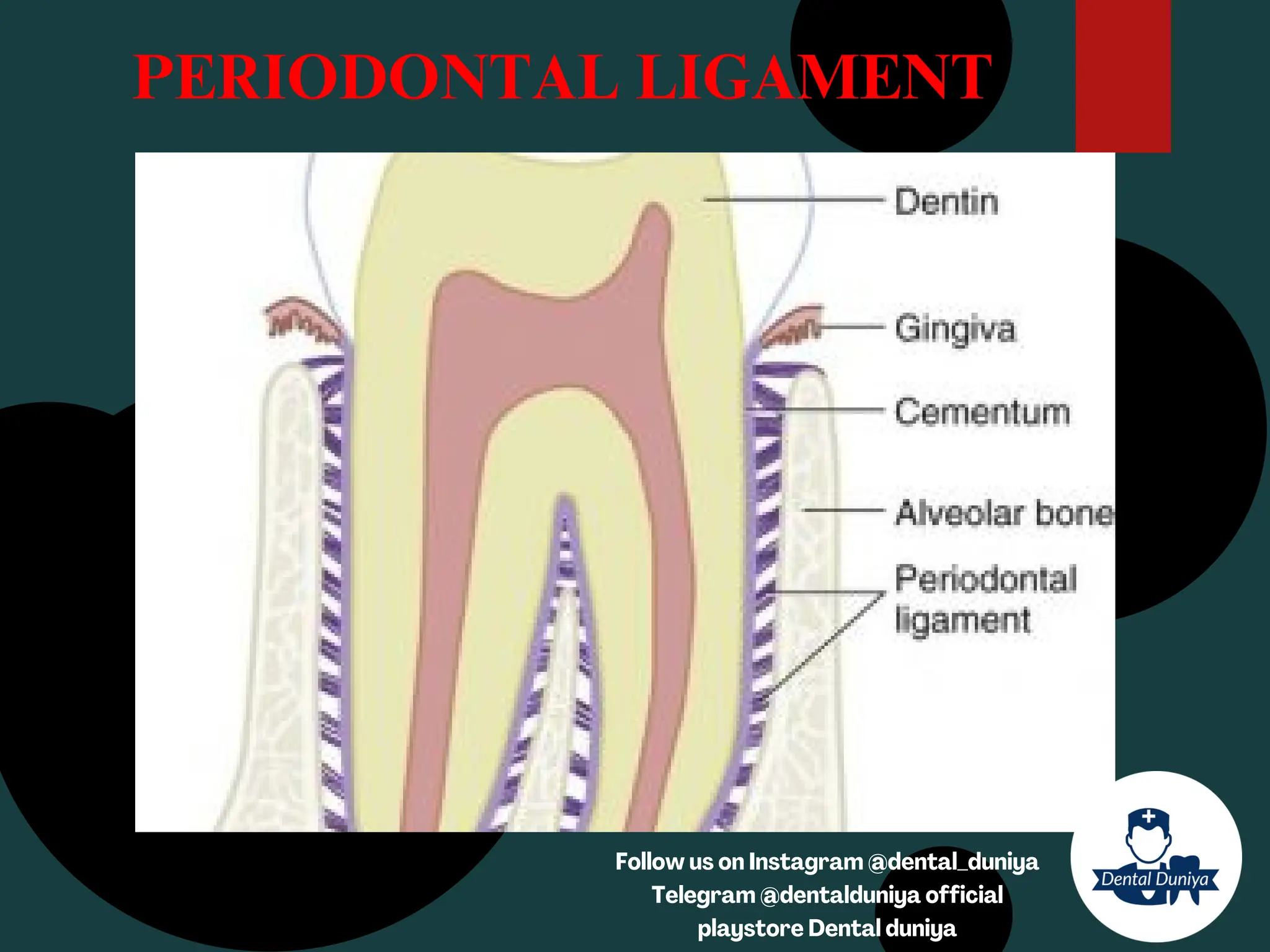
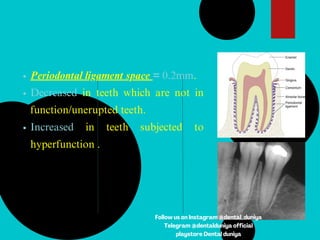
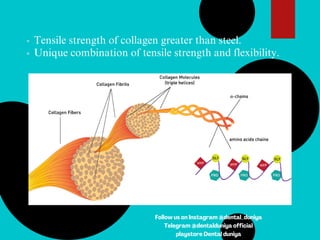
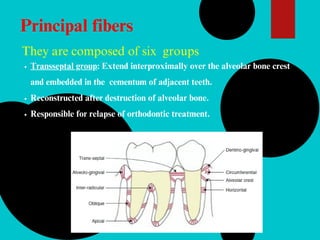
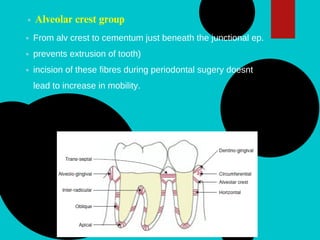
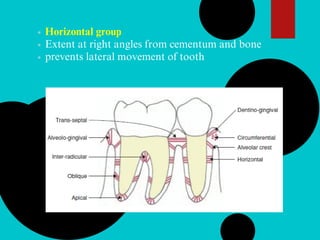
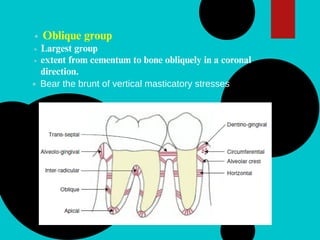
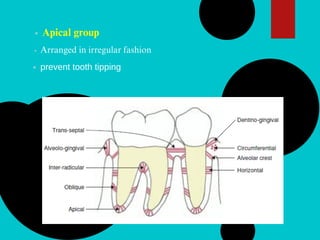
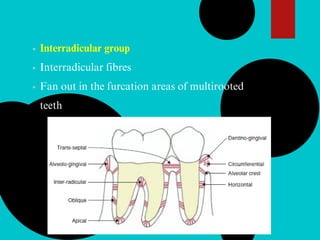
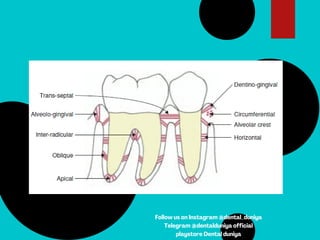
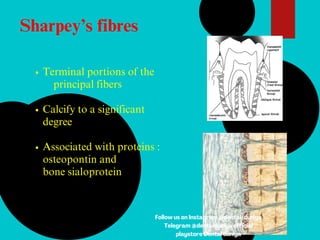
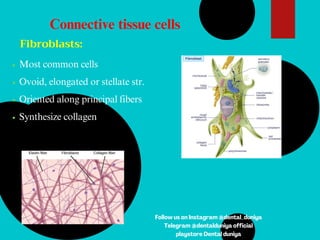
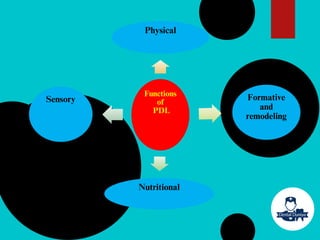
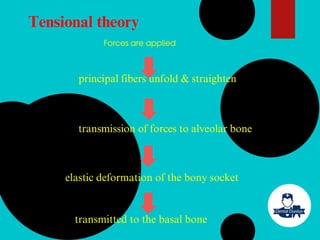
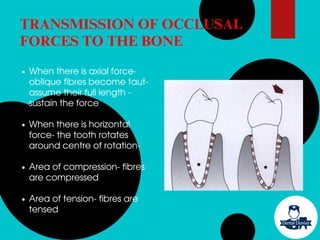
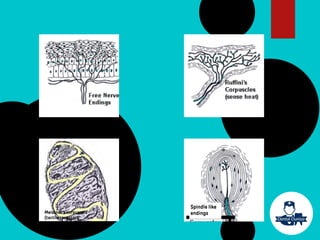
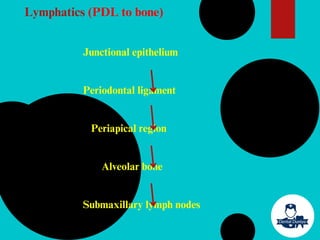
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the periodontal ligament (PDL), detailing its definition, structure, and functions within the dental anatomy. It explains the components of PDL, including various types of collagen fibers and cellular elements, and discusses the ligament's role in tooth support and the transmission of occlusal forces. Additionally, it describes the blood supply, sensory functions, and clinical considerations associated with the periodontal ligament.