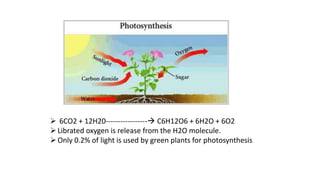
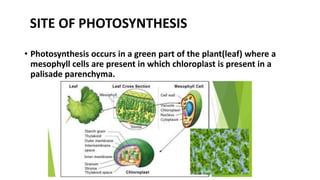
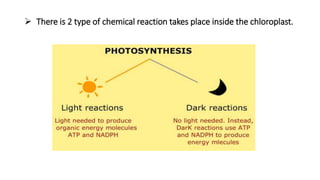
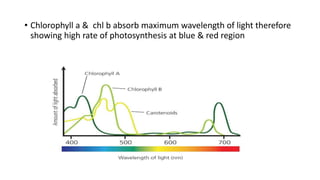
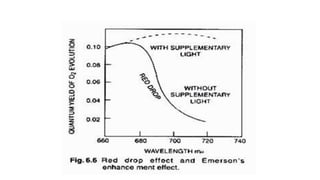
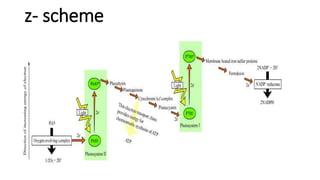
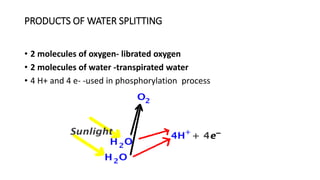
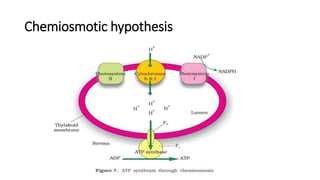
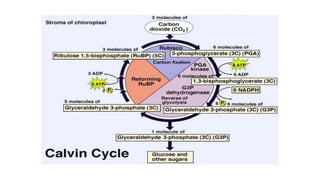
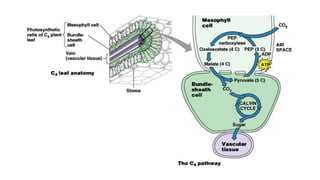
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants synthesize food from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant leaves. There are two key stages - the light-dependent reactions where ATP and NADPH are produced, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbohydrates are produced. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and utilize chlorophyll to drive the electron transport chain and create the proton gradient needed for ATP production. Oxygen is released as a byproduct of splitting water. The Calvin cycle then uses ATP and NADPH to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into glucose.