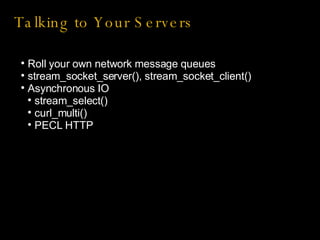
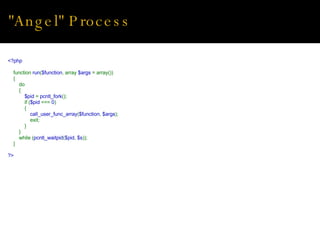
Andrew Minerd and Mike Lively at Selling Source need to perform background processing tasks like sending emails and transferring funds. The document discusses using PHP from the command line to create single and multiple background processes, addressing challenges like shared resources, memory usage, and distributing processes across multiple servers. It provides examples of writing cron jobs, using signals, daemonizing processes, and communicating between processes.






















![Forking Multiple Children <?php define ( 'MAX_CHILDREN' , 5 ); $children = array(); $jobs = get_jobs (); while ( count ( $jobs )) { if ( count ( $children ) < MAX_CHILDREN ) { $data = array_shift ( $jobs ); $pid = pcntl_fork (); if ( $pid == - 1 ) { die( "Could not fork!" ); } else if ( $pid ) { $children [ $pid ] = true ; } else { process_data ( $data ); exit( 0 ); } } while ( $wait_pid = pcntl_waitpid (- 1 , $status , WNOHANG )) { if ( $wait_pid == - 1 ) { die( "problem in pcntl_waitpid!" ); } unset( $children [ $wait_pid ]); } } ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-cli2-1212588120708000-8/85/PHP-CLI-A-Cinderella-Story-23-320.jpg)

![Shared Resources <?php // ... // bad time to open a database connection $db = new PDO ( 'mysql:host=localhost' , 'dbuser' , 'pass' ); while ( count ( $data )) { if ( count ( $children ) < MAX_CHILDREN ) { $data = array_shift ( $jobs ); $pid = pcntl_fork (); if ( $pid == - 1 ) { die( "Could not fork!" ); } else if ( $pid ) { $children [ $pid ] = true ; } else { process_data ( $data , $db ); exit( 0 ); // When the child exits the database connection // will be disposed of. } } // ... } ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-cli2-1212588120708000-8/85/PHP-CLI-A-Cinderella-Story-25-320.jpg)
![Shared Resources <?php // ... while ( count ( $data )) { if ( count ( $children ) < MAX_CHILDREN ) { $data = array_shift ( $jobs ); $pid = pcntl_fork (); if ( $pid == - 1 ) { die( "Could not fork!" ); } else if ( $pid ) { $children [ $pid ] = true ; } else { // Much safer $db = new PDO ( 'mysql:host=localhost' , 'dbuser' , 'pass' ); process_data ( $data , $db ); exit( 0 ); // When the child exits the database connection // will be disposed of. } } // ... } ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-cli2-1212588120708000-8/85/PHP-CLI-A-Cinderella-Story-26-320.jpg)

![Memory Usage <?php define ( 'MAX_CHILDREN' , 5 ); $children = array(); $jobs = get_jobs (); while ( count ( $jobs )) { if ( count ( $children ) < MAX_CHILDREN ) { $data = array_shift ( $jobs ); $pid = pcntl_fork (); if ( $pid == - 1 ) { die( "Could not fork!" ); } else if ( $pid ) { $children [ $pid ] = true ; } else { unset ( $jobs ); // <--- will save memory in your child where you do not need $jobs around anymore process_data ( $data ); exit( 0 ); } } while ( $wait_pid = pcntl_waitpid (- 1 , $status , WNOHANG )) { if ( $wait_pid == - 1 ) { die( "problem in pcntl_waitpid!" ); } unset( $children [ $wait_pid ]); } } ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-cli2-1212588120708000-8/85/PHP-CLI-A-Cinderella-Story-28-320.jpg)



![How to Talk to Your Kids <?php $socks = stream_socket_pair ( STREAM_PF_UNIX , STREAM_SOCK_STREAM , STREAM_IPPROTO_IP ); $pid = pcntl_fork (); if ( $pid == - 1 ) { die( 'could not fork!' ); } else if ( $pid ) { // parent fclose ( $socks [ 1 ]); fwrite ( $socks [ 0 ], "Hi kid\n" ); echo fgets ( $socks [ 0 ]); fclose ( $socks [ 0 ]); } else { // child fclose ( $socks [ 0 ]); fwrite ( $socks [ 1 ], "Hi parent\n" ); echo fgets ( $socks [ 1 ]); fclose ( $socks [ 1 ]); } /* Output: Hi kid Hi parent */ ?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-cli2-1212588120708000-8/85/PHP-CLI-A-Cinderella-Story-32-320.jpg)