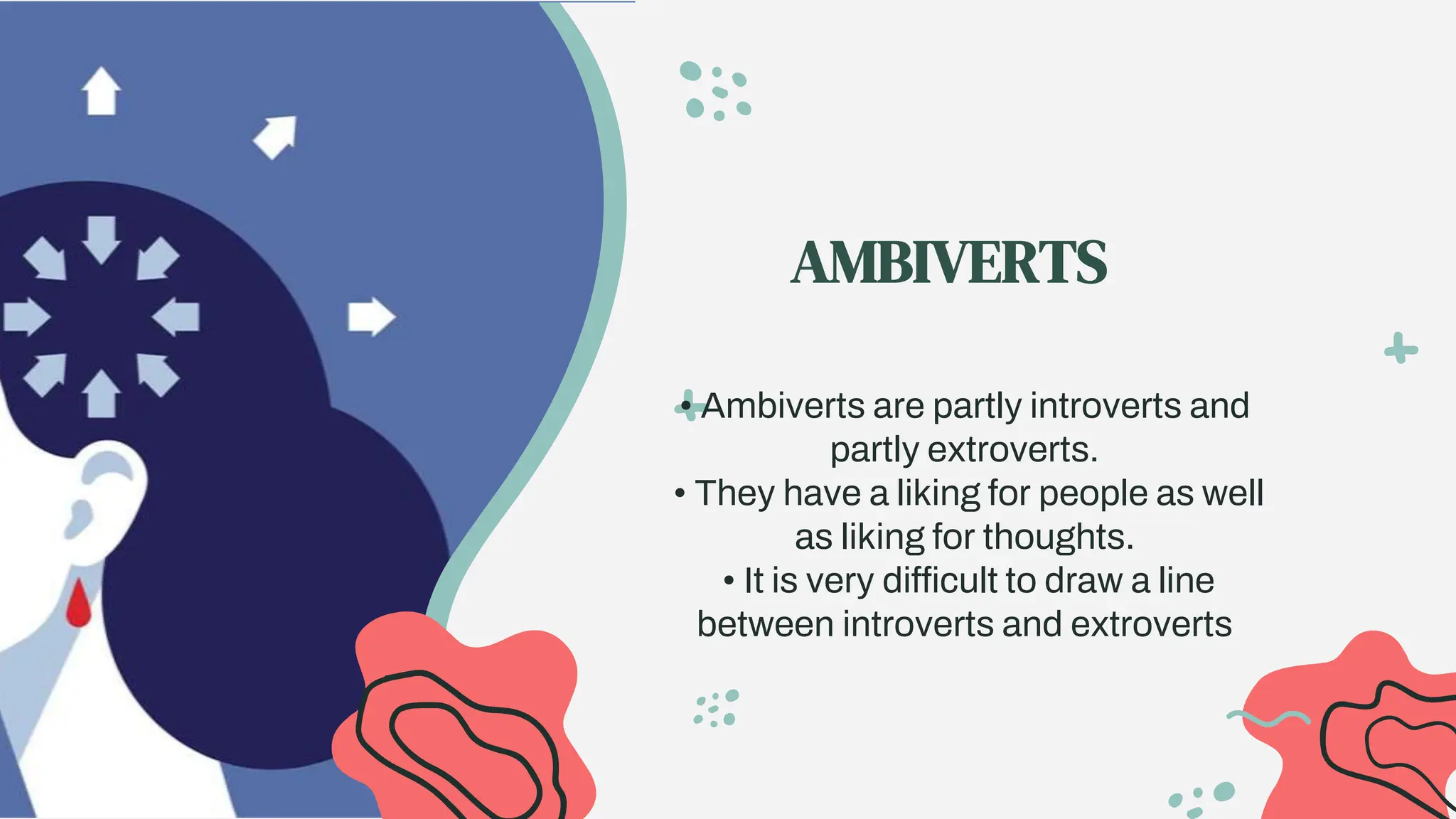
The document discusses personality development as a lifelong process influenced by genetics, environment, experiences, and personal choices. It categorizes personalities into introverts, extroverts, and ambiverts, highlighting their distinct traits and behaviors. Additionally, it outlines essential dimensions of personality development, including self-confidence, self-awareness, emotional intelligence, interpersonal skills, and adaptability.