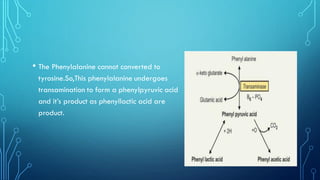
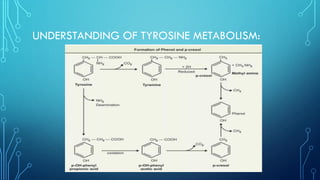
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a genetic disorder caused by the deficiency of the phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme, leading to high levels of phenylalanine in the blood, which can cause severe cognitive and physical issues if untreated. It is classified into five types, with classical PKU being autosomal recessive, and is diagnosed through newborn screening and blood tests. Treatment primarily involves a strict low-phenylalanine diet and may include medications like sapropterin for some patients.