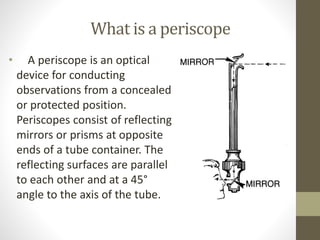
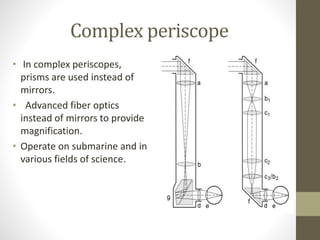
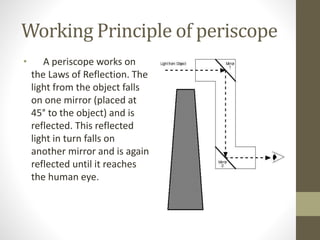
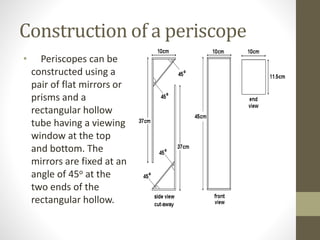
A periscope is an optical device used to observe one's surroundings from a concealed position. It consists of mirrors or prisms set at 45 degree angles within a tube to redirect light. Periscopes allow observation over barriers without exposure. They were used in World War I and II trenches and submarines. Periscopes operate on the principle of light reflection and come in simple and complex forms. They have various applications including in submarines, tanks, medicine, laboratories, and fuel tanks to enable observation of dangerous areas from a safe position.