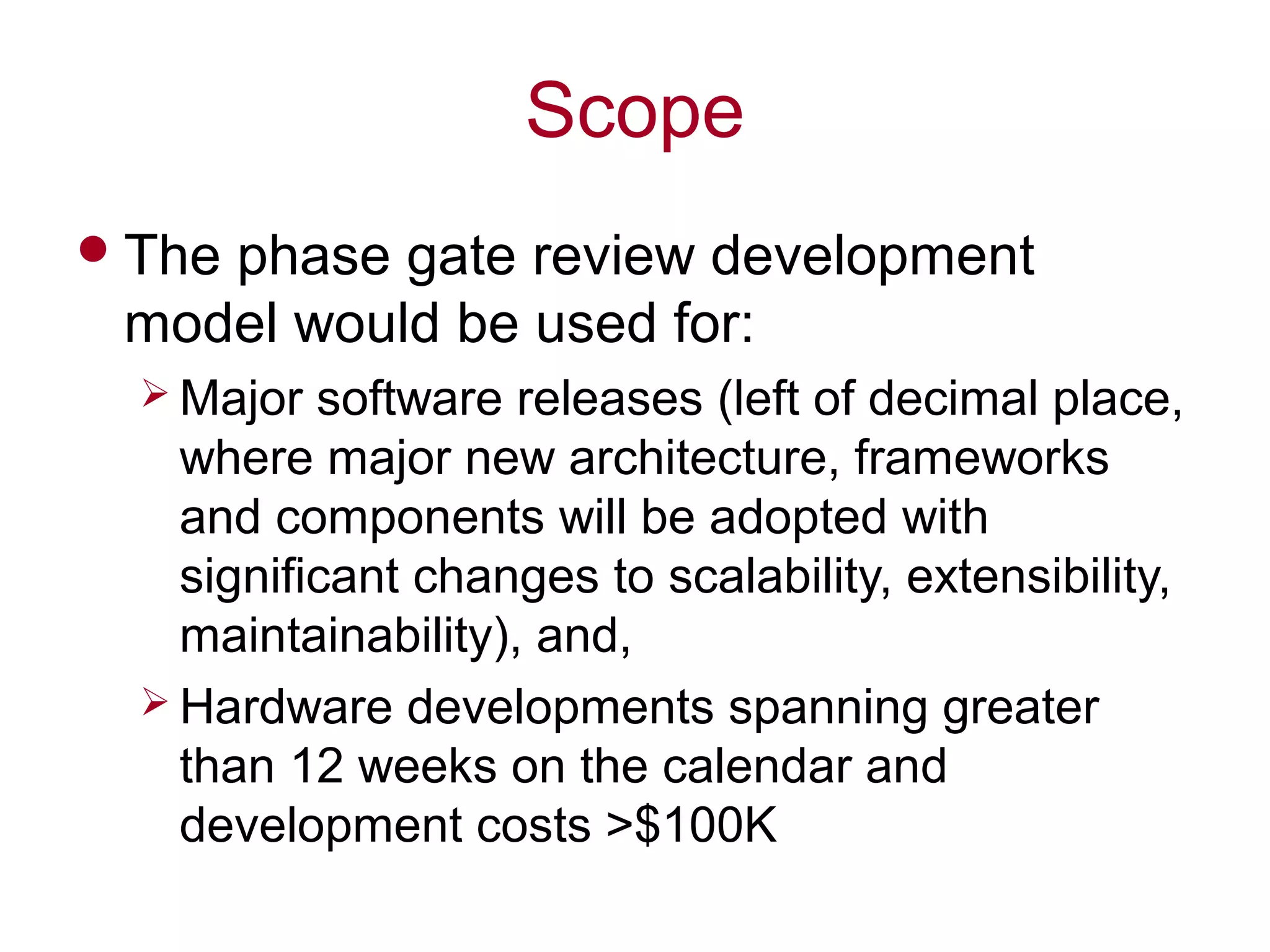
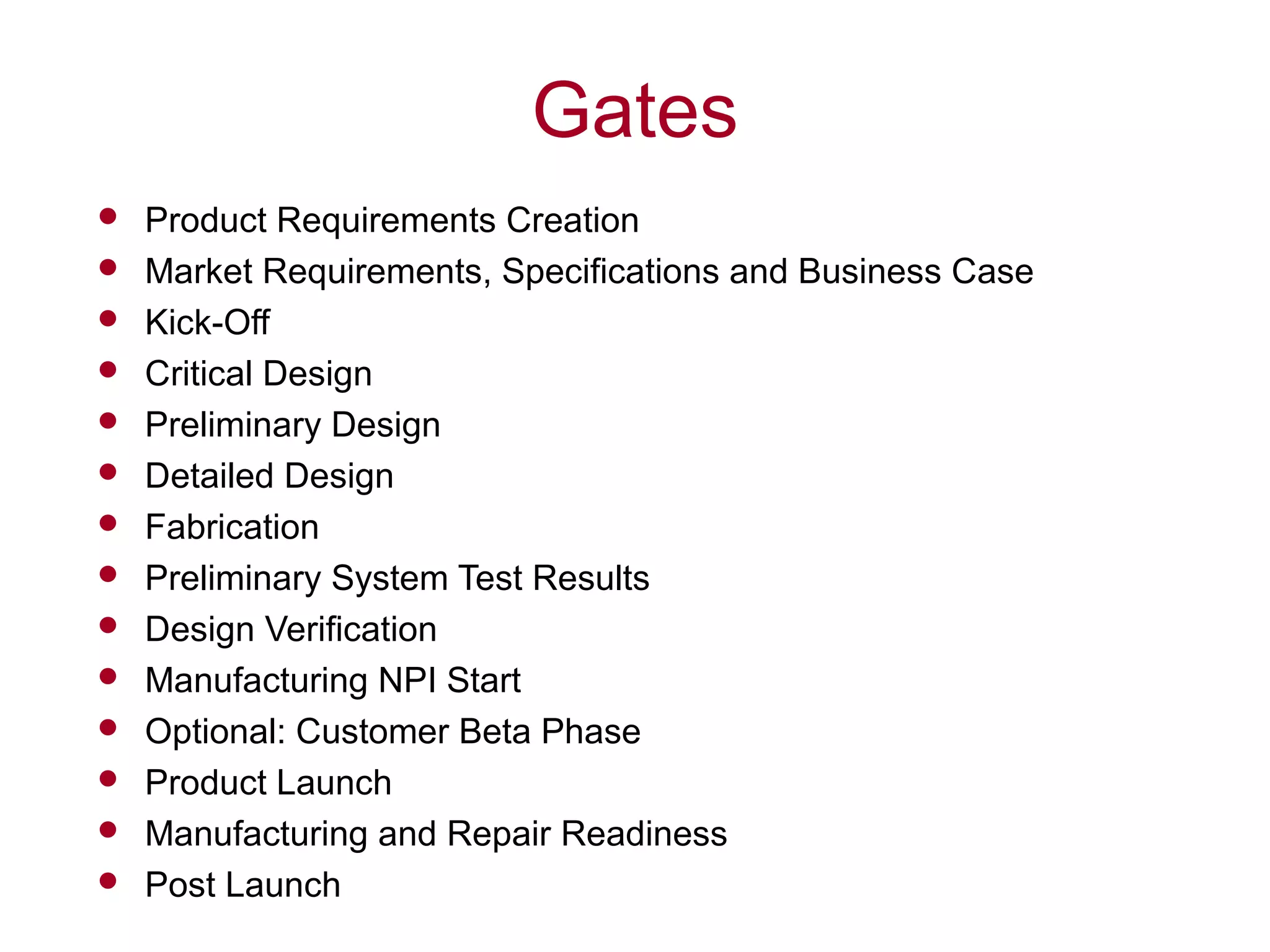
The document outlines a phase gate review development model designed to systematically manage product development processes for both software releases and hardware projects over 12 weeks and $100k in costs. It details various review gates and their respective outputs, including product specifications, market requirements, design reviews, and manufacturing readiness, aiming to enhance communication and efficiency within R&D efforts. The model emphasizes collaborative decision-making to ensure alignment with strategic objectives and successful product launches.