century classical mechanics has been extended into the complex domain and complex
classical mechanics exhibits behaviors very similar to quantum mechanics.[2]
Description of the theory
The analysis of projectile motion is a part of classical mechanics.
The following introduces the basic concepts of classical mechanics. For simplicity, it often
models real-world objects as point particles, objects with negligible size. The motion of a point
particle is characterized by a small number of parameters: its position, mass, and the forces
applied to it. Each of these parameters is discussed in turn.
In reality, the kind of objects that classical mechanics can describe always have a non-zero size.
(The physics of very small particles, such as the electron, is more accurately described by](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-7-320.jpg)

![energy kg·m2·s−2
power kg·m2·s−3
pressure and energy density kg·m−1·s−2
surface tension kg·s−2
spring constant kg·s−2
irradiance and energy flux kg·s−3
kinematic viscosity m2·s−1
dynamic viscosity kg·m−1·s−1
density (mass density) kg·m−3
density (weight density) kg·m−2·s−2
number density m−3
action kg·m2·s−1
The position of a point particle is defined with respect to an arbitrary fixed reference point, O, in
space, usually accompanied by a coordinate system, with the reference point located at the origin
of the coordinate system. It is defined as the vector r from O to the particle. In general, the point
particle need not be stationary relative to O, so r is a function of t, the time elapsed since an
arbitrary initial time. In pre-Einstein relativity (known as Galilean relativity), time is considered
an absolute, i.e., the time interval between any given pair of events is the same for all observers.
In addition to relying on absolute time, classical mechanics assumes Euclidean geometry for the
structure of space.[3]
Velocity and speed
Main articles: Velocity and speed
The velocity, or the rate of change of position with time, is defined as the derivative of the
position with respect to time or
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-9-320.jpg)



![is known that particle A exerts a force F on another particle B, it follows that B must exert an
equal and opposite reaction force, −F, on A. The strong form of Newton's third law requires that
F and −F act along the line connecting A and B, while the weak form does not. Illustrations of
the weak form of Newton's third law are often found for magnetic forces.
Work and energy
Main articles: Work (physics), kinetic energy, and potential energy
If a constant force F is applied to a particle that achieves a displacement Δr,[note 2] the work done
by the force is defined as the scalar product of the force and displacement vectors:
More generally, if the force varies as a function of position as the particle moves from r1 to r2
along a path C, the work done on the particle is given by the line integral
If the work done in moving the particle from r1 to r2 is the same no matter what path is taken, the
force is said to be conservative. Gravity is a conservative force, as is the force due to an idealized
spring, as given by Hooke's law. The force due to friction is non-conservative.
The kinetic energy Ek of a particle of mass m travelling at speed v is given by
For extended objects composed of many particles, the kinetic energy of the composite body is
the sum of the kinetic energies of the particles.
The work–energy theorem states that for a particle of constant mass m the total work W done on
the particle from position r1 to r2 is equal to the change in kinetic energy Ek of the particle:
Conservative forces can be expressed as the gradient of a scalar function, known as the potential
energy and denoted Ep:
If all the forces acting on a particle are conservative, and Ep is the total potential energy (which is
defined as a work of involved forces to rearrange mutual positions of bodies), obtained by
summing the potential energies corresponding to each force](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-13-320.jpg)




![Electrical Force
o Electrical force is an attraction between positively and negatively charged objects.
The closer the objects are to each other, the higher the electrical force.
Magnetic Force
o Magnetic force is an attraction force usually associated with electrical currents
and magnets. Magnetic force attracts opposite forces. Each magnet has a north
and a south end, each of which attracts the opposite ends of another magnet. For
example, a north magnetic end will attract a south magnetic end, and vice versa.
North ends of magnets repel each other, and vice versa. Magnets also create an
attractive force with certain metals.
Upthrust Force
o Upthrust is more commonly known as buoyancy. This is the upward thrust that is
caused by fluid pressure on objects, such as the pressure that allows boats to float.
Read more: Ten Different Types of Forces | eHow.com http://www.ehow.com/list_7459343_ten-
different-types-forces.html#ixzz2CfShdh8d
Average power
As a simple example, burning a kilogram of coal releases much more energy than does
detonating a kilogram of TNT,[3] but because the TNT reaction releases energy much more
quickly, it delivers far more power than the coal. If ΔW is the amount of work performed during
a period of time of duration Δt, the average power Pavg over that period is given by the formula
It is the average amount of work done or energy converted per unit of time. The average power is
often simply called "power" when the context makes it clear.
The instantaneous power is then the limiting value of the average power as the time interval Δt
approaches zero.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-20-320.jpg)


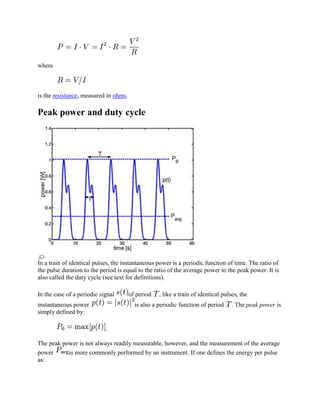
![then the average power is:
.
One may define the pulse length such that so that the ratios
are equal. These ratios are called the duty cycle of the pulse train.
A free body diagram, also called a force diagram,[1] is a pictorial representation
often used by physicists and engineers to analyze the forces acting on a body of
interest. A free body diagram shows all forces of all types acting on this body.
Drawing such a diagram can aid in solving for the unknown forces or the
equations of motion of the body. Creating a free body diagram can make it easier
to understand the forces, and torques or moments, in relation to one another and
suggest the proper concepts to apply in order to find the solution to a problem.
The diagrams are also used as a conceptual device to help identify the internal
forces—for example, shear forces and bending moments in beams—which are
developed within structures.[2][3] Number of sides
Polygons are primarily classified by the number of sides. See table below.
Convexity and types of non-convexity
Polygons may be characterized by their convexity or type of non-convexity:
Convex: any line drawn through the polygon (and not tangent to an edge or corner) meets
its boundary exactly twice. Equivalently, all its interior angles are less than 180°.
Non-convex: a line may be found which meets its boundary more than twice. In other
words, it contains at least one interior angle with a measure larger than 180°.
Simple: the boundary of the polygon does not cross itself. All convex polygons are
simple.
Concave: Non-convex and simple.
Star-shaped: the whole interior is visible from a single point, without crossing any edge.
The polygon must be simple, and may be convex or concave.
Self-intersecting: the boundary of the polygon crosses itself. Branko Grünbaum calls
these coptic, though this term does not seem to be widely used. The term complex is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-24-320.jpg)
![sometimes used in contrast to simple, but this risks confusion with the idea of a complex
polygon as one which exists in the complex Hilbert plane consisting of two complex
dimensions.
Star polygon: a polygon which self-intersects in a regular way.
Symmetry
Equiangular: all its corner angles are equal.
Cyclic: all corners lie on a single circle.
Isogonal or vertex-transitive: all corners lie within the same symmetry orbit. The
polygon is also cyclic and equiangular.
Equilateral: all edges are of the same length. (A polygon with 5 or more sides can be
equilateral without being convex.) [1]
Isotoxal or edge-transitive: all sides lie within the same symmetry orbit. The polygon is
also equilateral.
Tangential: all sides are tangent to an inscribed circle.
Regular: A polygon is regular if it is both cyclic and equilateral. A non-convex regular
polygon is called a regular star polygon.
Miscellaneous
Rectilinear: a polygon whose sides meet at right angles, i.e., all its interior angles are 90
or 270 degrees.
Monotone with respect to a given line L, if every line orthogonal to L intersects the
polygon not more than twice.
Properties
Euclidean geometry is assumed throughout.
Angles
Any polygon, regular or irregular, self-intersecting or simple, has as many corners as it has sides.
Each corner has several angles. The two most important ones are:
Interior angle – The sum of the interior angles of a simple n-gon is (n − 2)π radians or (n
− 2)180 degrees. This is because any simple n-gon can be considered to be made up of (n
− 2) triangles, each of which has an angle sum of π radians or 180 degrees. The measure
of any interior angle of a convex regular n-gon is radians or
degrees. The interior angles of regular star polygons were first studied by Poinsot, in the
same paper in which he describes the four regular star polyhedra.
Exterior angle – Tracing around a convex n-gon, the angle "turned" at a corner is the
exterior or external angle. Tracing all the way around the polygon makes one full turn, so
the sum of the exterior angles must be 360°. This argument can be generalized to concave](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-25-320.jpg)
![simple polygons, if external angles that turn in the opposite direction are subtracted from
the total turned. Tracing around an n-gon in general, the sum of the exterior angles (the
total amount one rotates at the vertices) can be any integer multiple d of 360°, e.g. 720°
for a pentagram and 0° for an angular "eight", where d is the density or starriness of the
polygon. See also orbit (dynamics).
The exterior angle is the supplementary angle to the interior angle. From this the sum of the
interior angles can be easily confirmed, even if some interior angles are more than 180°: going
clockwise around, it means that one sometime turns left instead of right, which is counted as
turning a negative amount. (Thus we consider something like the winding number of the
orientation of the sides, where at every vertex the contribution is between −1⁄2 and 1⁄2 winding.)
Area and centroid
Nomenclature of a 2D polygon.
The area of a polygon is the measurement of the 2-dimensional region enclosed by the polygon.
For a non-self-intersecting (simple) polygon with n vertices, the area and centroid are given by:[2]
To close the polygon, the first and last vertices are the same, i.e., xn, yn = x0, y0. The vertices must
be ordered according to positive or negative orientation (counterclockwise or clockwise,
respectively); if they are ordered negatively, the value given by the area formula will be negative
but correct in absolute value. This is commonly called the Surveyor's Formula.[3]
The area formula is derived by taking each edge AB, and calculating the (signed) area of triangle
ABO with a vertex at the origin O, by taking the cross-product (which gives the area of a
parallelogram) and dividing by 2. As one wraps around the polygon, these triangles with positive
and negative area will overlap, and the areas between the origin and the polygon will be
cancelled out and sum to 0, while only the area inside the reference triangle remains. This is why
the formula is called the Surveyor's Formula, since the "surveyor" is at the origin; if going](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-26-320.jpg)
![counterclockwise, positive area is added when going from left to right and negative area is added
when going from right to left, from the perspective of the origin.
The formula was described by Meister[citation needed] in 1769 and by Gauss in 1795. It can be
verified by dividing the polygon into triangles, but it can also be seen as a special case of Green's
theorem.
The area A of a simple polygon can also be computed if the lengths of the sides, a1, a2, ..., an and
the exterior angles, θ1, θ2, ..., θn are known. The formula is
The formula was described by Lopshits in 1963.[4]
If the polygon can be drawn on an equally spaced grid such that all its vertices are grid points,
Pick's theorem gives a simple formula for the polygon's area based on the numbers of interior
and boundary grid points.
In every polygon with perimeter p and area A , the isoperimetric inequality holds.[5]
If any two simple polygons of equal area are given, then the first can be cut into polygonal pieces
which can be reassembled to form the second polygon. This is the Bolyai-Gerwien theorem.
The area of a regular polygon is also given in terms of the radius r of its inscribed circle and its
perimeter p by
.
This radius is also termed its apothem and is often represented as a.
The area of a regular n-gon with side s inscribed in a unit circle is
.
The area of a regular n-gon in terms of the radius r of its circumscribed circle and its perimeter p
is given by
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-27-320.jpg)
![The area of a regular n-gon, inscribed in a unit-radius circle, with side s and interior angle θ can
also be expressed trigonometrically as
.
The sides of a polygon do not in general determine the area.[6] However, if the polygon is cyclic
the sides do determine the area. Of all n-gons with given sides, the one with the largest area is
cyclic. Of all n-gons with a given perimeter, the one with the largest area is regular (and
therefore cyclic).[7]
Self-intersecting polygons
The area of a self-intersecting polygon can be defined in two different ways, each of which gives
a different answer:
Using the above methods for simple polygons, we discover that particular regions within
the polygon may have their area multiplied by a factor which we call the density of the
region. For example the central convex pentagon in the center of a pentagram has density
2. The two triangular regions of a cross-quadrilateral (like a figure 8) have opposite-
signed densities, and adding their areas together can give a total area of zero for the
whole figure.
Considering the enclosed regions as point sets, we can find the area of the enclosed point
set. This corresponds to the area of the plane covered by the polygon, or to the area of a
simple polygon having the same outline as the self-intersecting one (or, in the case of the
cross-quadrilateral, the two simple triangles).
Degrees of freedom
An n-gon has 2n degrees of freedom, including 2 for position, 1 for rotational orientation, and 1
for overall size, so 2n − 4 for shape. In the case of a line of symmetry the latter reduces to n − 2.
Let k ≥ 2. For an nk-gon with k-fold rotational symmetry (Ck), there are 2n − 2 degrees of
freedom for the shape. With additional mirror-image symmetry (Dk) there are n − 1 degrees of
freedom.
Product of distances from a vertex to other vertices of a regular polygon
For a regular n-gon inscribed in a unit-radius circle, the product of the distances from a given
vertex to all other vertices equals n.
Generalizations of polygons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-28-320.jpg)

![exceptions. For large numbers, mathematicians usually write the numeral itself, e.g. 17-gon. A
variable can even be used, usually n-gon. This is useful if the number of sides is used in a
formula.
Some special polygons also have their own names; for example the regular star pentagon is also
known as the pentagram.
Polygon names
Name Edges Remarks
henagon (or In the Euclidean plane, degenerates to a closed curve with a
1
monogon) single vertex point on it.
In the Euclidean plane, degenerates to a closed curve with two
digon 2
vertex points on it.
triangle (or trigon) 3 The simplest polygon which can exist in the Euclidean plane.
quadrilateral (or
quadrangle or 4 The simplest polygon which can cross itself.
tetragon)
The simplest polygon which can exist as a regular star. A star
pentagon 5
pentagon is known as a pentagram or pentacle.
hexagon 6 Avoid "sexagon" = Latin [sex-] + Greek.
Avoid "septagon" = Latin [sept-] + Greek. The simplest
polygon such that the regular form is not constructible with
heptagon 7
compass and straightedge. However, it can be constructed
using a Neusis construction.
octagon 8
"Nonagon" is commonly used but mixes Latin [novem = 9]
enneagon or nonagon 9 with Greek. Some modern authors prefer "enneagon", which is
pure Greek.
decagon 10
Avoid "undecagon" = Latin [un-] + Greek. The simplest
hendecagon 11 polygon such that the regular form cannot be constructed with
compass, straightedge, and angle trisector.
dodecagon 12 Avoid "duodecagon" = Latin [duo-] + Greek.
tridecagon (or
13
triskaidecagon)
tetradecagon (or
14
tetrakaidecagon)
pentadecagon (or
quindecagon or 15
pentakaidecagon)
hexadecagon (or
16
hexakaidecagon)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-30-320.jpg)
![heptadecagon (or
17
heptakaidecagon)
octadecagon (or
18
octakaidecagon)
enneadecagon (or
enneakaidecagon or 19
nonadecagon)
icosagon 20
triacontagon 30
"hectogon" is the Greek name (see hectometer), "centagon" is a
hectogon 100
Latin-Greek hybrid; neither is widely attested.
René Descartes,[8] Immanuel Kant,[9] David Hume, [10] and
chiliagon 1000 others have used the chiliagon as an example in philosophical
discussion.
myriagon 10,000
As with René Descartes' example of the chiliagon, the million-
sided polygon has been used as an illustration of a well-defined
megagon[11][12][13] 1,000,000 concept that cannot be visualised.[14][15][16][17][18][19][20] The
megagon is also used as an illustration of the convergence of
regular polygons to a circle.[21]
apeirogon A degenerate polygon of infinitely many sides
Constructing higher names
To construct the name of a polygon with more than 20 and less than 100 edges, combine the
prefixes as follows
and Ones final suffix
Tens
1 -hena-
20 icosa- 2 -di-
30 triaconta- 3 -tri-
40 tetraconta- 4 -tetra-
50 pentaconta- -kai- 5 -penta- -gon
60 hexaconta- 6 -hexa-
70 heptaconta- 7 -hepta-
80 octaconta- 8 -octa-
90 enneaconta- 9 -ennea-
The "kai" is not always used. Opinions differ on exactly when it should, or need not, be used (see
also examples above).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-31-320.jpg)



![associated torque.[1] The term resultant force should be understood to refer to both the forces and
torques acting on a rigid body, which is why some use the term resultant force-torque.
The resultant force, or resultant force-torque, fully replaces the effects of all forces on the motion
of the rigid body they act upon.
Associated torque
If a point R is selected as the point of application of the resultant force F of a system of n forces
Fi then the associated torque T is determined from the formulas
and
It is useful to note that the point of application R of the resultant force may be anywhere along
the line of action of F without changing the value of the associated torque. To see this add the
vector kF to the point of application R in the calculation of the associated torque,
The right side of this equation can be separated into the original formula for T plus the additional
term including kF,
Now because F is the sum of the vectors Fi this additional term is zero, that is
and the value of the associated torque is unchanged.
Torque-free resultant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-35-320.jpg)
![it is useful to consider whether there is a point of application R such that the associated torque is
zero. This point is defined by property
where F is resultant force and Fi form the system of forces.
Notice that this equation for R has a solution only if the sum of the individual torques on the
right side yield a vector that is perpendicular to F. Thus, the condition that a system of forces has
a torque-free resultant can be written as
If this condition is not satisfied, then the system of forces includes a pure torque.
The diagram illustrates simple graphical methods for finding the line of application of the
resultant force of simple planar systems.
1. Lines of application of the actual forces and on the leftmost illustration intersect.
After vector addition is performed "at the location of ", the net force obtained is
translated so that its line of application passes through the common intersection point.
With respect to that point all torques are zero, so the torque of the resultant force is
equal to the sum of the torques of the actual forces.
2. Illustration in the middle of the diagram shows two parallel actual forces. After vector
addition "at the location of ", the net force is translated to the appropriate line of
application, where it becomes the resultant force . The procedure is based on
decomposition of all forces into components for which the lines of application (pale
dotted lines) intersect at one point (the so called pole, arbitrarily set at the right side of the
illustration). Then the arguments from the previous case are applied to the forces and
their components to demonstrate the torque relationships.
3. The rightmost illustration shows a couple, two equal but opposite forces for which the
amount of the net force is zero, but they produce the net torque where is the
distance between their lines of application. This is "pure" torque, since there is no
resultant force.
Wrench
The forces and torques acting on a rigid body can be assembled into the pair of vectors called a
wrench.[2] Let P be the point of application of the force F and let R be the vector locating this
point in a fixed frame. Then the pair of vectors W=(F, R×F) is called a wrench. Vectors of this
form are know as screws and their mathematics formulation is called screw theory.[3][4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-36-320.jpg)

![and direction. A related concept is a pseudoscalar, which is invariant under proper rotations but
(like a pseudovector) flips sign under improper rotations. The concept of a scalar in physics is
essentially the same as in mathematics.
An example of a scalar quantity is temperature; the temperature at a given point is a single
number. Velocity, for example, is a vector quantity. Velocity in four-dimensional space is
specified by three values; in a Cartesian coordinate system the values are the speeds relative to
each coordinate axis.
Vector, a Latin word meaning "carrier",In mathematics,
Direction is the information contained in the relative position of one point with respect to another point
without the distance information. Directions may be either relative to some indicated reference (the
violins in a full orchestra are typically seated to the left of the conductor), or absolute according to some
previously agreed upon frame of reference (New York City lies due west of Madrid). Direction is often
indicated manually by an extended index finger or written as an arrow. On a vertically oriented sign
representing a horizontal plane, such as a road sign, "forward" is usually indicated by an upward arrow.
Mathematically, direction may be uniquely specified by a unit vector, or equivalently by the angles made
by the most direct path with respect to a specified set of axes.
magnitude is the "size" of a mathematical object, a property by which the object can be compared as
larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind. More formally, an object's magnitude is an
ordering (or ranking) of the class of objects to which it belongs.
When referring to a two and three-dimensional plane, the x-axis or horizontal axis refers to the
horizontal width of a two or three-dimensional object. In the picture to the right, the x-axis plane goes
left-to-right and intersects with the y-axis and z-axis. A good example of where the x-axis is used on a
computer is with the mouse. By assigning a value to the x-axis, when the mouse is moved left-to-right
the x-axis value increases and decreases, which allows the computer to know where the mouse cursor is
on the screen.
he vertical axis of a two-dimensional plot in Cartesian coordinates. Physicists and astronomers
sometimes call this axis the ordinate, although that term is more commonly used to refer to
coordinates along the -axis. n physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo
a certain change, either concerning its movement, direction, or geometrical construction. It is
measured with the SI unit of newtons and represented by the symbol F. In other words, a force is
that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (which includes to begin moving
from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform. Force can
also be described by intuitive concepts such as a push or pull. A force has both magnitude and
direction, making it a vector quantity.
The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal
to the rate at which its momentum changes.[1] This law is further given to mean that the
acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-38-320.jpg)
![direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional the mass of the object. As a formula, this
is expressed as:
where the arrows imply a vector quantity possessing both magnitude and direction.
Related concepts to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which
decreases the velocity of an object; and torque which produces changes in rotational speed of an
object. Forces which do not act uniformly on all parts of a body will also cause mechanical
stresses,[2] a technical term for influences which cause deformation of matter. While mechanical
stress can remain embedded in a solid object, gradually deforming it, mechanical stress in a fluid
determines changes in its pressure and volume.[3][4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physics-121201034327-phpapp01/85/Physics-39-320.jpg)