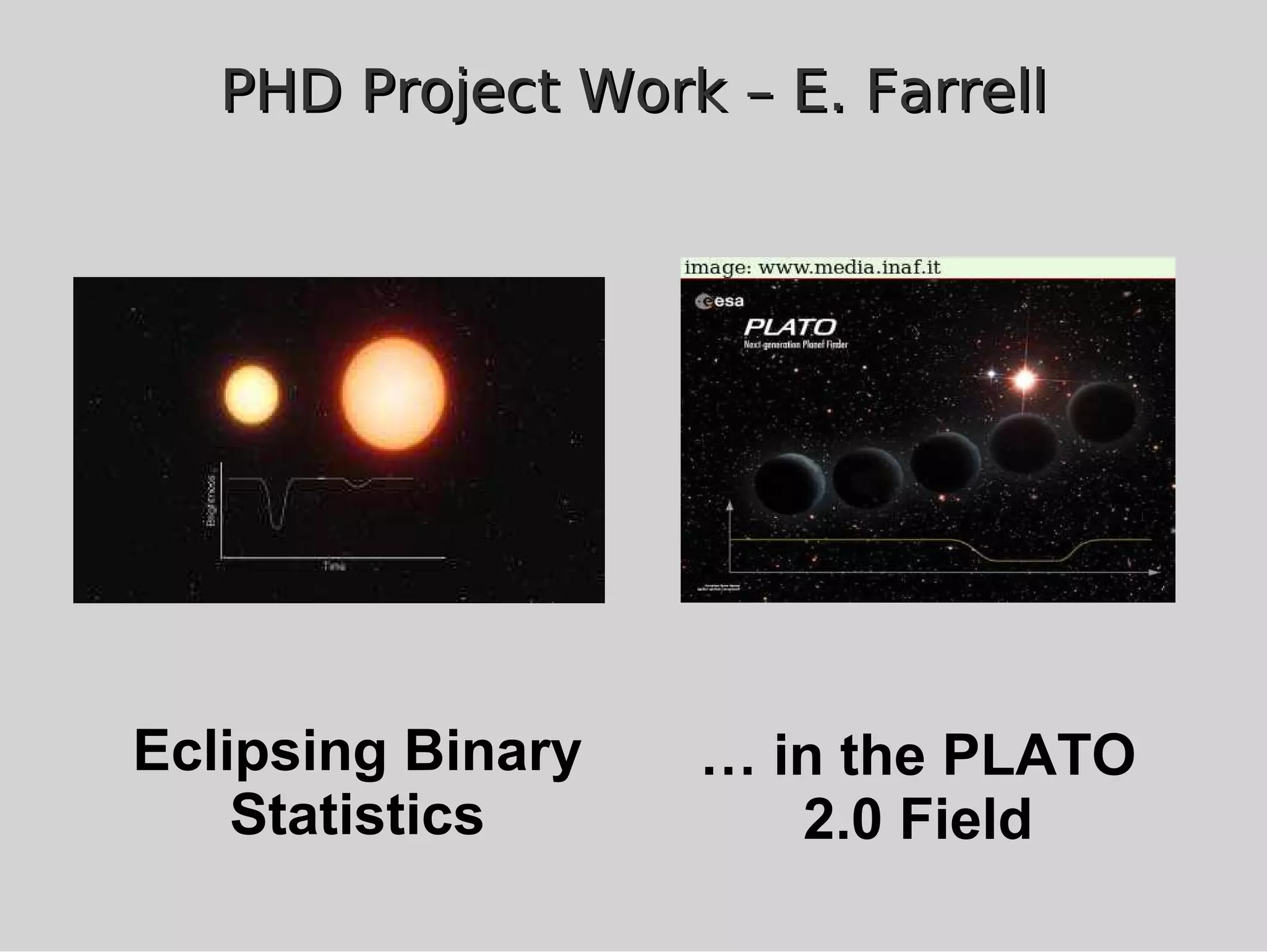
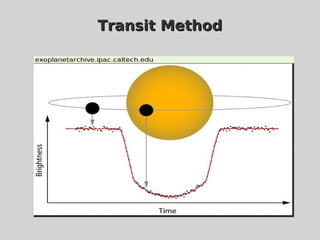
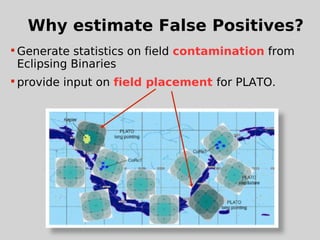
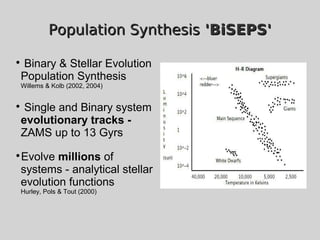
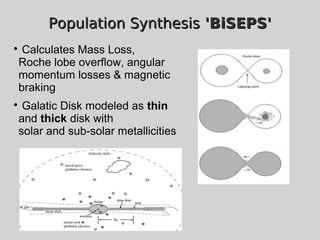
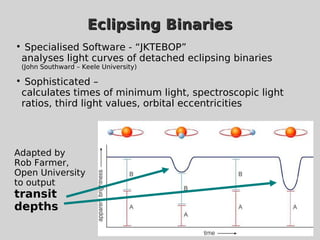
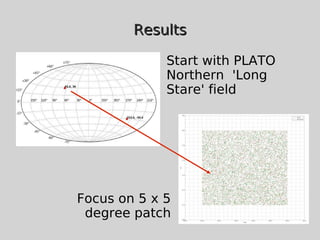
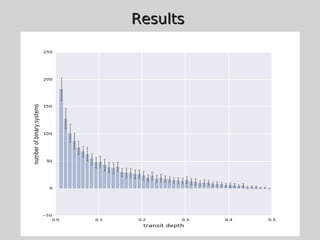
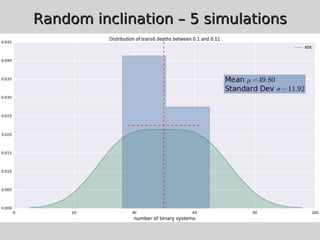
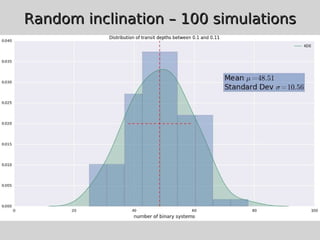
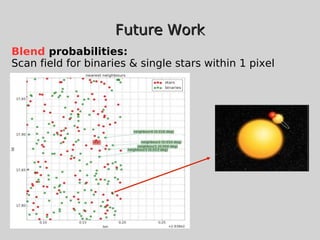
This document discusses using population synthesis modeling to estimate the number of eclipsing binary stars that could contaminate exoplanet detections in the PLATO 2.0 mission. It describes generating synthetic binary star systems, evolving them, analyzing their light curves to determine transit depths, and applying this to simulated PLATO fields to output the expected number of eclipsing binaries at different transit depths. The results from simulations of random inclinations for binaries in patches of the PLATO northern field are also presented. Future work discussed includes calculating blend probabilities and applying the method to other surveys.