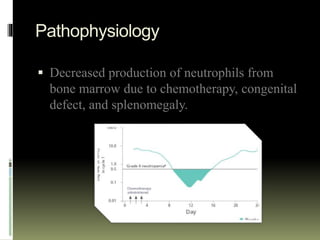
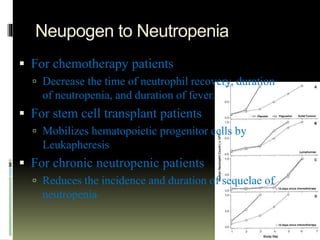
Neupogen is a human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor used to treat neutropenia. It works by stimulating the bone marrow to produce neutrophils. Neupogen reduces the duration of neutropenia and fever in patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy or stem cell transplants. It is also used to treat chronic and congenital neutropenia. Common side effects include bone and muscle pain, while serious adverse reactions include splenic rupture and respiratory distress. Neupogen is administered subcutaneously and absorbed rapidly, with a half-life of 3.5 hours. It is important to monitor white blood cell counts in patients receiving Neupogen.