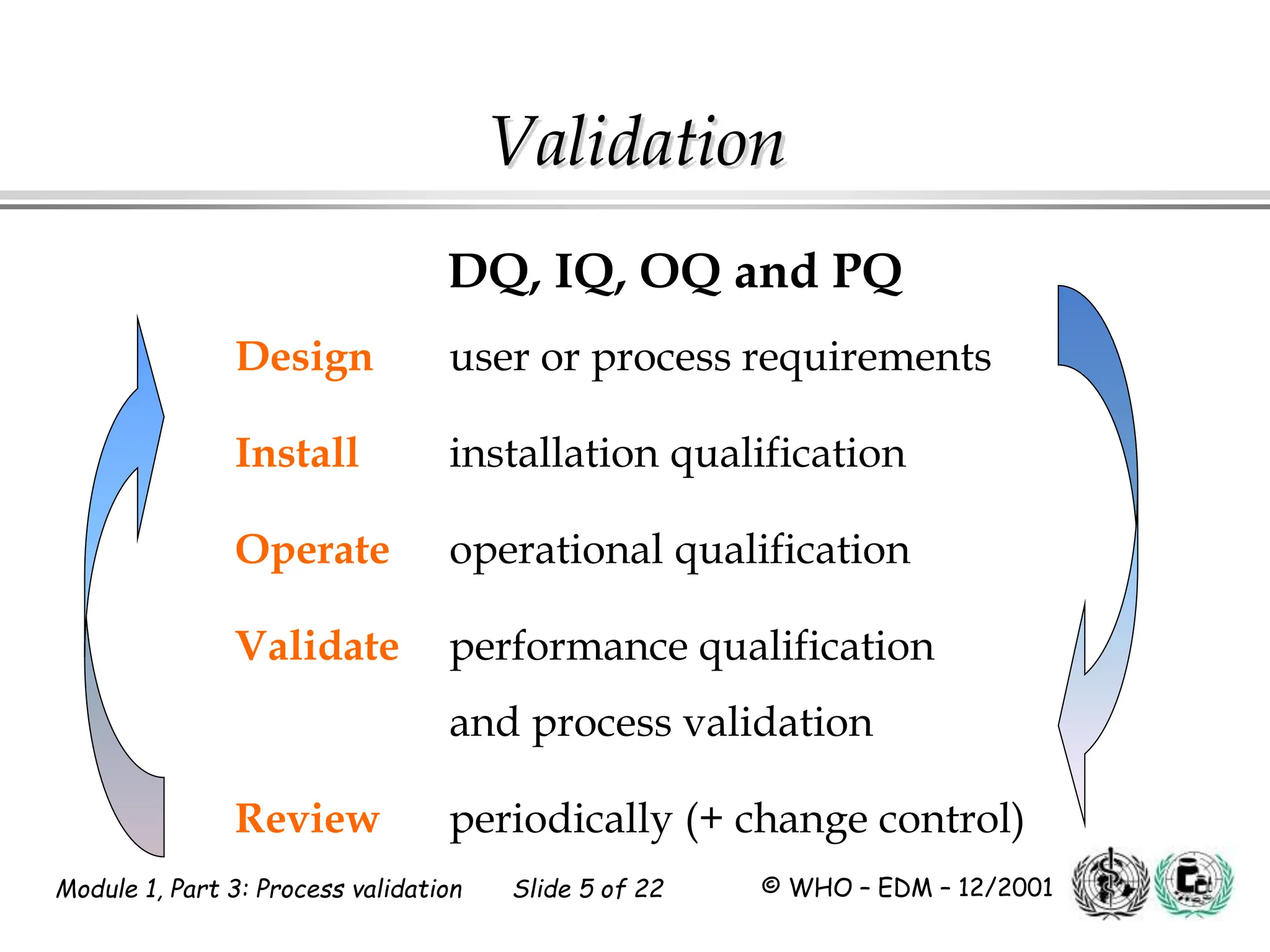
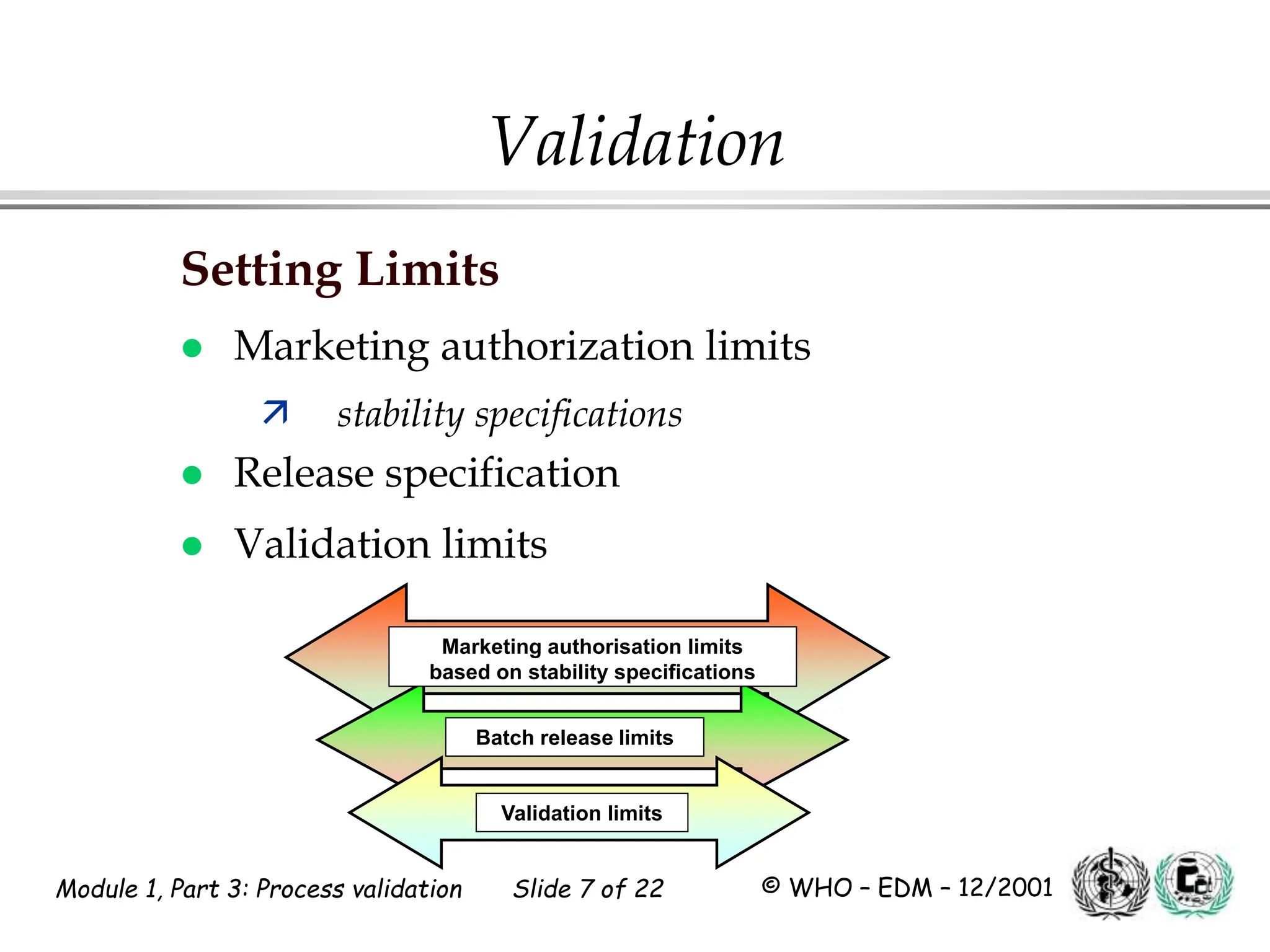
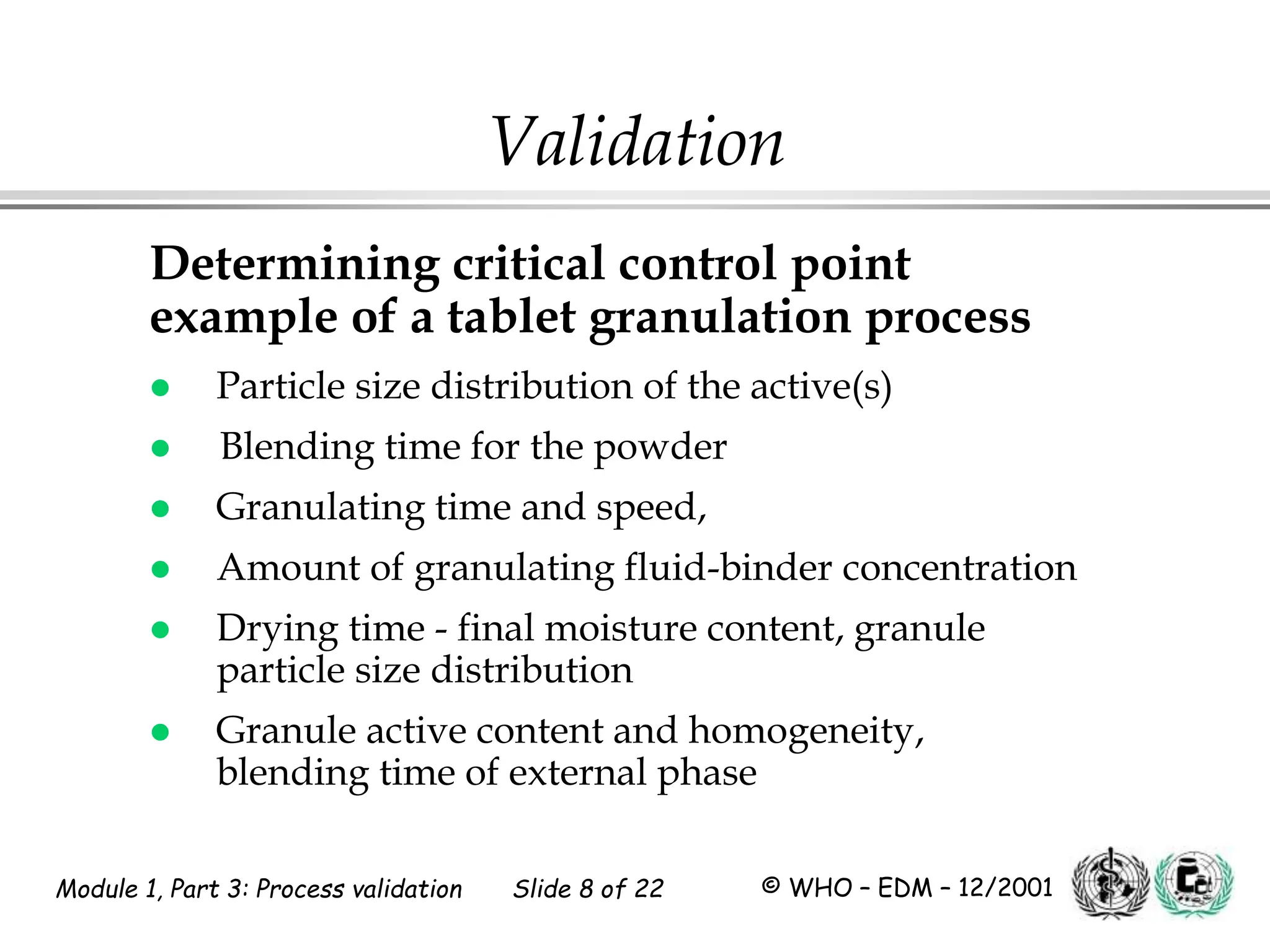
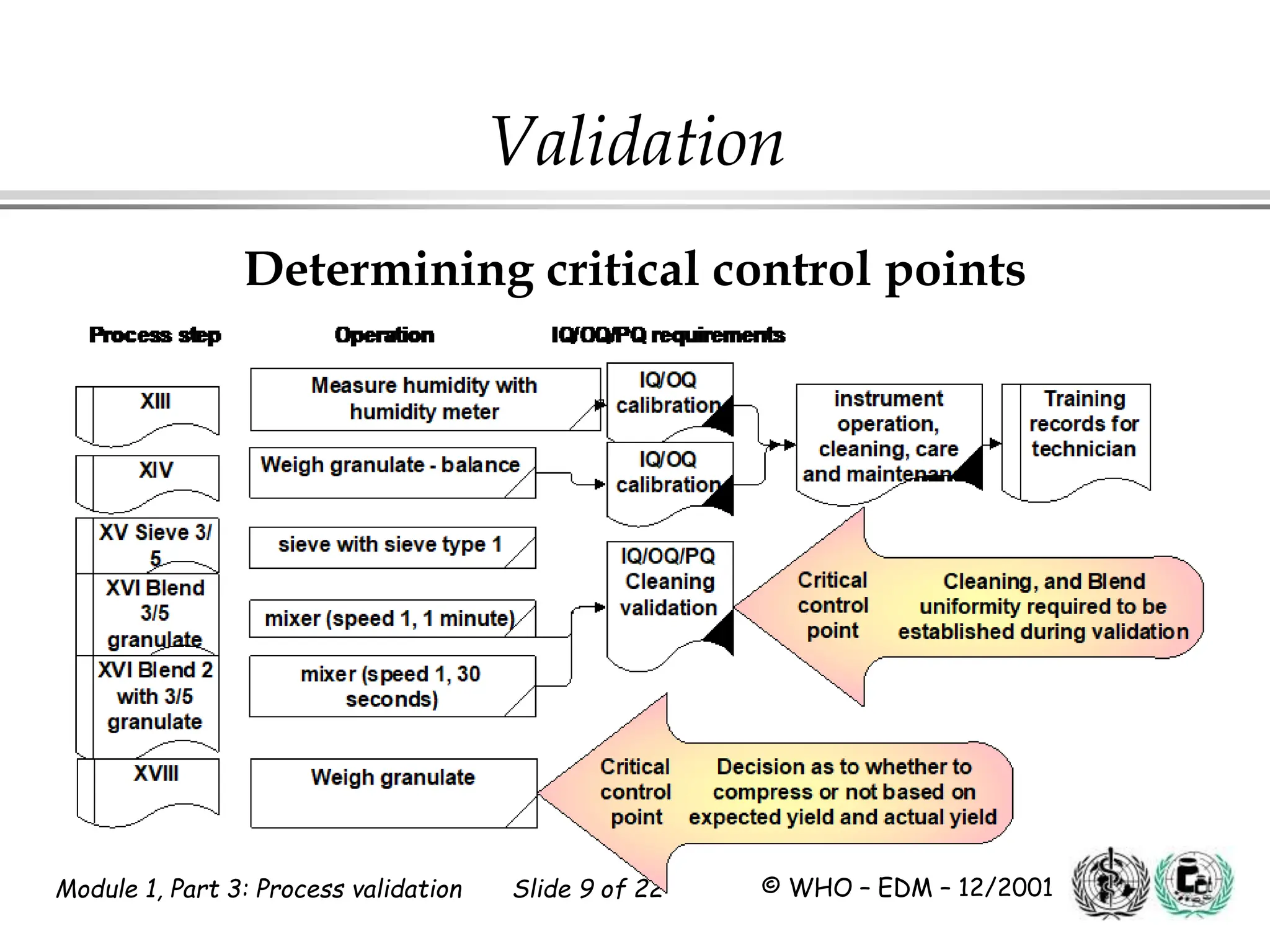
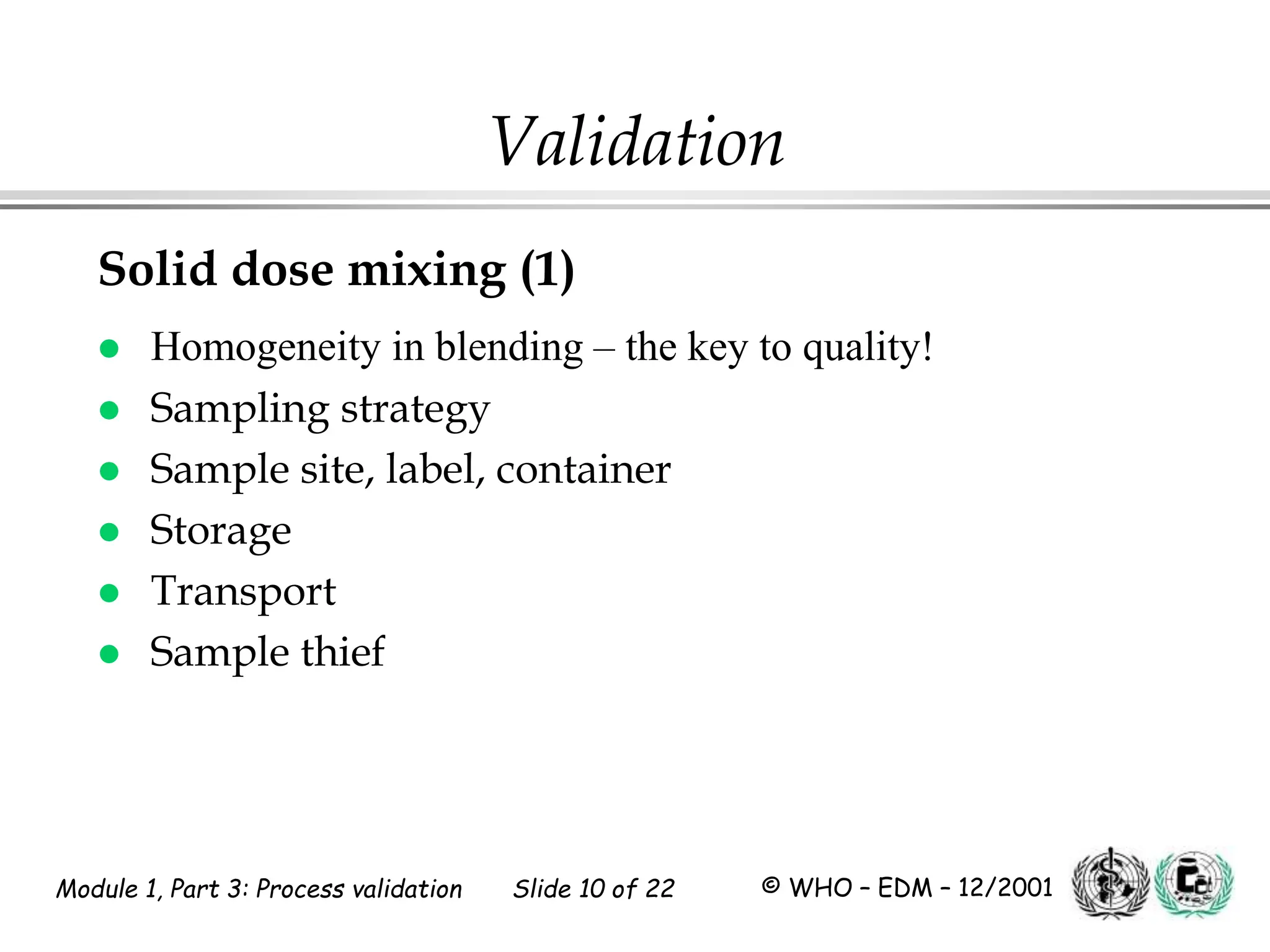
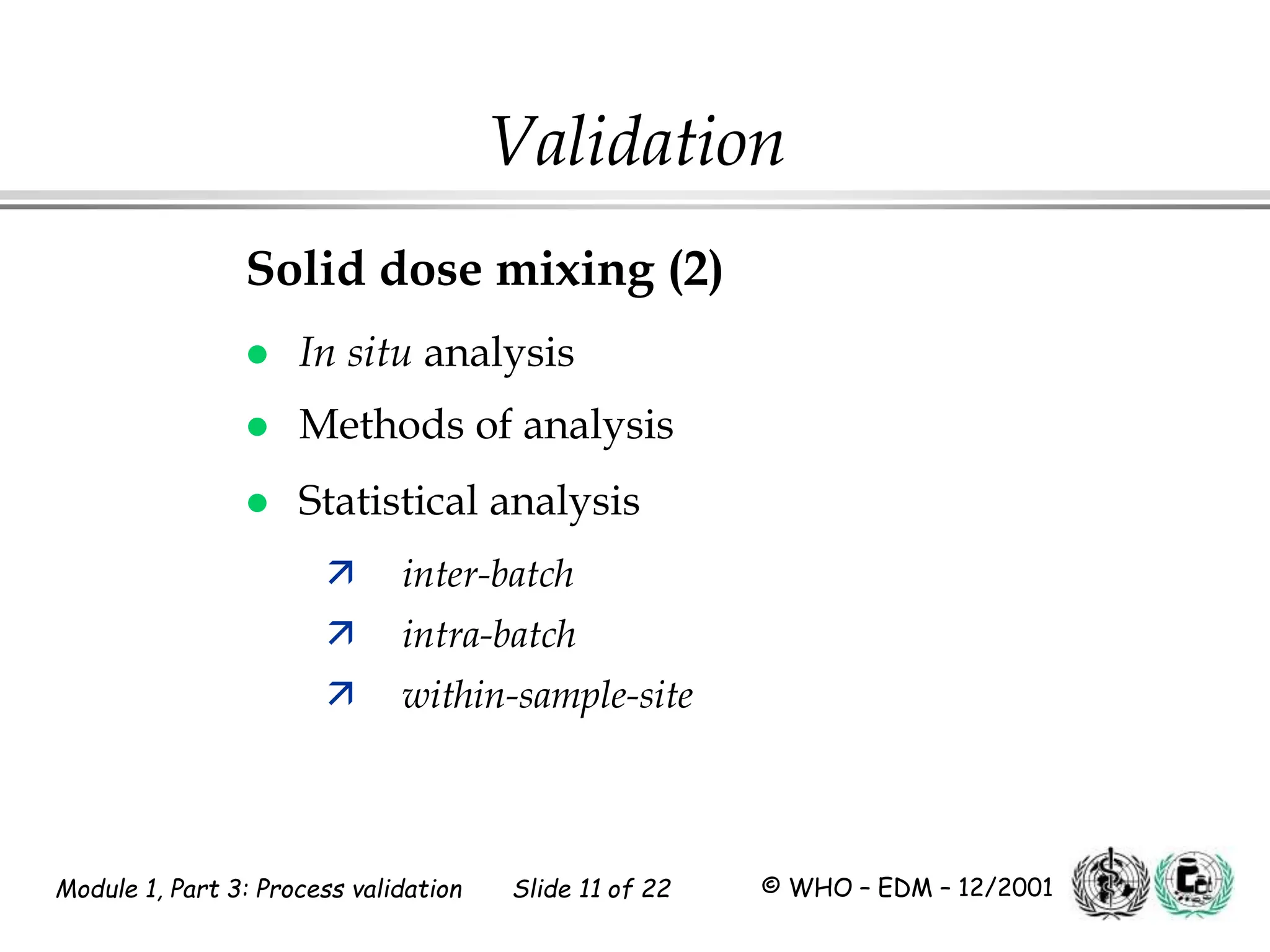
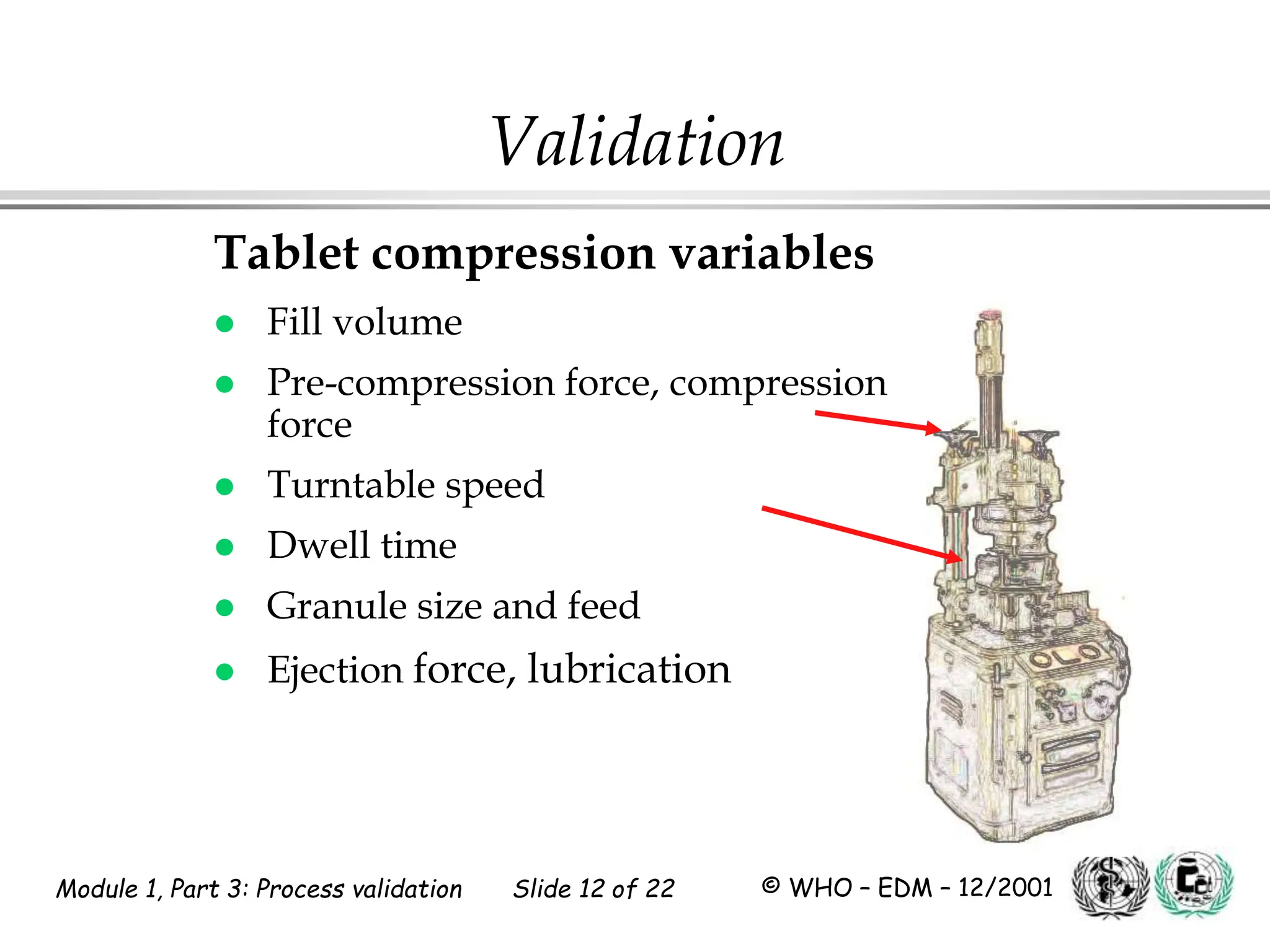
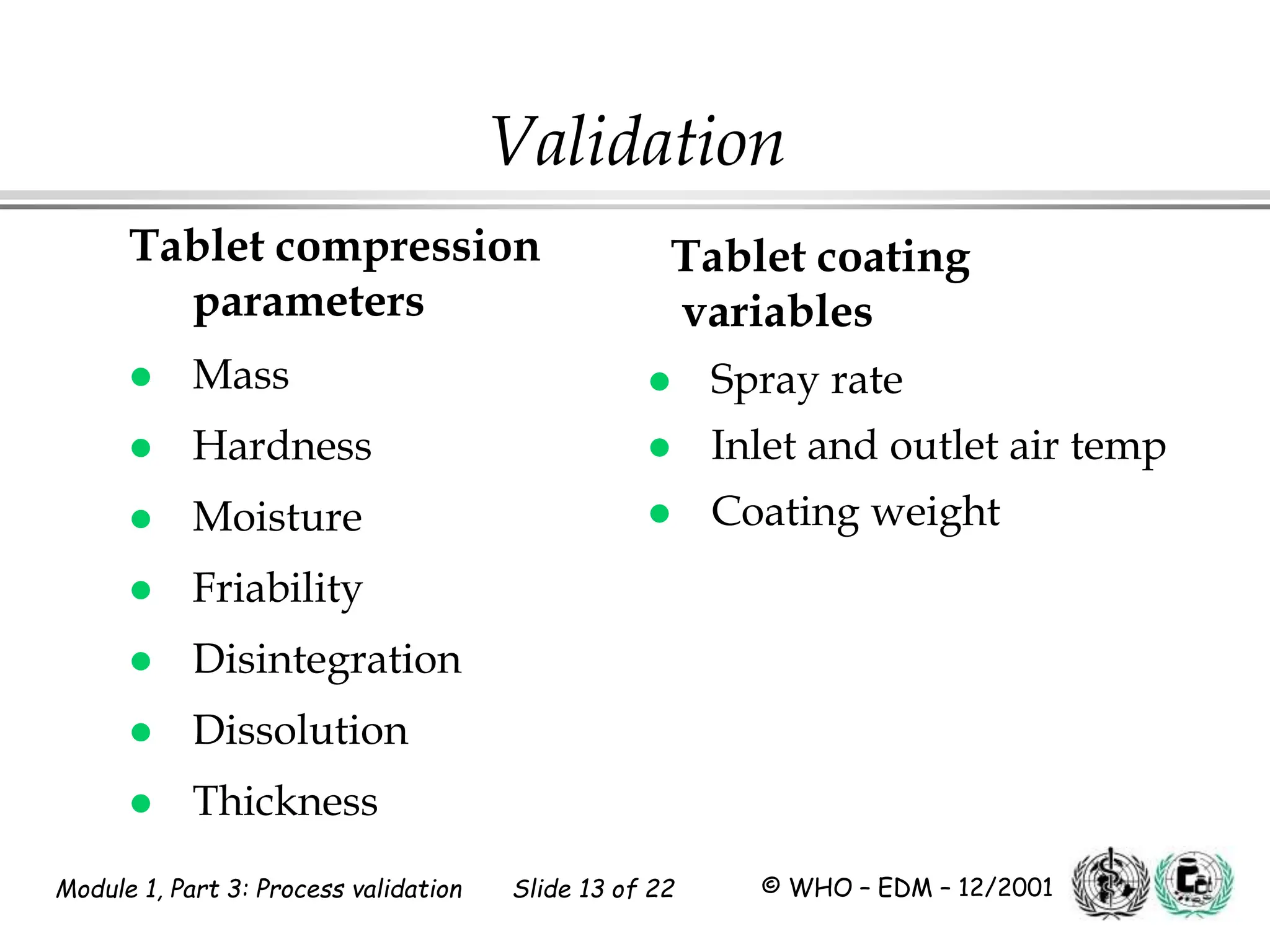
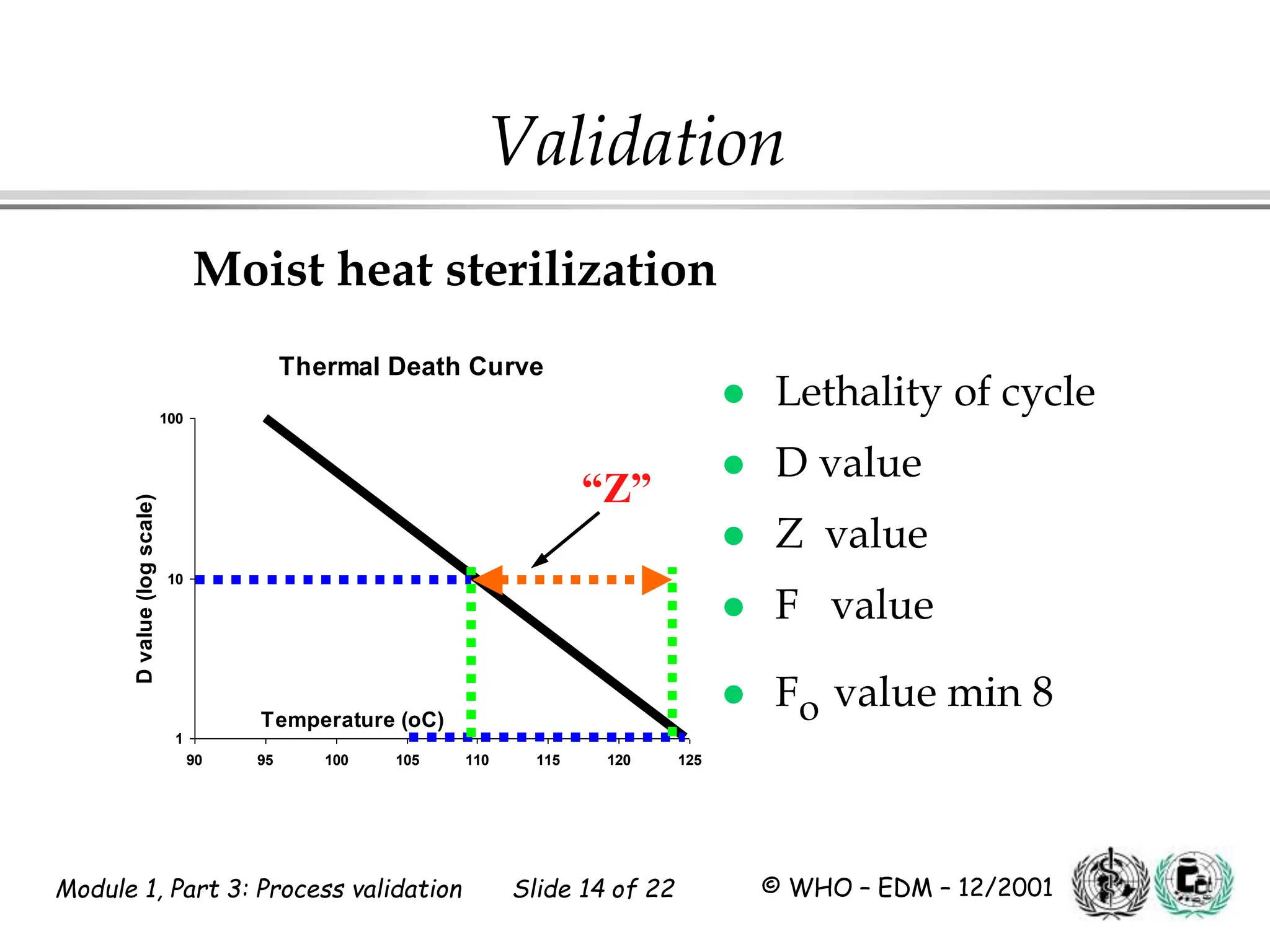
This document discusses process validation for pharmaceutical manufacturing. It outlines the objectives of process validation which are to review validation, risk analysis, and critical steps for processes like solid dose mixing, tablet compression, and sterilization. It discusses determining critical process parameters and control points. Specific parameters that should be monitored and validated are identified for various unit operations like mixing, tablet compression, coating, and sterilization. The importance of change control procedures when making changes to validated processes is also covered.