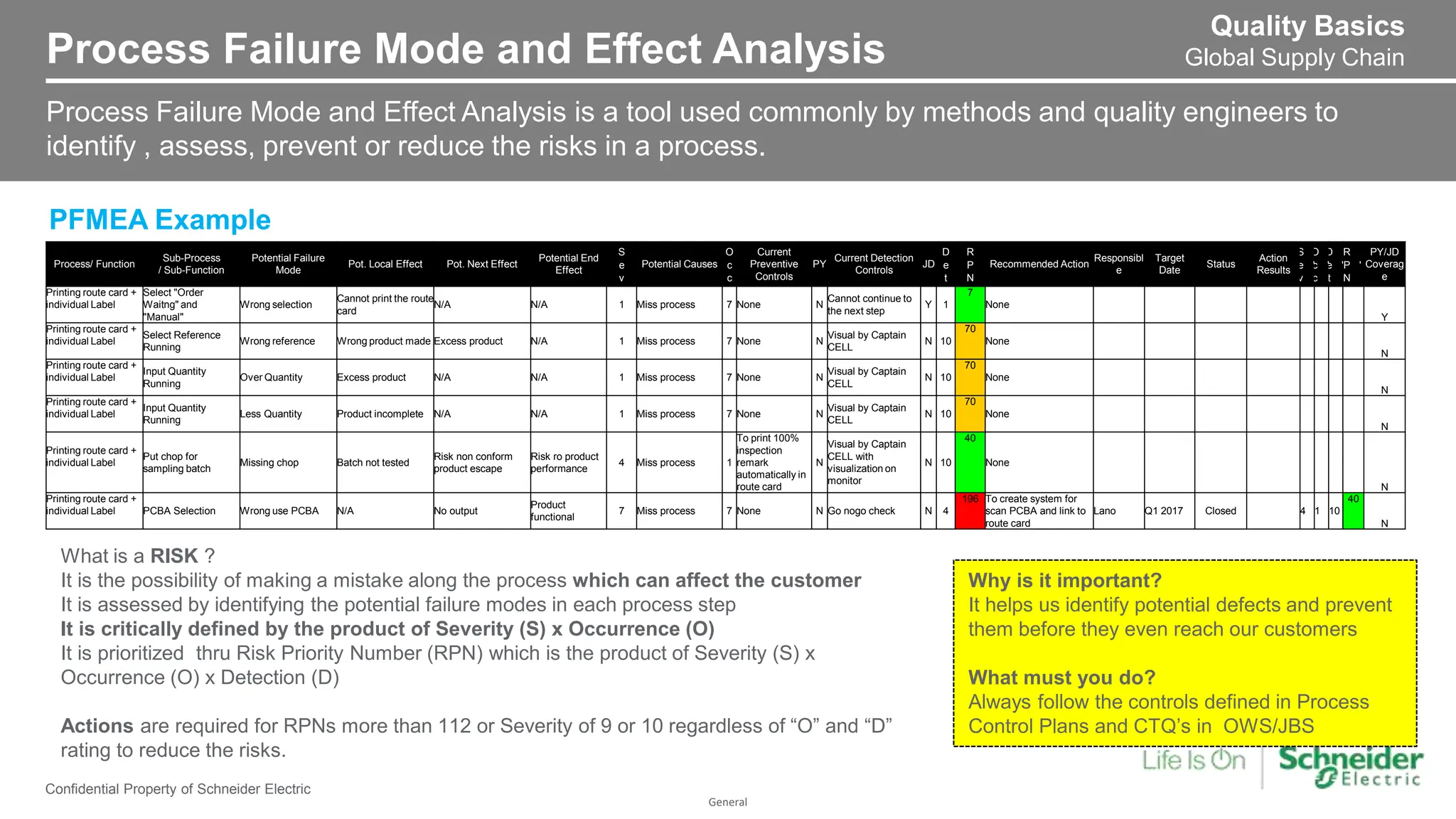
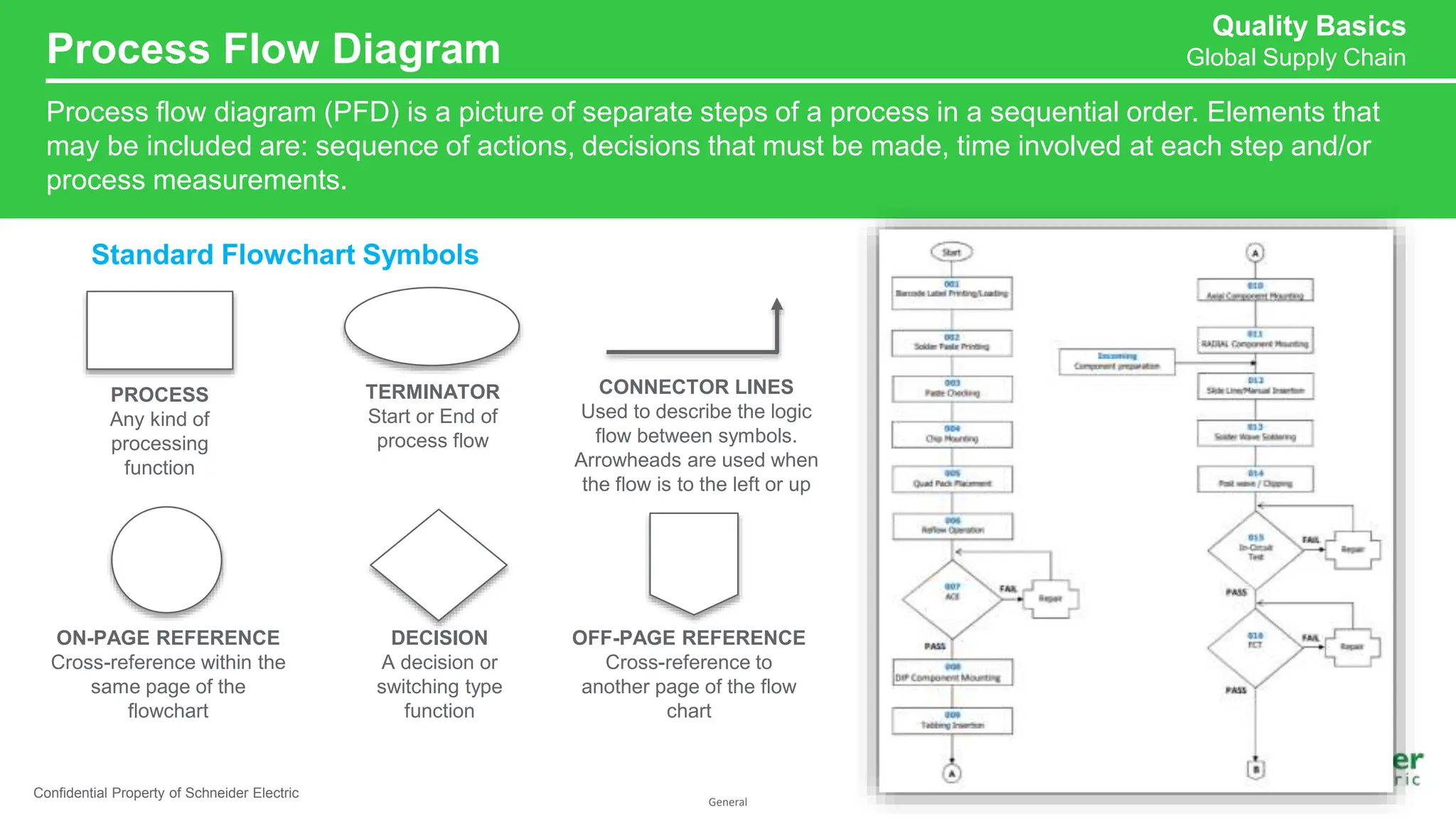
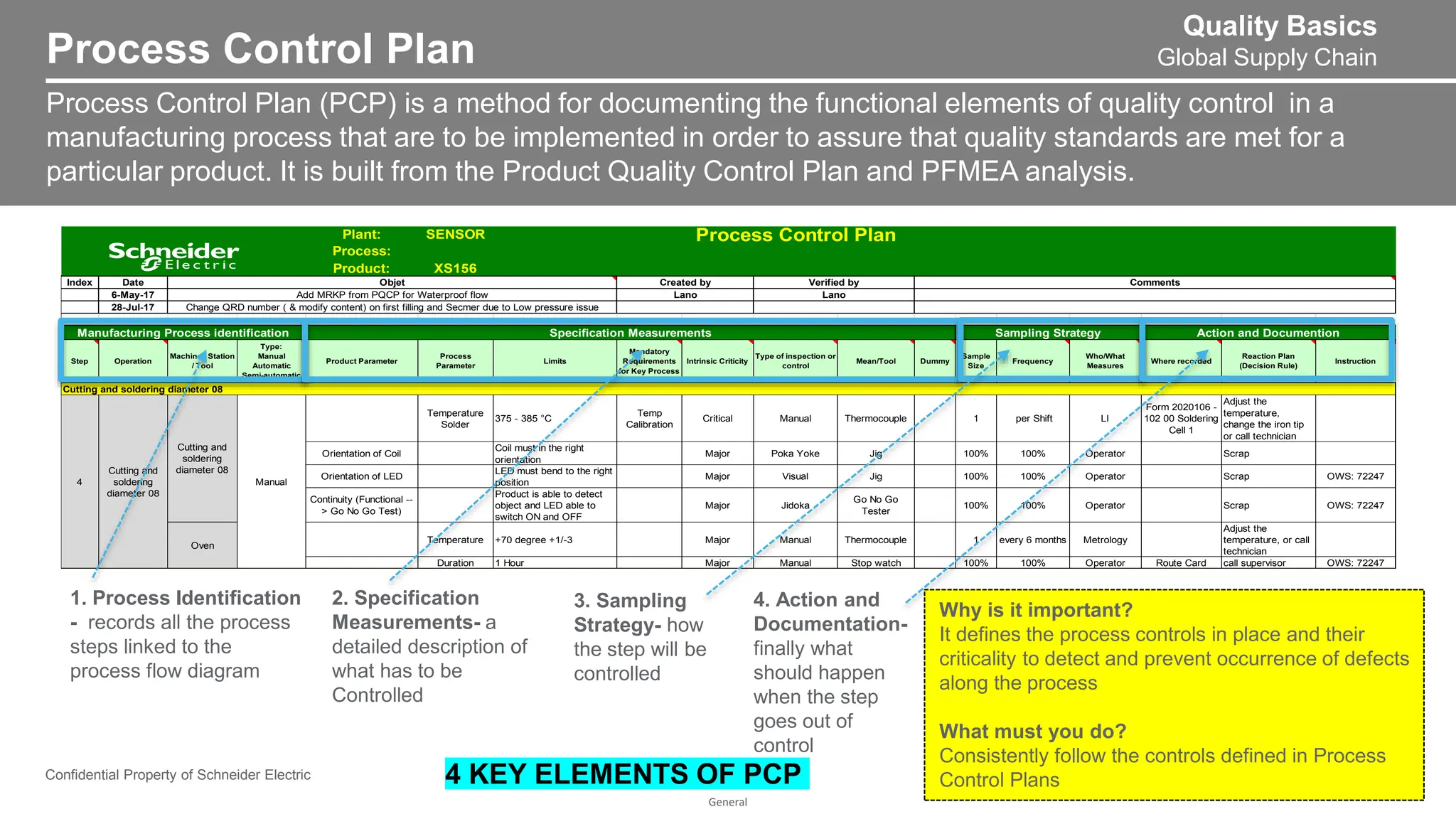
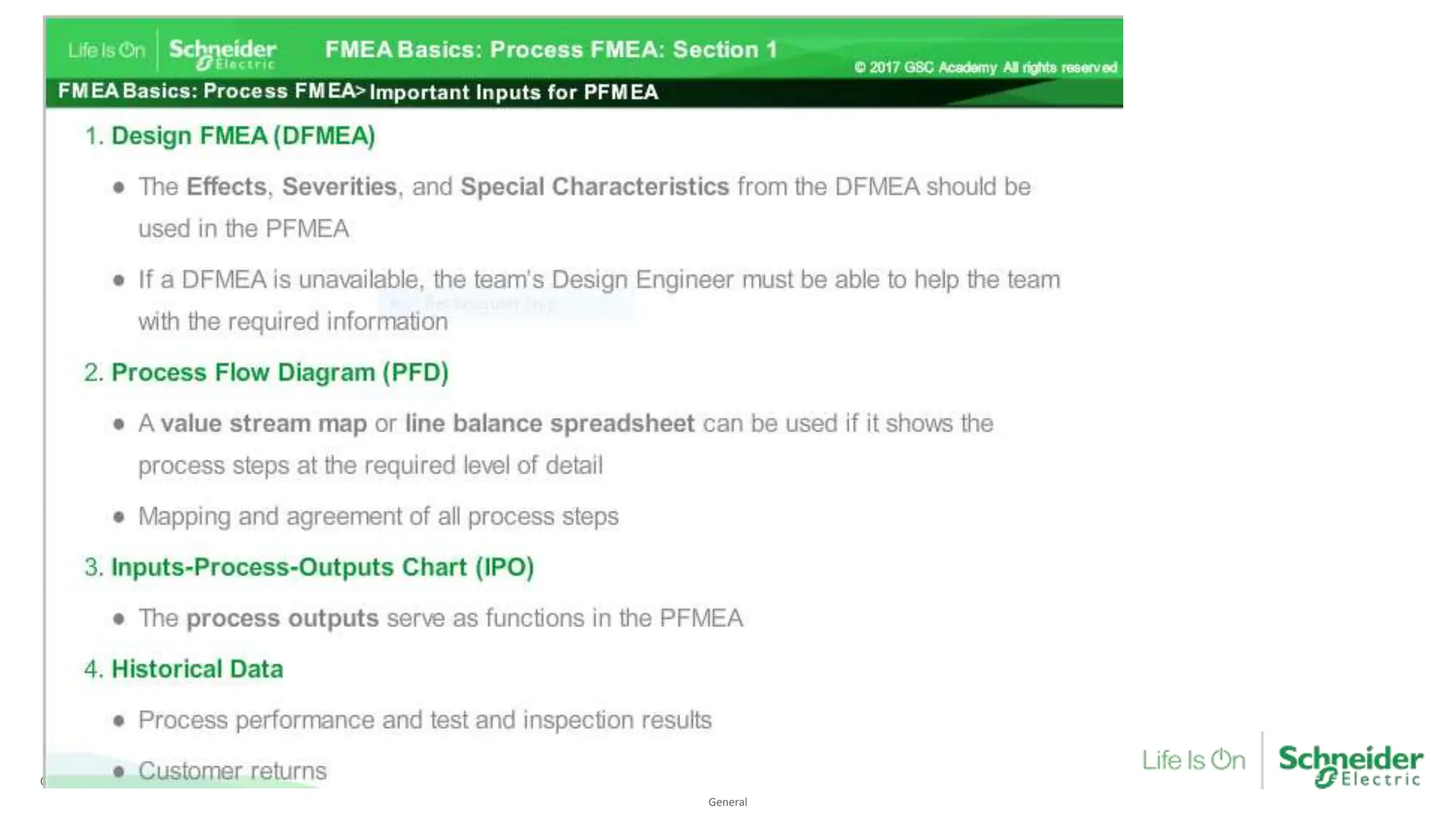
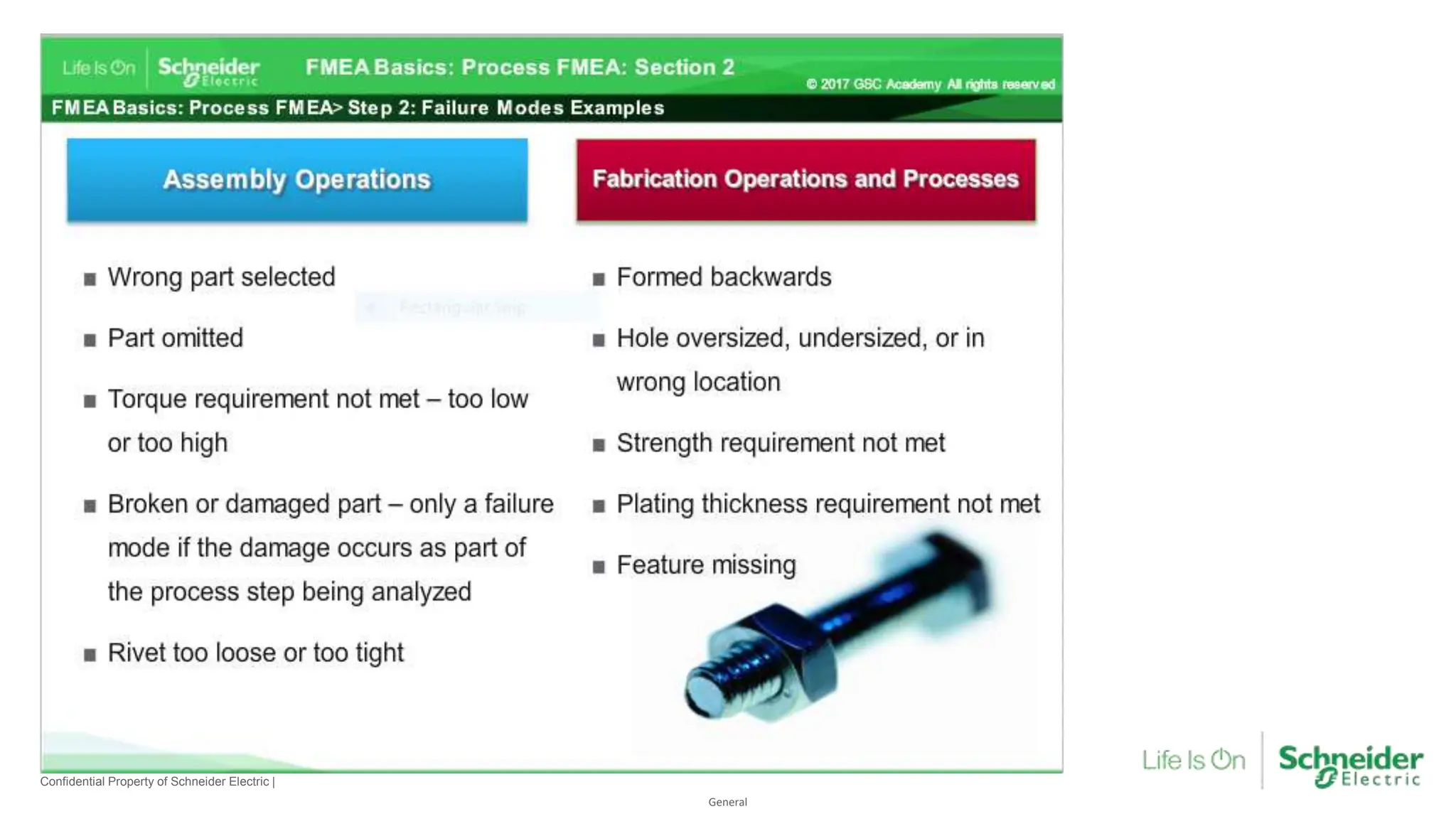
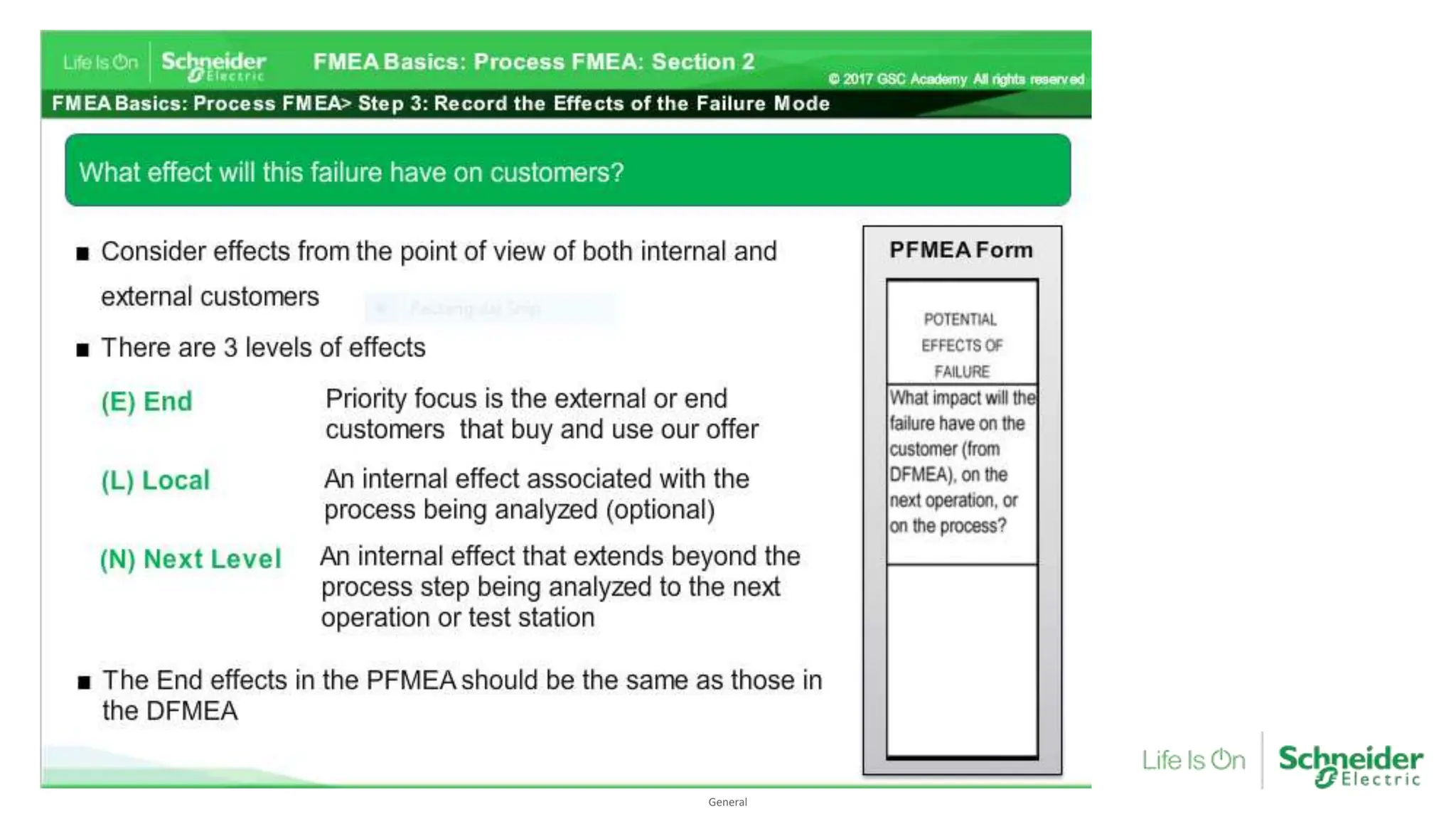
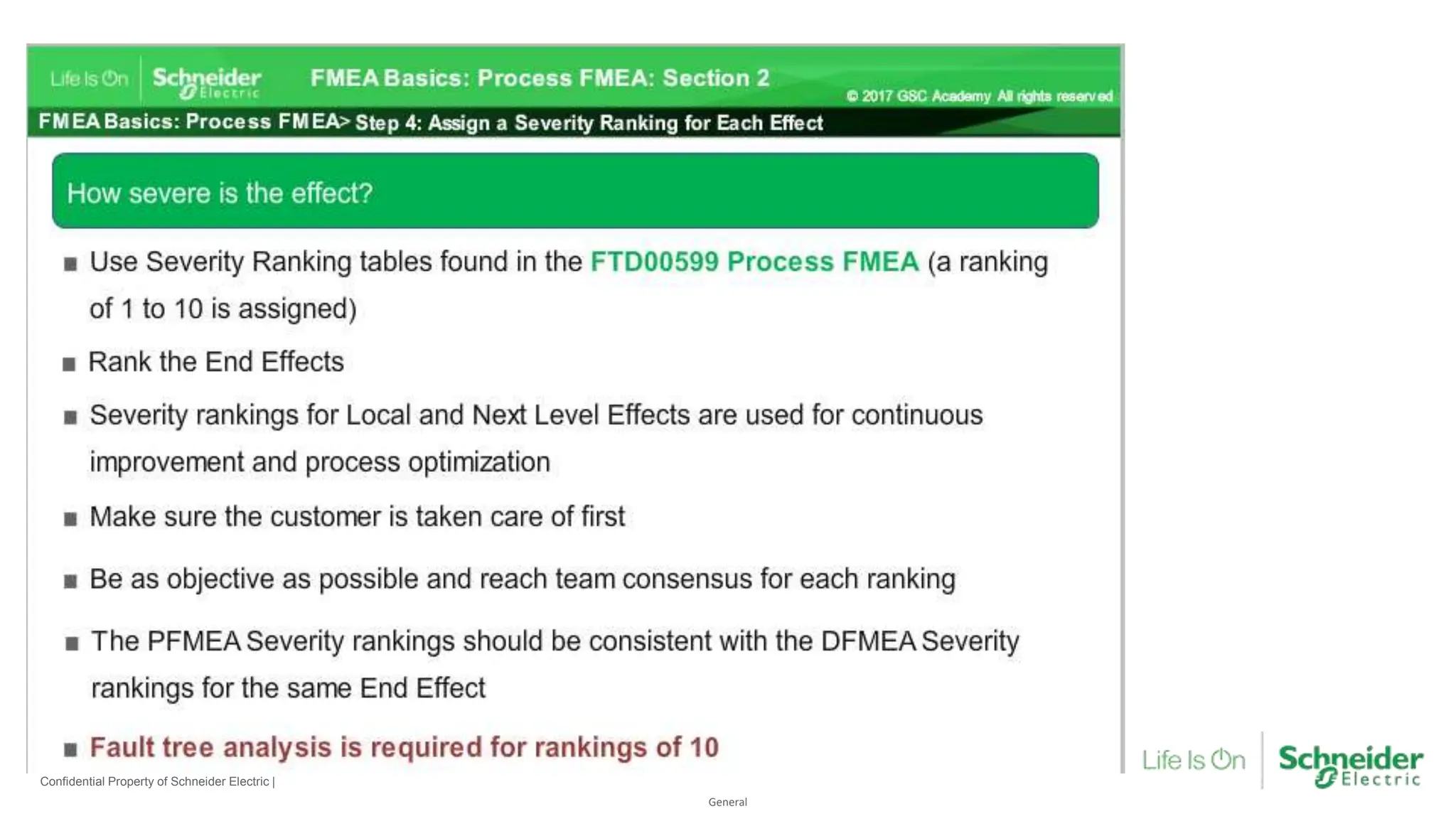
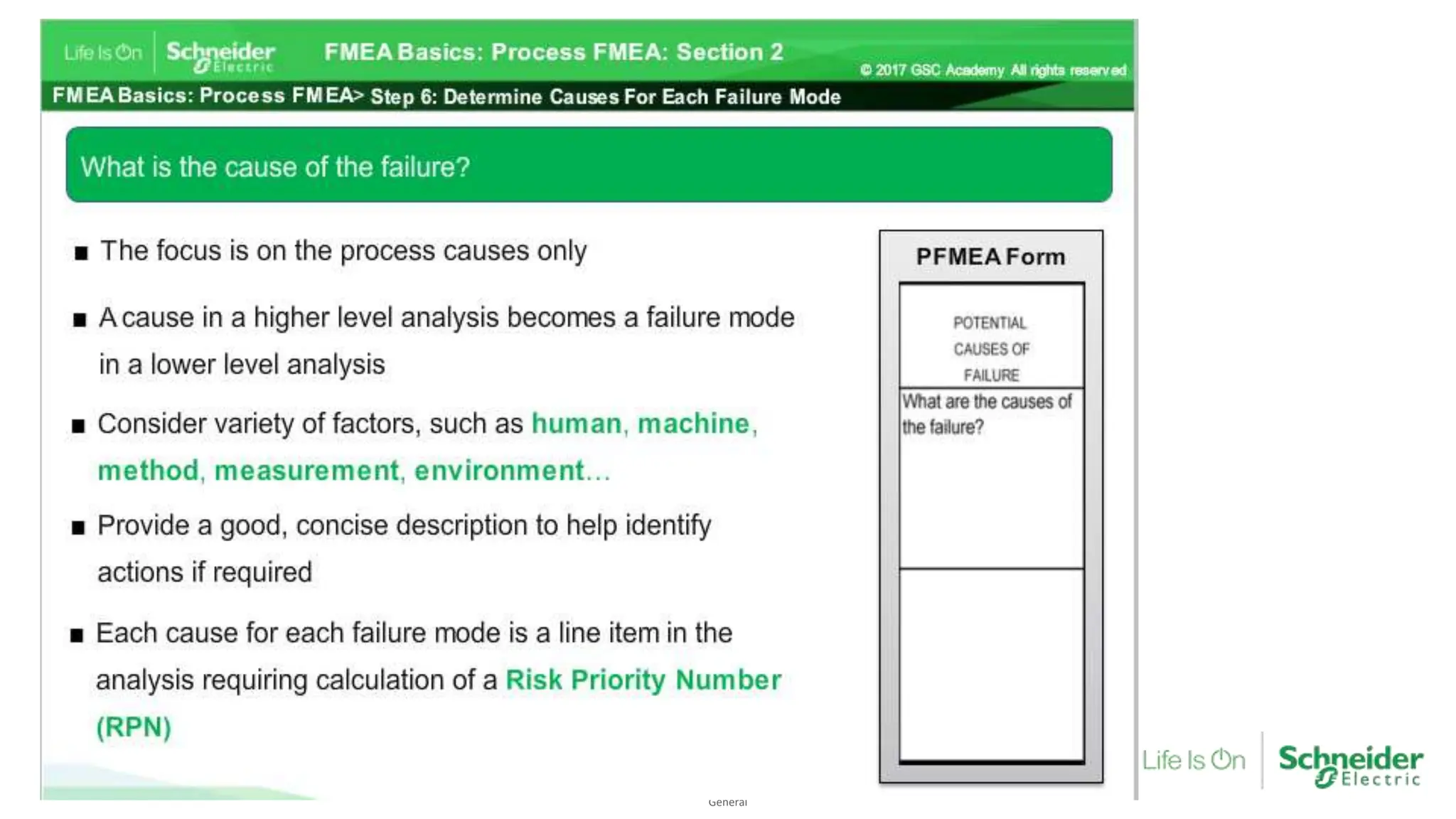
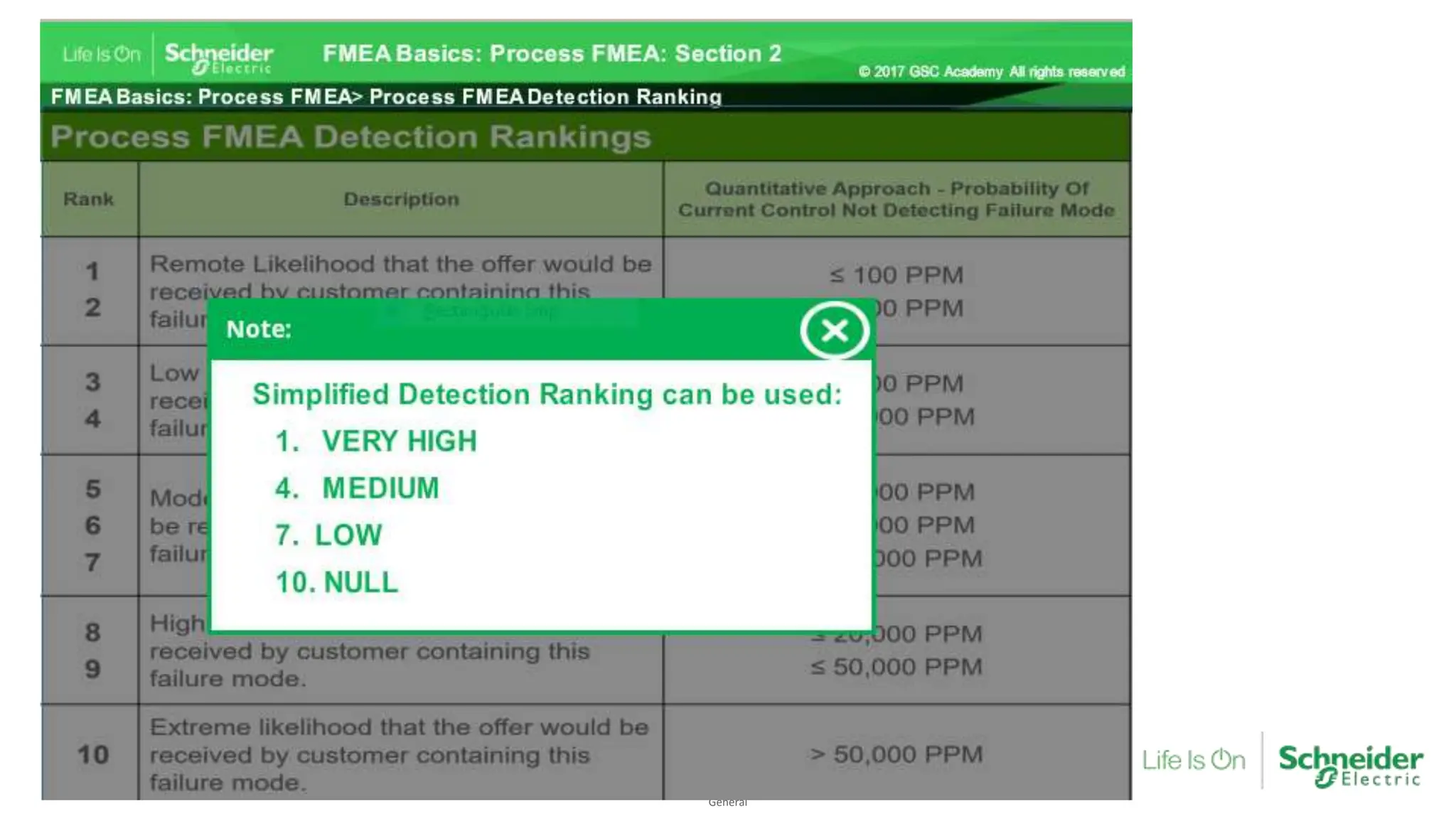
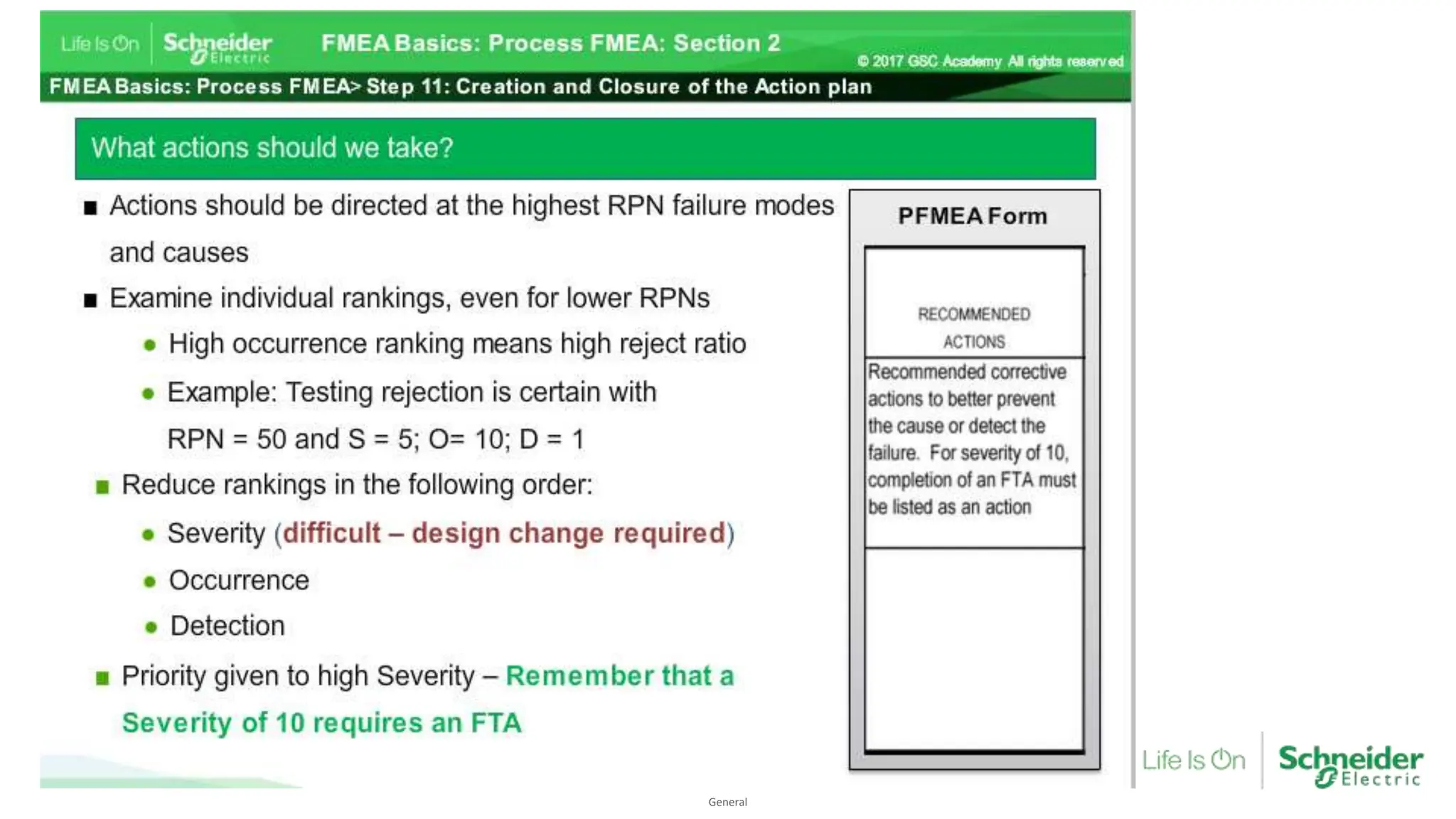
The document provides an overview of Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (PFMEA), a risk management tool used to identify and mitigate potential failure points in manufacturing processes. It emphasizes the importance of systematically reviewing failures to prevent defects from reaching customers, detailing specific process control plans and measurements. Additionally, it outlines the significance of adhering to defined controls to ensure quality and compliance in manufacturing operations.