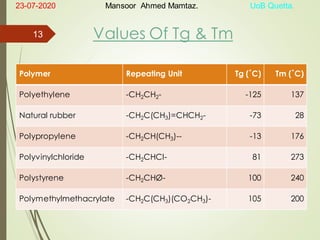
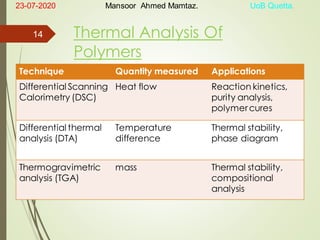
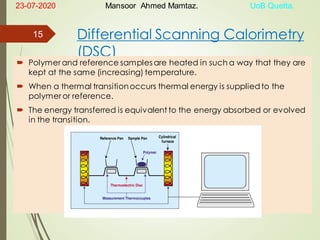
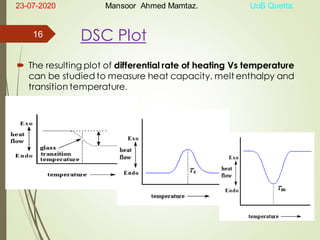
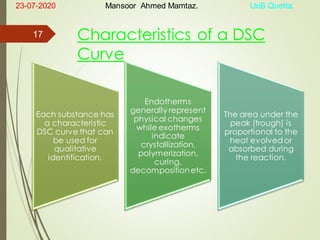
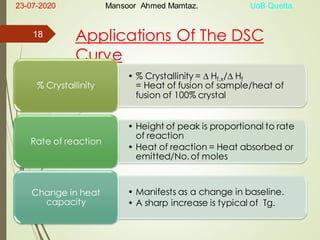
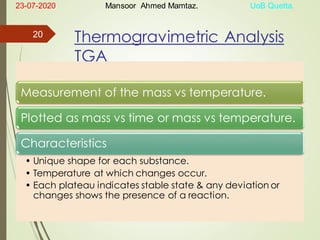
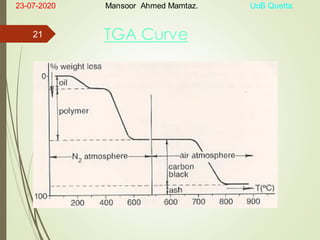
Mansoor Ahmed presented on the topic of thermal transitions in polymers to Miss Habiba Taj Sahiba on July 23, 2020 at the University of Balochistan in Quetta. The presentation discussed glass transition temperature (Tg), crystalline melting point (Tm), and factors that affect Tg and Tm such as polymer structure, molecular weight, and intermolecular interactions. It also described techniques for analyzing polymer thermal behavior including differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis.