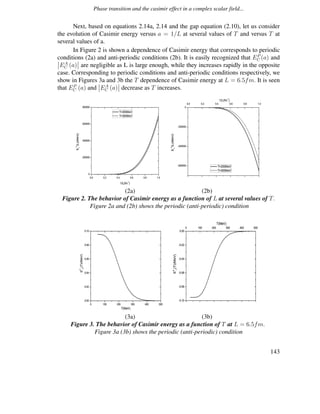
The paper investigates phase transitions and the Casimir effect in a complex scalar field within a compactified spatial dimension. It finds that the phase transition is of the second order and that the Casimir effect varies significantly between periodic and anti-periodic boundary conditions. The study concludes that the Casimir force is repulsive for periodic conditions and attractive for anti-periodic ones, with both forces being temperature-dependent and influenced by the distance between plates.
![JOURNAL OF SCIENCE OF HNUE
Mathematical and Physical Sci., 2013, Vol. 58, No. 7, pp. 138-146
This paper is available online at http://stdb.hnue.edu.vn
PHASE TRANSITION AND THE CASIMIR EFFECT IN A COMPLEX SCALAR
FIELD WITH ONE COMPACTIFIED SPATIAL DIMENSION
Tran Huu Phat1
and Nguyen Thi Tham2
1
Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute,
2
Faculty of Physics, Hanoi University of Education No. 2, Xuan Hoa, Vinh Phuc
Abstract. Phase transition and the Casimir effect are studied in the complex scalar
field with one spatial dimension to be compactified. It is shown that the phase
transition is of the second order and the Casimir effect behaves quite differently
depending on whether it’s under periodic or anti-periodic boundary conditions.
Keywords: Phase transition, Casimir effect, complex scalar field, compactified
spatial.
1. Introduction
It is well known that a characteristic of quantum field theory in space-time with
nontrivial topology is the existence of non-equivalent types of fields with the same spin
[1, 2, 3]. For a scalar system in space-time which is locally flat but with topolog, that is
a Minkowskian space with one of the spatial dimensions compactified in a circle of finite
radius L, the non-trivial topology is transferred into periodic (sign +) and anti-periodic
(sign -) boundary conditions:
φ(t, x, y, z) = ±φ(t, x, y, z + L) (1.1)
The seminal discovery in this direction is the so-called Casimir effect [4, 5], where the
Casimir force generated by the electromagnetic field that exists in the area between two
parallel planar plates was found to be
F = −
π2
cS
240L4
,
here S is the area of the parallel plates and L is the distance between two plates fulfilling
the condition L2
≪ S. The Casimir effect was first written about in 1948 [4], but since the
Received June 30, 2013. Accepted August 27, 2013.
Contact Nguyen Thi Tham, e-mail address: nguyenthamhn@gmail.com
138](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phasetransitionandcasimireffect-170526072233/85/Phase-transition-and-casimir-effect-1-320.jpg)
![Phase transition and the casimir effect in a complex scalar field...
1970s this effect has received increasing attention of scientists. Newer and more precise
experiments demonstrating the Casimir force have been performed and more are under
way. Recently, the Casimir effect has become a hot topic in various domains of science
and technology, ranging from cosmology to nanophysics [5, 6, 7]. Calculations of the
Casimir effect do not exist below zero degrees. It has been seen that the strength of the
Casimir force decreases as the distance between two plates increases. At this time it is
not possible to predict the repulsive or attractive force for different objects and there is
no indication that the Casimir force is dependent on distance at finite temperatures. The
Lagrangian we consider is of the form
L = ∂µφ∗
∂φ − U, U = m2
φ∗
φ +
λ
2
(φ∗
φ)2
. (1.2)
in which φ is a complex scalar field and m and λ are coupling constants. In the present
article, we calculate the effective potential in a complex scalar field and, based on this, the
phase transition in compactified space-time is derived. We then study the Casimir effect
at a finite temperature and calculate Casimir energies and Casimir forces that correspond
to both boundary conditions (periodic and anti-periodic).
2. Content
2.1. Effective potential and phase transition
The space is compactified along the oz axis with length L. Then the Euclidian
Action is defined as
SE = i
L∫
0
dz
∫
LEdτdx⊥, dx⊥ = dxdy, (2.1)
where LE is the Euclidian form of the Lagrangian (1.2) and t = iτ. Assume that when
λ > 0 and m2
< 0, the field operator φ develops vacuum expectation value
⟨φ⟩ = ⟨φ∗
⟩ = u,
then the U(1) symmetry of the complex scalar field given in (1.2) is spontaneously broken.
In the tree approximation u corresponds to the minimum of U,
(
∂U
∂φ
)
φ=φ∗=0
= 0,
yielding u =
√
−
m2
λ
. At minimum the potential energy U reads U = m2
u2
+
λ
2
u4
. Let
us next decompose φ and φ∗
φ =
1
√
2
(u + φ1 + iφ2) , φ∗
=
1
√
2
(u + φ1 − iφ2) . (2.2)
Inserting (2.2) into (1.2) we get the matrix D representing the interaction betweenφ1, φ2
139](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phasetransitionandcasimireffect-170526072233/85/Phase-transition-and-casimir-effect-2-320.jpg)
![Tran Huu Phat and Nguyen Thi Tham
iD−1
= ∥Aik∥ , A11 = ω2
+ ⃗k2
+ 2λu2
, A22 = ω2
+ ⃗k2
, A12 = A21 = 0.
The partition function is established as
Z =
∫
Dφ∗
Dφ exp [−SE]
In a one-loop approximation we have that
Z = e−V LU
∫
Dφ1Dφ2 exp
[
−
∫
dxϕ+
iD−1
ϕ
]
where ϕ+
= (φ1, φ2) The effective potential is defined as
Ω = −
ln Z
V L
= Ωs + U, (2.3)
in which
ΩS =
T
2L
∞∑
m=−∞
∞∑
n=−∞
∫
dk⊥
(2π)2
{
ln
[
ω2
m + E2
1n
]
+ ln
[
ω2
m + E2
2n
]}
. (2.4)
with
E1n =
√
k2
⊥ + k2
3n + M2, E2n =
√
k2
⊥ + k2
3n, M2
= 2λu2
(2.5)
and
k3n = (2n + 1)
π
L
, n = 0, ±1, ±2, .... (2.6)
for anti-periodic boundary conditions, and
k3n = 2n
π
L
, n = ±1, ±2, ... (2.7)
for periodic boundary conditions. Note that En in (2.5) is exactly the gapless spectrum of
the Goldston boson in the broken phase and there is a similarity between L appearing in
(2.6) and (2.7) with T in the Matsubara formula β = 1/T, and therefore it is convenient
to impose a = 1/L for later use. Parameter a has the dimension of energy. Making use of
the formula:
T
∞∑
n=−∞
ln
(
ω2
+ E2
)
= E + T ln
(
1 − e−E/T
)
,
and taking into account (2.5), (2.6) and (2.7), we arrive at the expression for ΩS
ΩS = −a
∞∑
n=−∞
∫
dk⊥
(2π)2
{
E1n + E2n + T ln
[
1 − e−βE1n
]
+ T ln
[
1 − e−βE2n
]}
.
(2.8)
140](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phasetransitionandcasimireffect-170526072233/85/Phase-transition-and-casimir-effect-3-320.jpg)

![Tran Huu Phat and Nguyen Thi Tham
2.2. Casimir effect
Let us mention that the vacuum energy caused by the electromagnetic field
restricted between two parallel planar plates is of the form
E(a) = −a
∫
dk⊥
(2π)2
∞∑
n=−∞
EnS, (2.11)
in which S is the area of planar plate, . It is evident that E(a) diverges. So we try to
renormalize it by introducing a rapid damping factor
ER (a) = −a
∫
dk⊥
(2π)3
∞∑
n=−∞
Ene−δEn
S, (2.12)
and the Casimir energy then reads
EC (a) = lim
δ→0
ER(a). (2.13)
Applying the Abel-Plana formula [8, 9]
∞∑
n=0
F(n) −
∞∫
0
F(t)dt =
1
2
F(0) + i
∞∫
0
dt
F(it) − F(−it)
e2πt − 1
,
for periodic conditions and
∞∑
n=0
F(n +
1
2
) − 2
∞∫
0
F(t)dt = i
∞∫
0
dt
∑
λ=±1
F (it) − F (−it)
e2π(t+i λ
2 ) − 1
.
for anti-periodic conditions to the calculation of (2.12) and (2.13), we derive the
expressions for the Casimir energy
EP
C (a) =
16π2
L3
∞∫
0
ydy
∞∫
b
dt
√
t2 − b2
e2πt − 1
,
2.14a
which correspond to periodic conditions and
EA
C (a) = −
16π2
L3
∞∫
0
ydy
∞∫
b
dt
√
t2 − b2
e2πt + 1
. (2.14)
which correspond to anti-periodic conditions. The parameters appearing in 2.14a and 2.14
are defined as
y = L
|k⊥|
2π
, b2
= y2
+ M2
∗ , M2
∗ = L2 M2
(2π)2
.
142](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phasetransitionandcasimireffect-170526072233/85/Phase-transition-and-casimir-effect-5-320.jpg)


![Tran Huu Phat and Nguyen Thi Tham
REFERENCES
[1] L. H. Ford, 1980. Vacuum polarization in a nonsimply connected spacetime.
Phys.Rev. D21, pp. 933-948.
[2] L. H. Ford, 1980. Instabilities in interacting quantum field theories in
non-Minkowskian spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D22, pp. 3003-3011.
[3] Modern Kaluza - Klein Theories, 1987. Edited by T. Appelquits, A. Chodos and
P.T.Freud (Addison - Wesley, Reading, MA, USA).
[4] H. B. G.Casimir, 1948. On the attraction between two perfectly conducting plates.
Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 51, p. 793.
[5] M. Bordag, V.Mohideen and V.M.Mostepanenk, 2001. New developments in the
Casimir effect. Phys. Rep. 353, 1, 1205.
[6] J. H. Schwarz. Update of String Theory. Astro-ph/0304507.
[7] N. Arkani-Hamed, S.Dimopoulos, and Dvali, 1998. The Hierarchy problem and new
dimensions at a millimeter. Phys.Lett. B429, p. 263.
[8] E. Elizalde, S. Nojiri and S. D. Odintsov, 2004. Late-time cosmology in a (phantom)
scalar-tensor theory: Dark energy and the cosmic speed-up. Phys.Rev. D70, 043539.
[9] E. Elizalde, 2006. Uses of zeta regularization in QFT with boundary conditions: a
cosmo-topological Casimir effect. J.Phys. A39, 6299.
146](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phasetransitionandcasimireffect-170526072233/85/Phase-transition-and-casimir-effect-9-320.jpg)