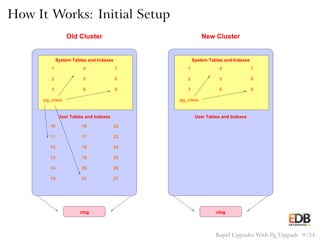
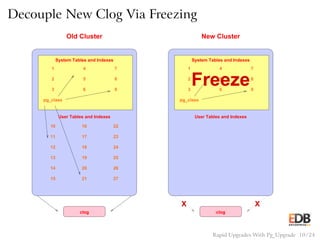
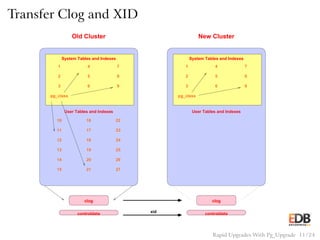
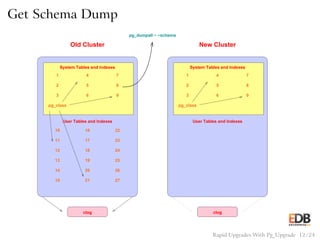
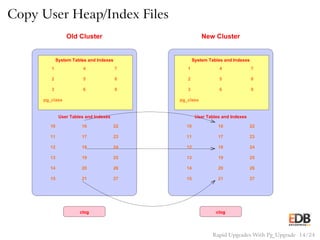
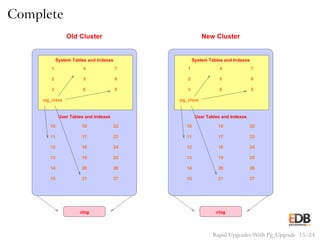
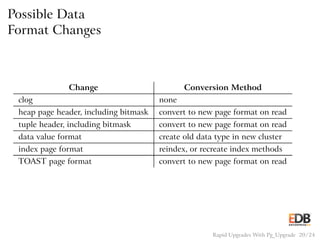
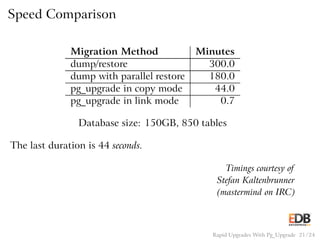
The document presents an overview of pg_upgrade, a tool that facilitates rapid upgrades between major releases of PostgreSQL without the need for data dumping and reloading. It explains the complexities of upgrading PostgreSQL, advantages of using pg_upgrade, and provides a detailed step-by-step process of how it works. Additionally, it includes a comparison of migration speeds and highlights the ongoing support and community contributions to PostgreSQL.