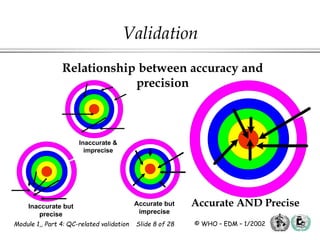
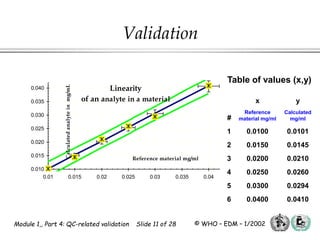
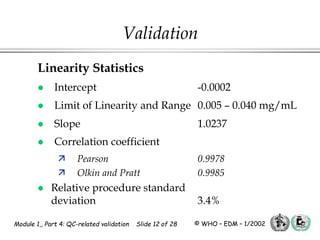
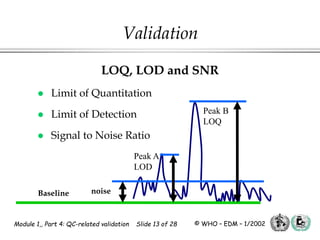
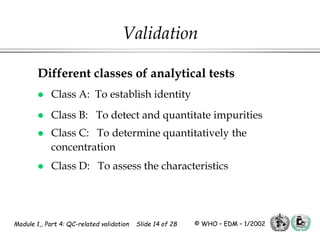
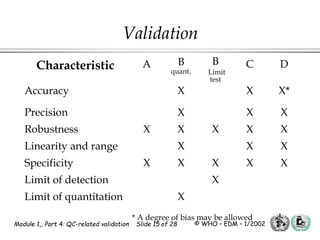
The document outlines the principles and practices necessary for quality control-related validation in analytical methods within good manufacturing practice. It details the objectives, requirements for validation, characteristics of analytical procedures, and specific validation protocols for various tests including microbiological methods. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of instrument qualification, method transfer, and maintaining sample integrity throughout the validation process.