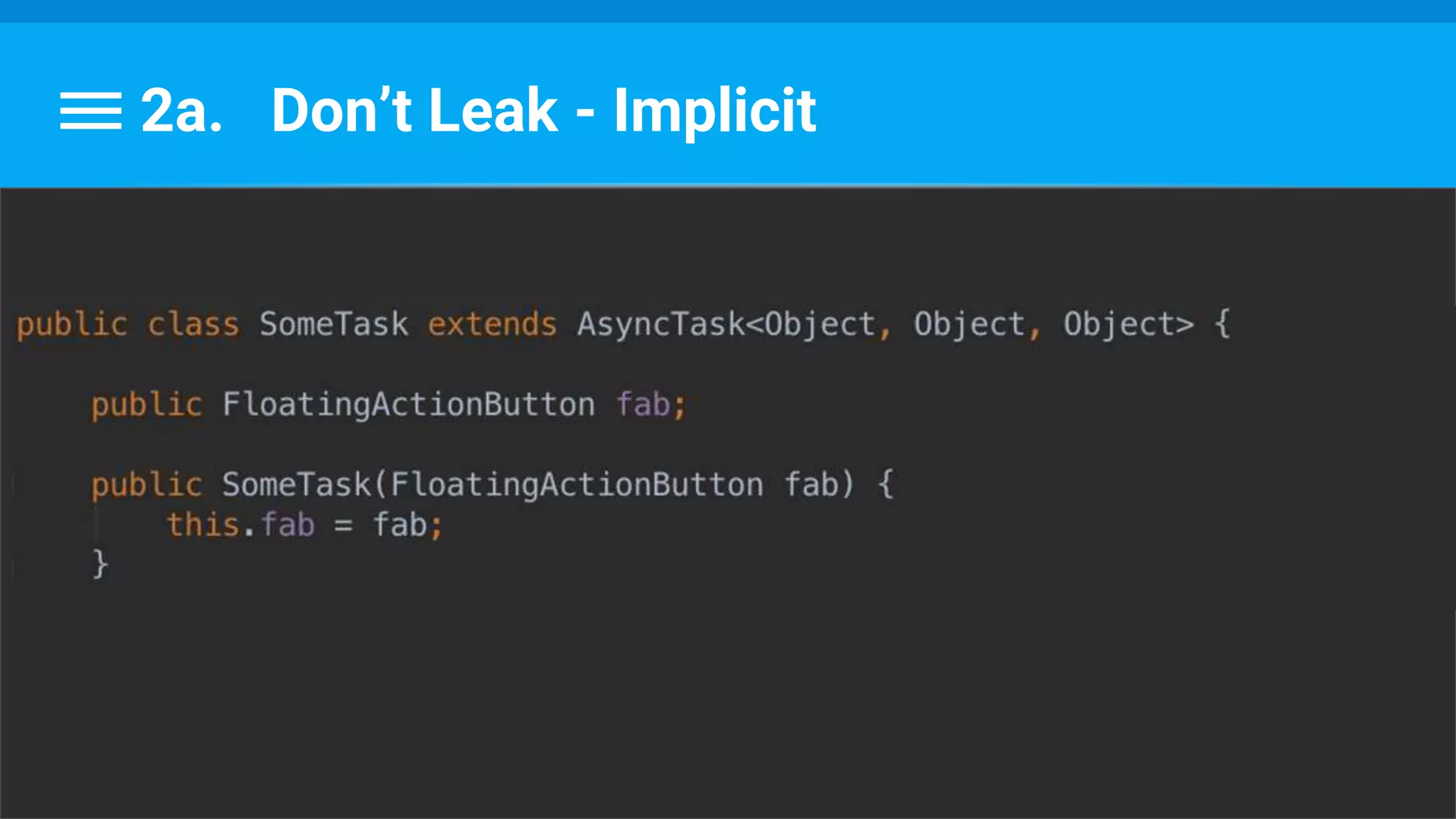
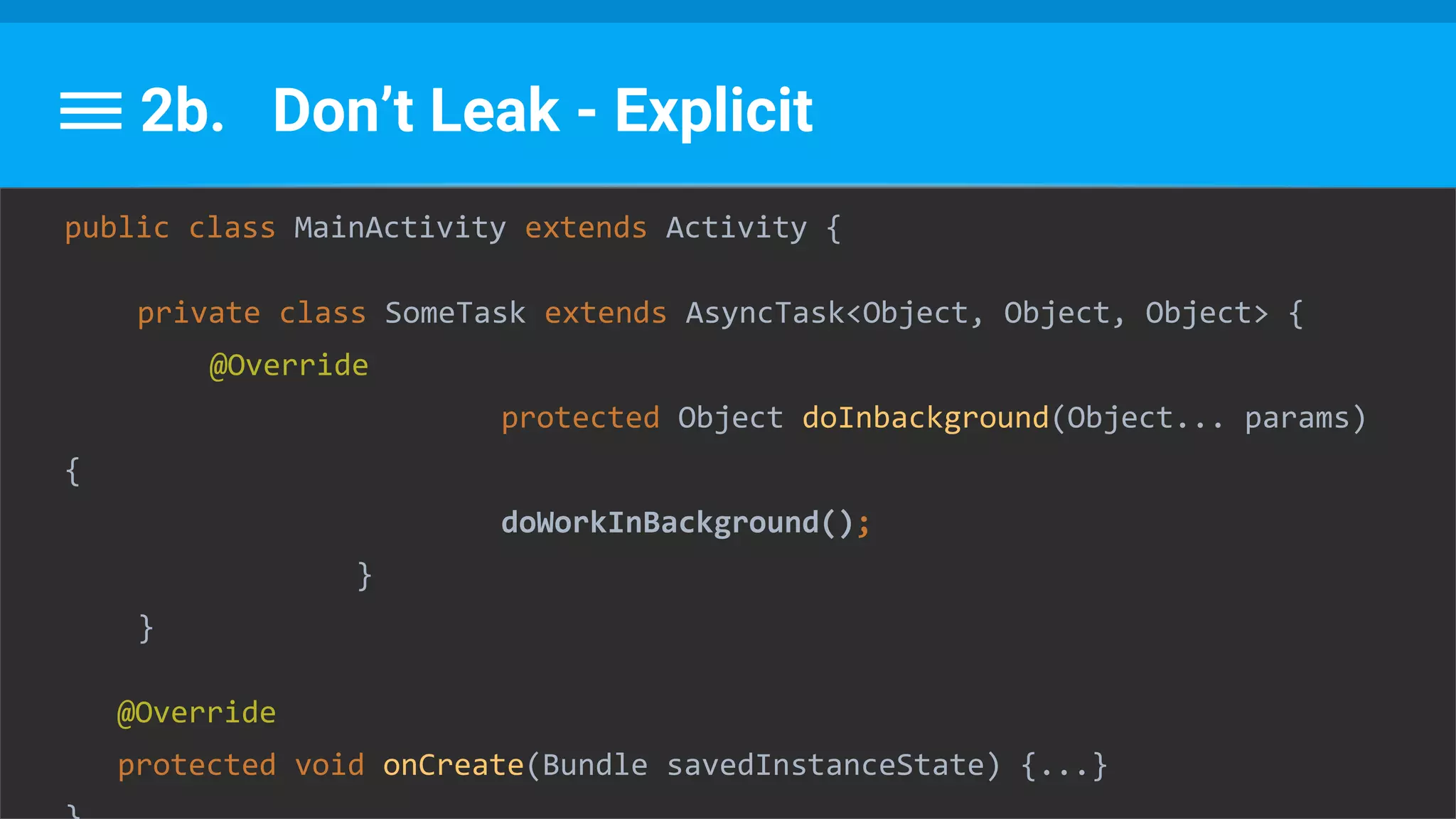
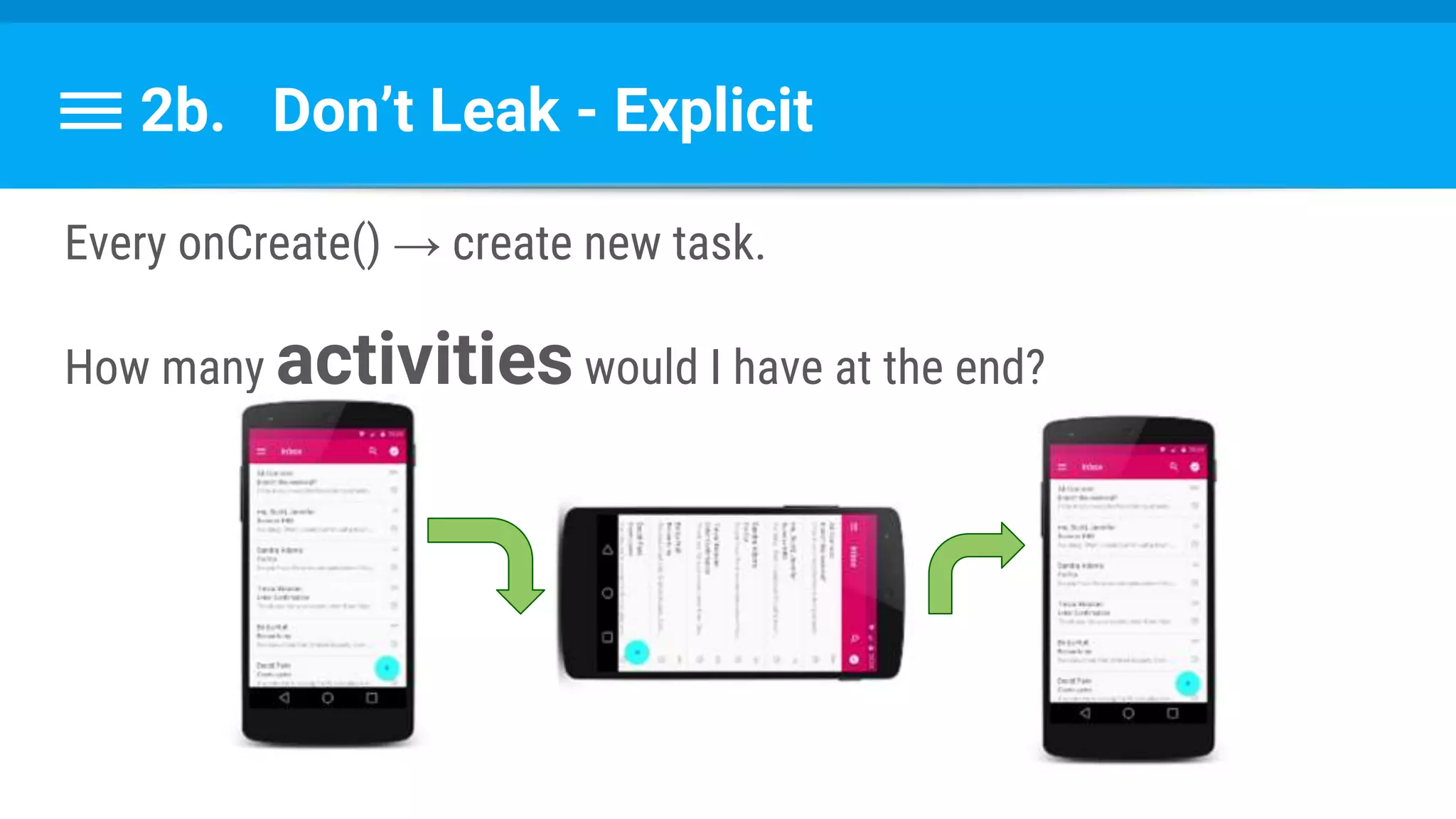
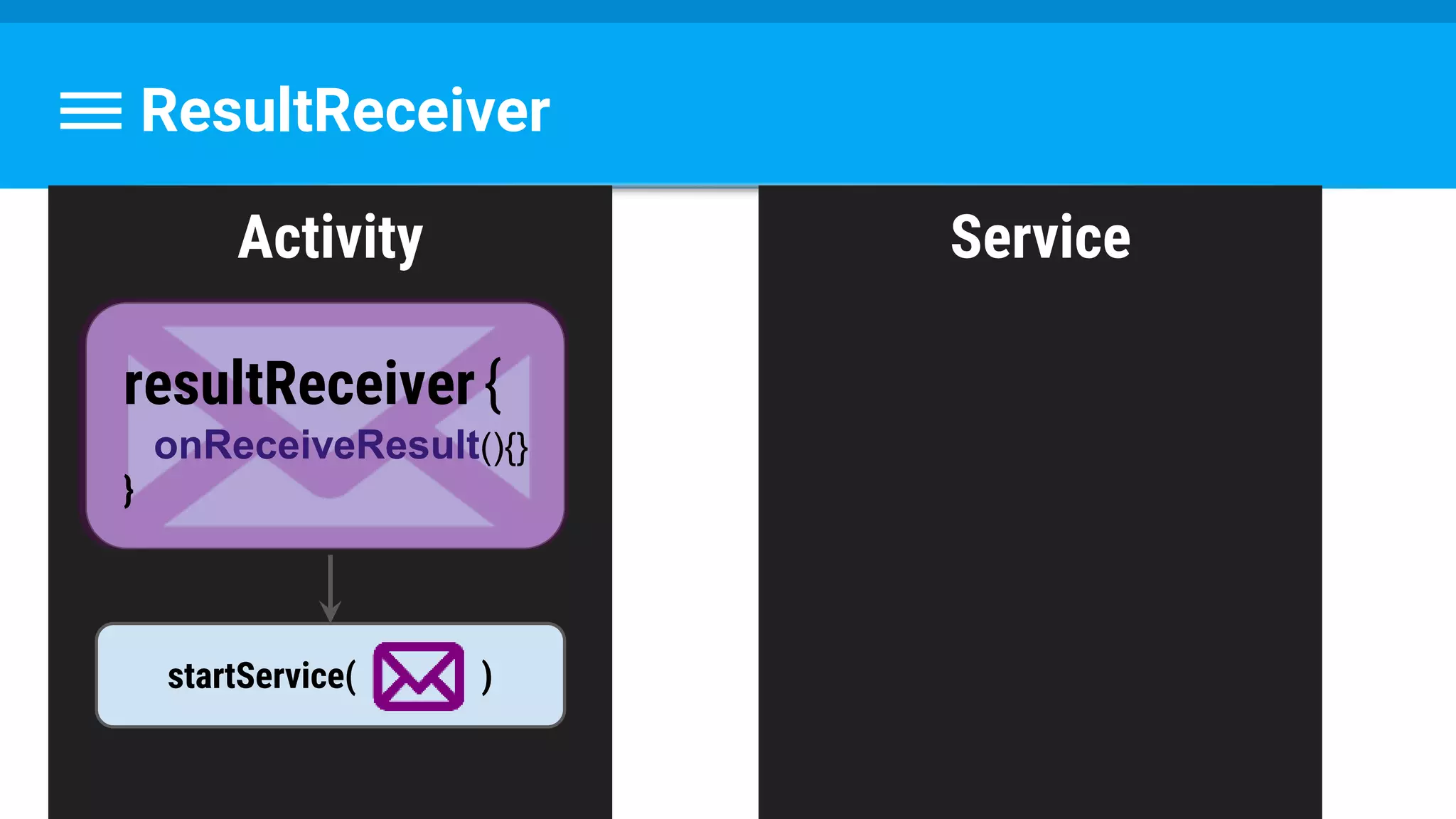
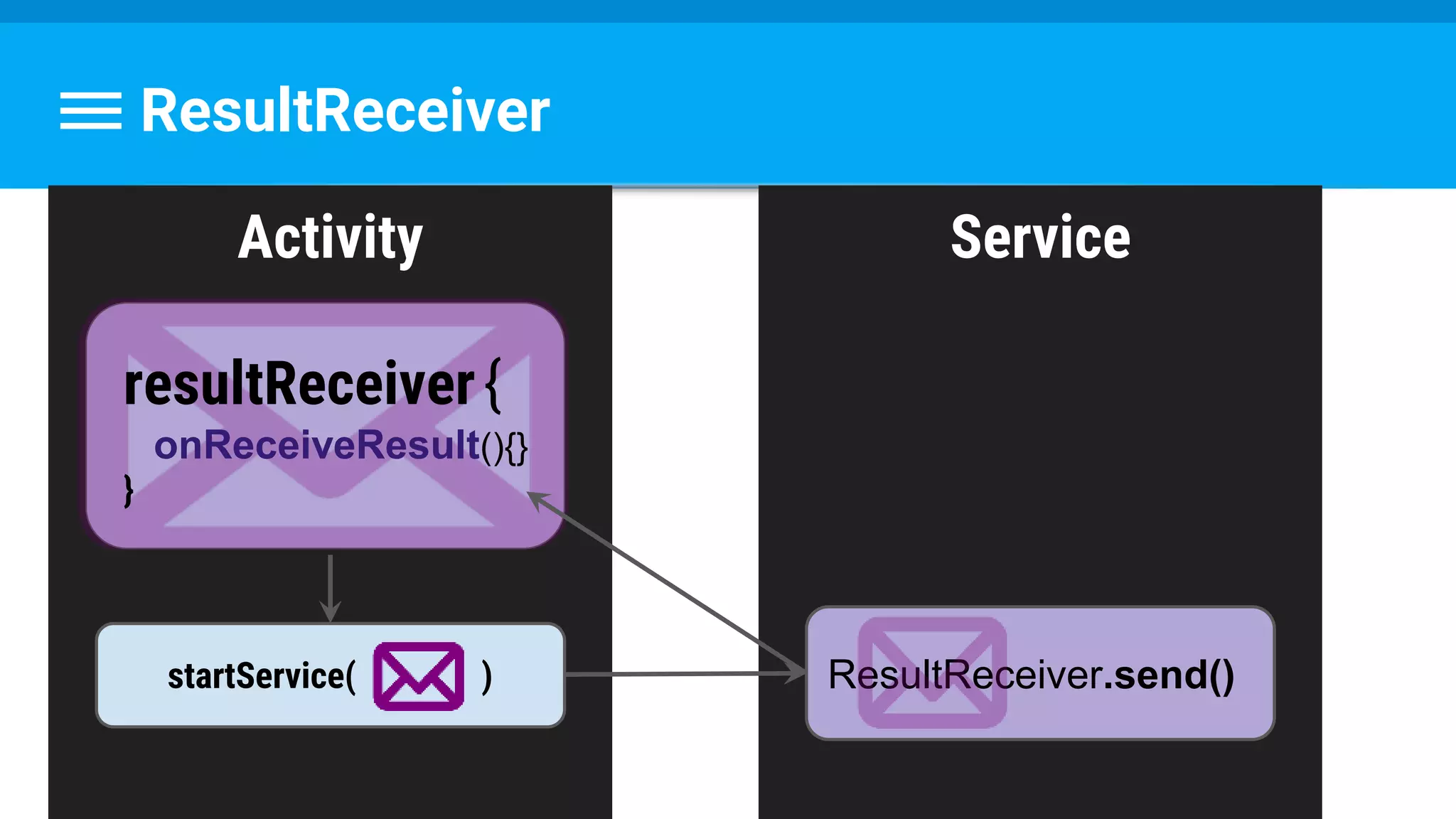
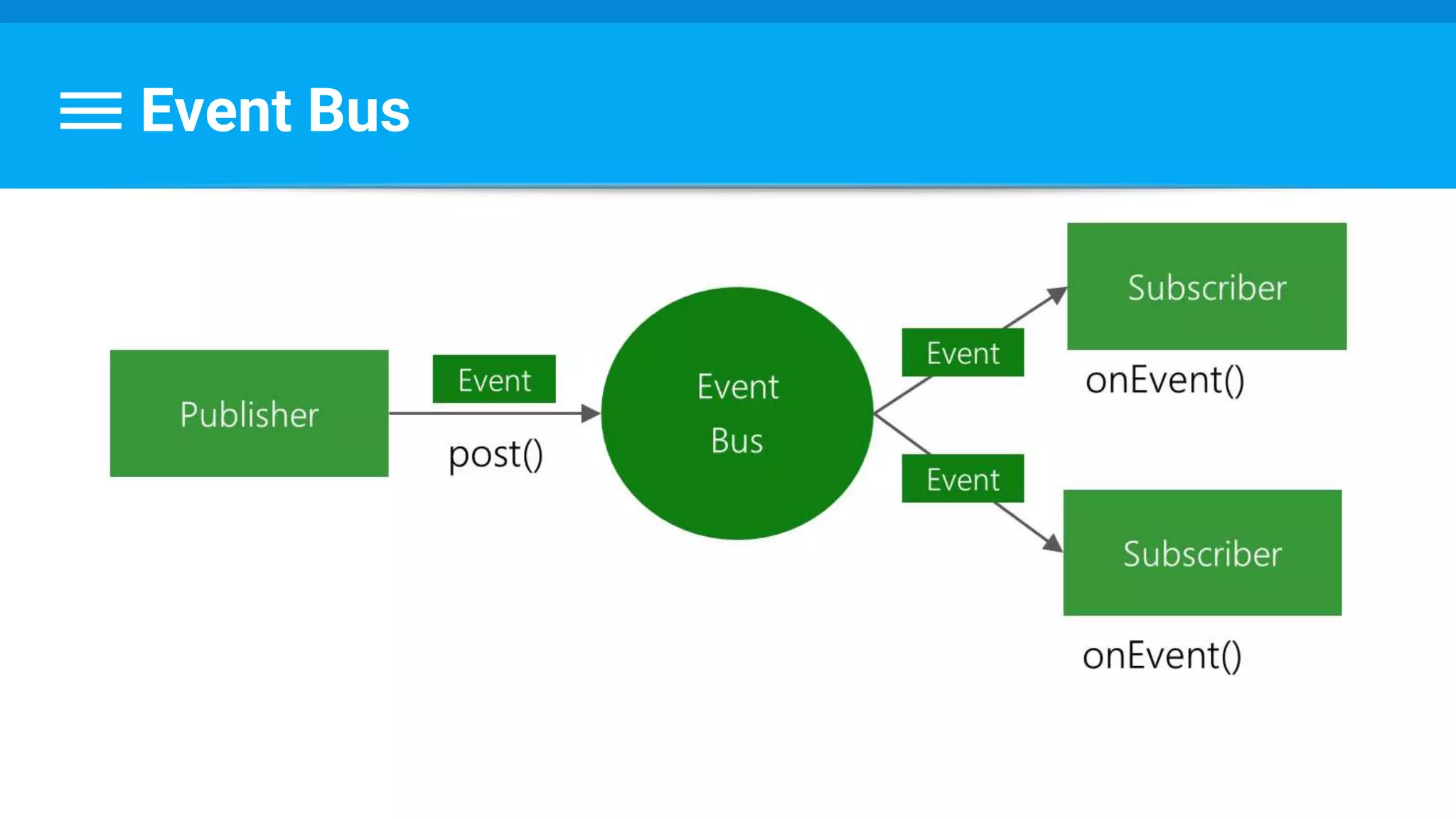
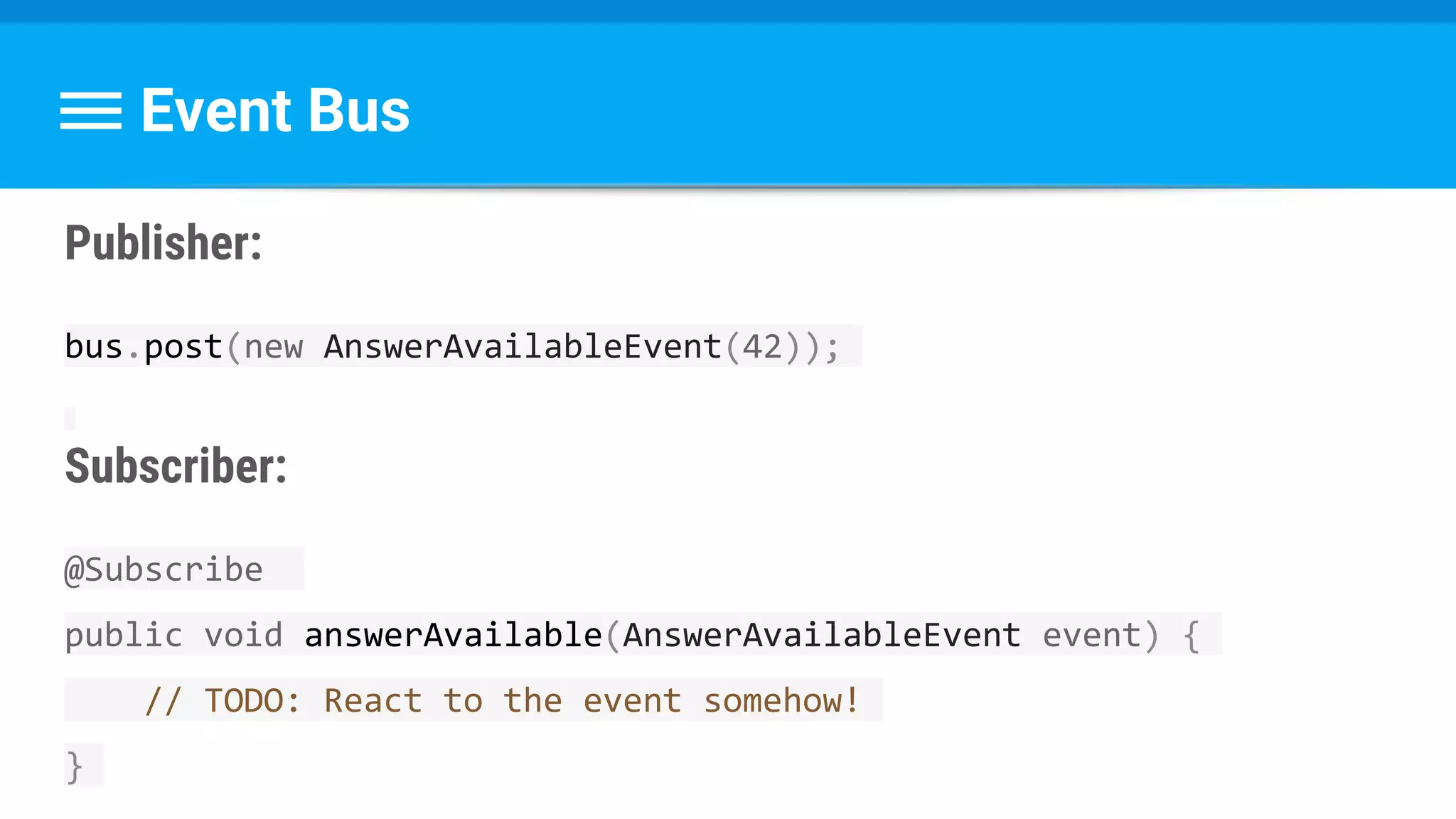
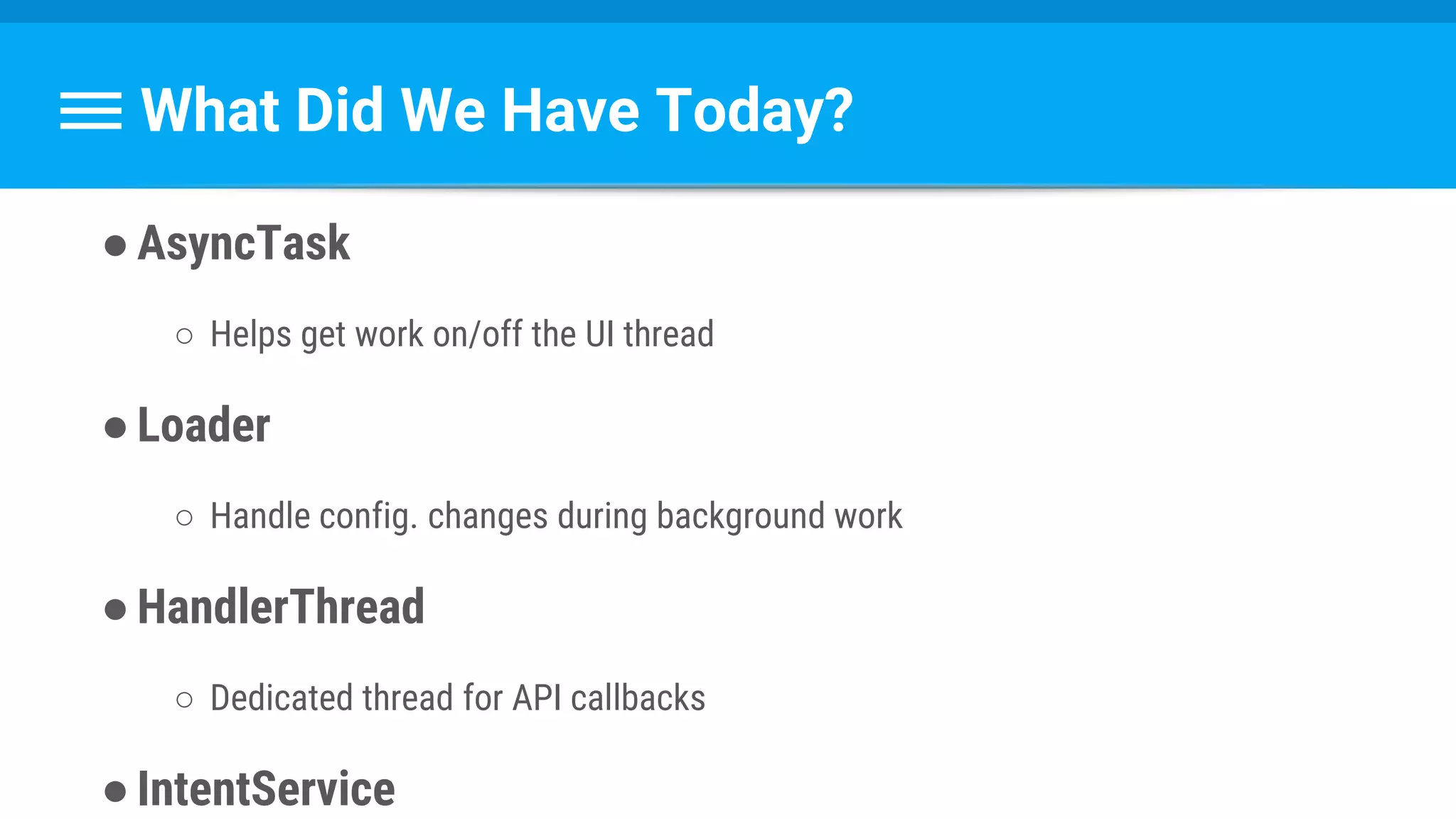
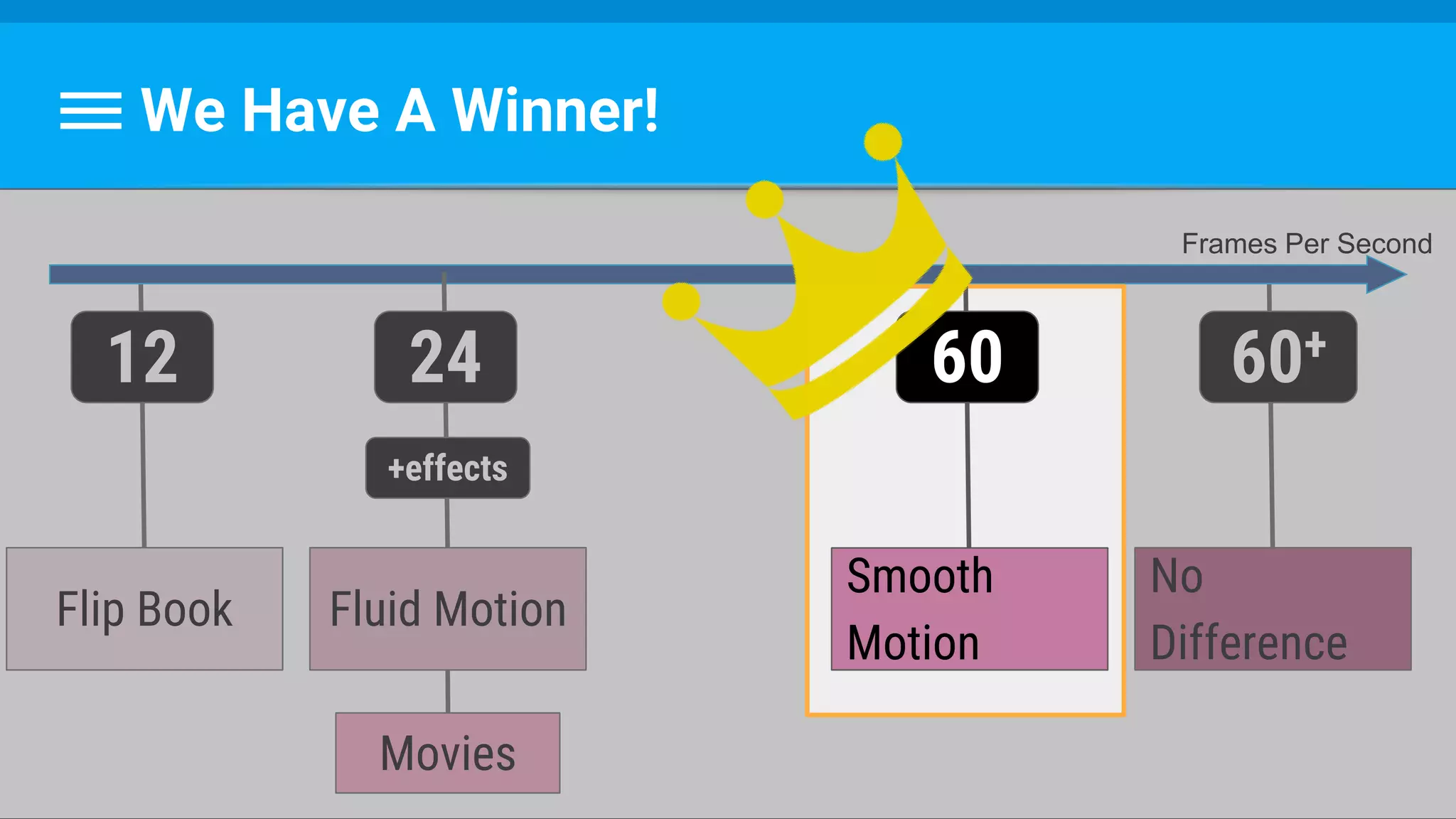
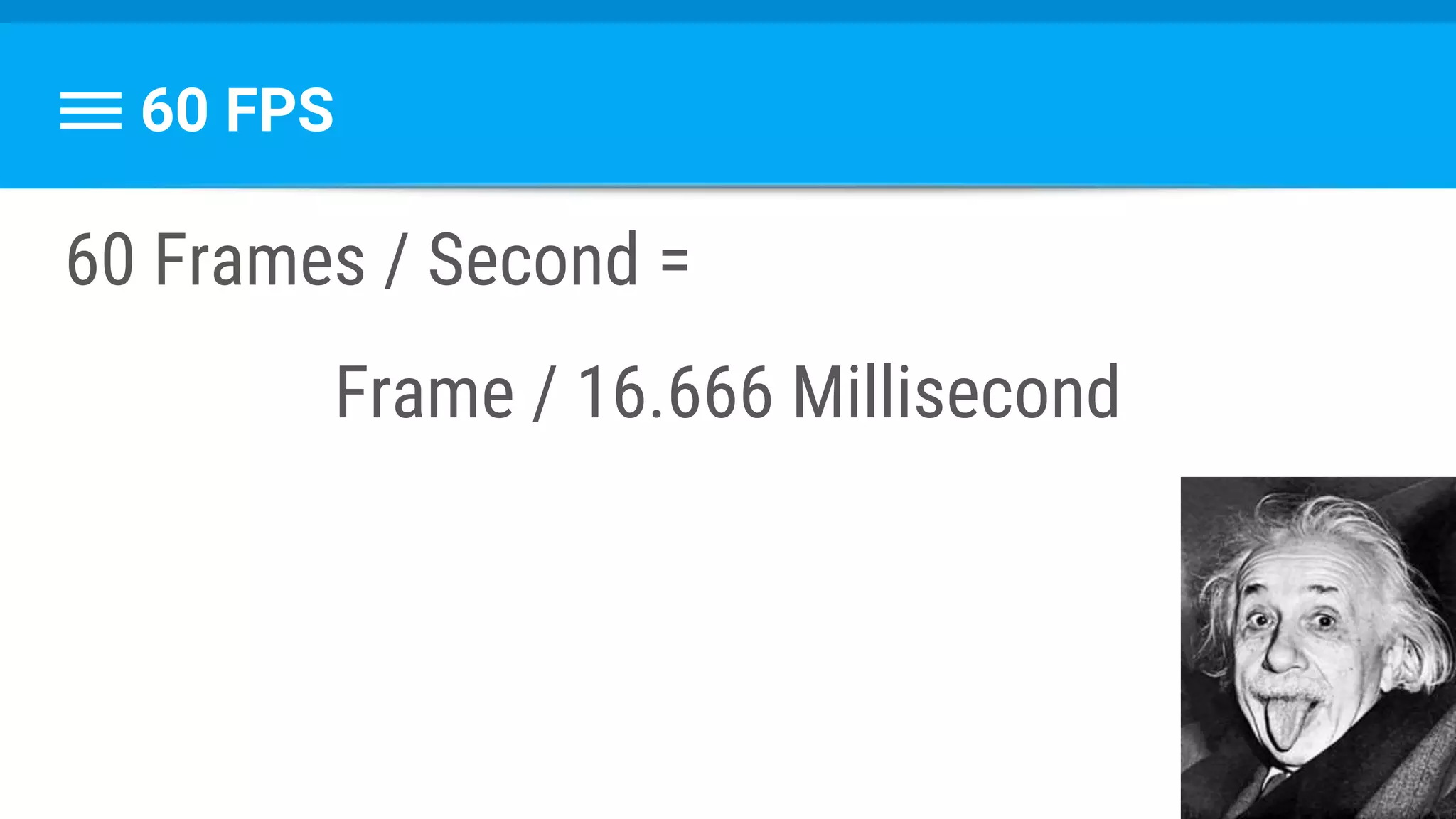
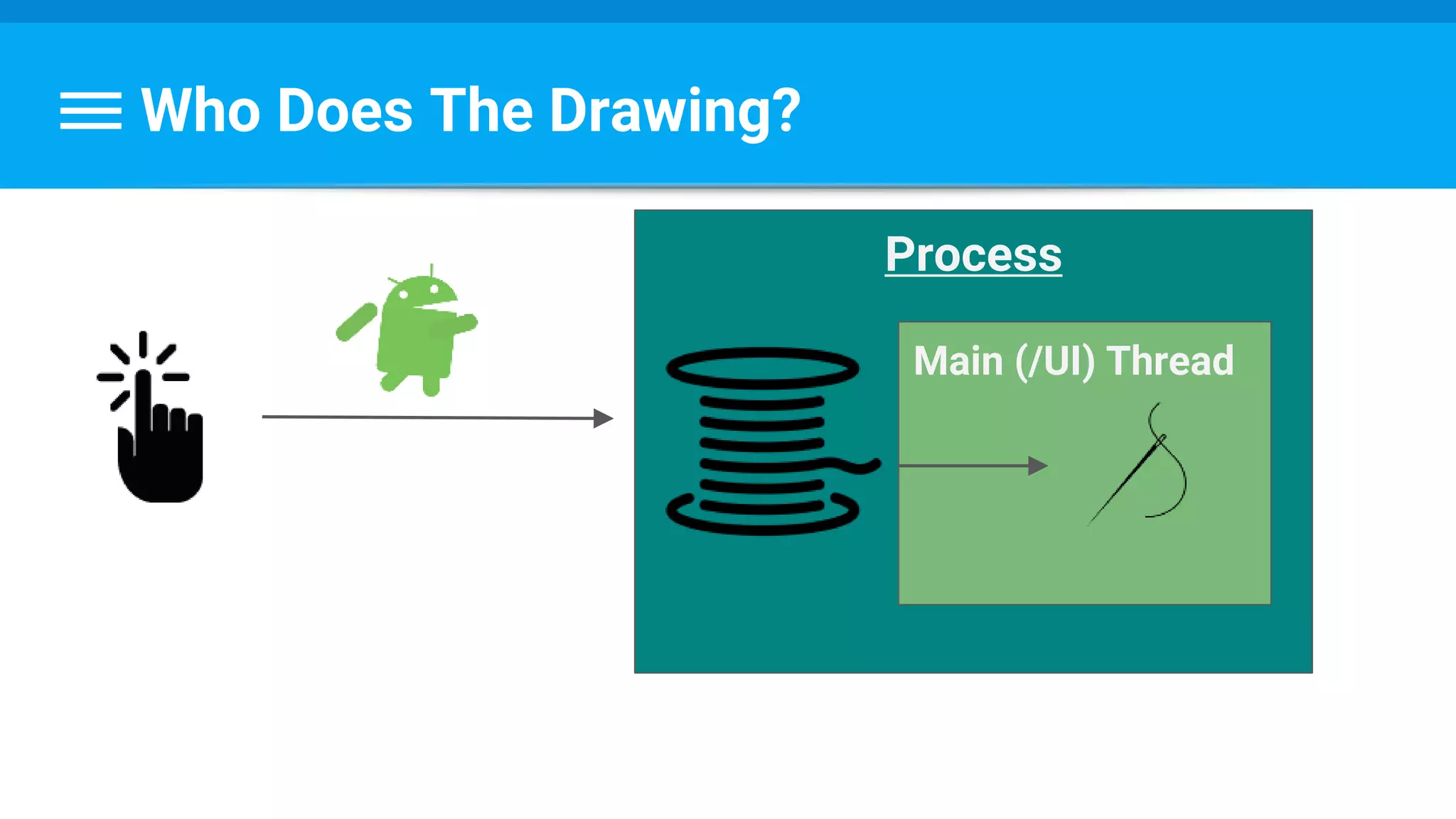
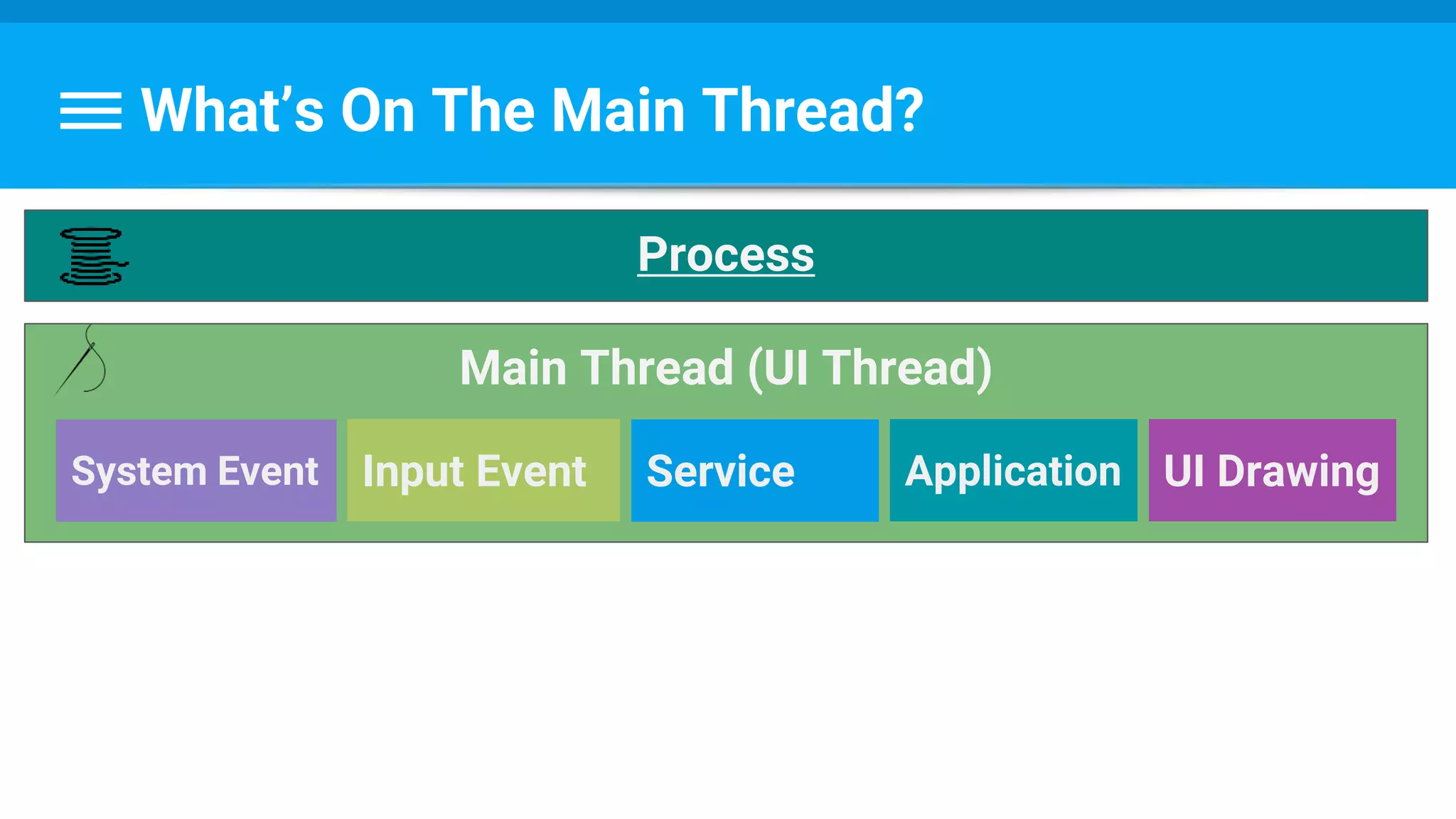
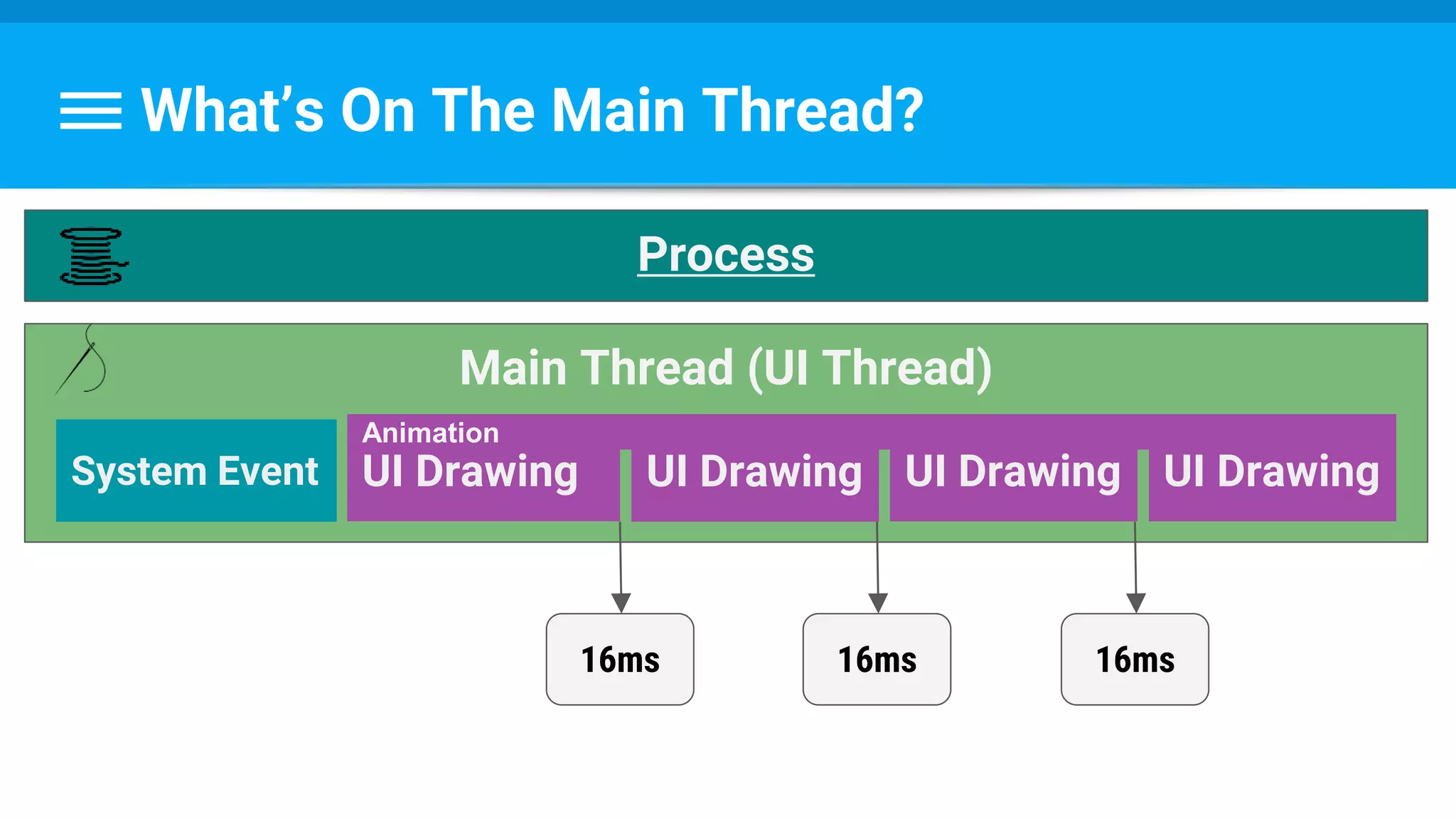
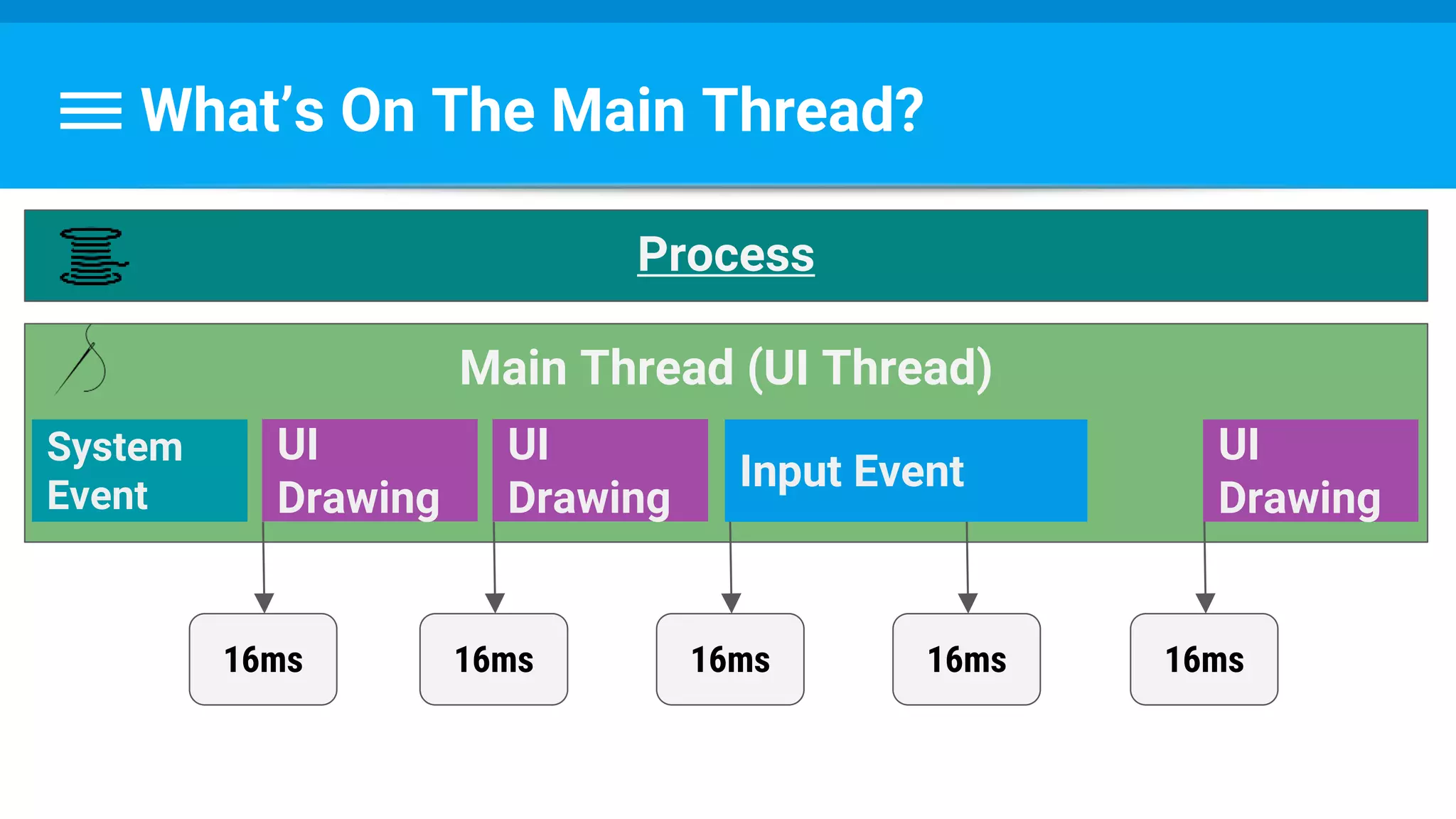
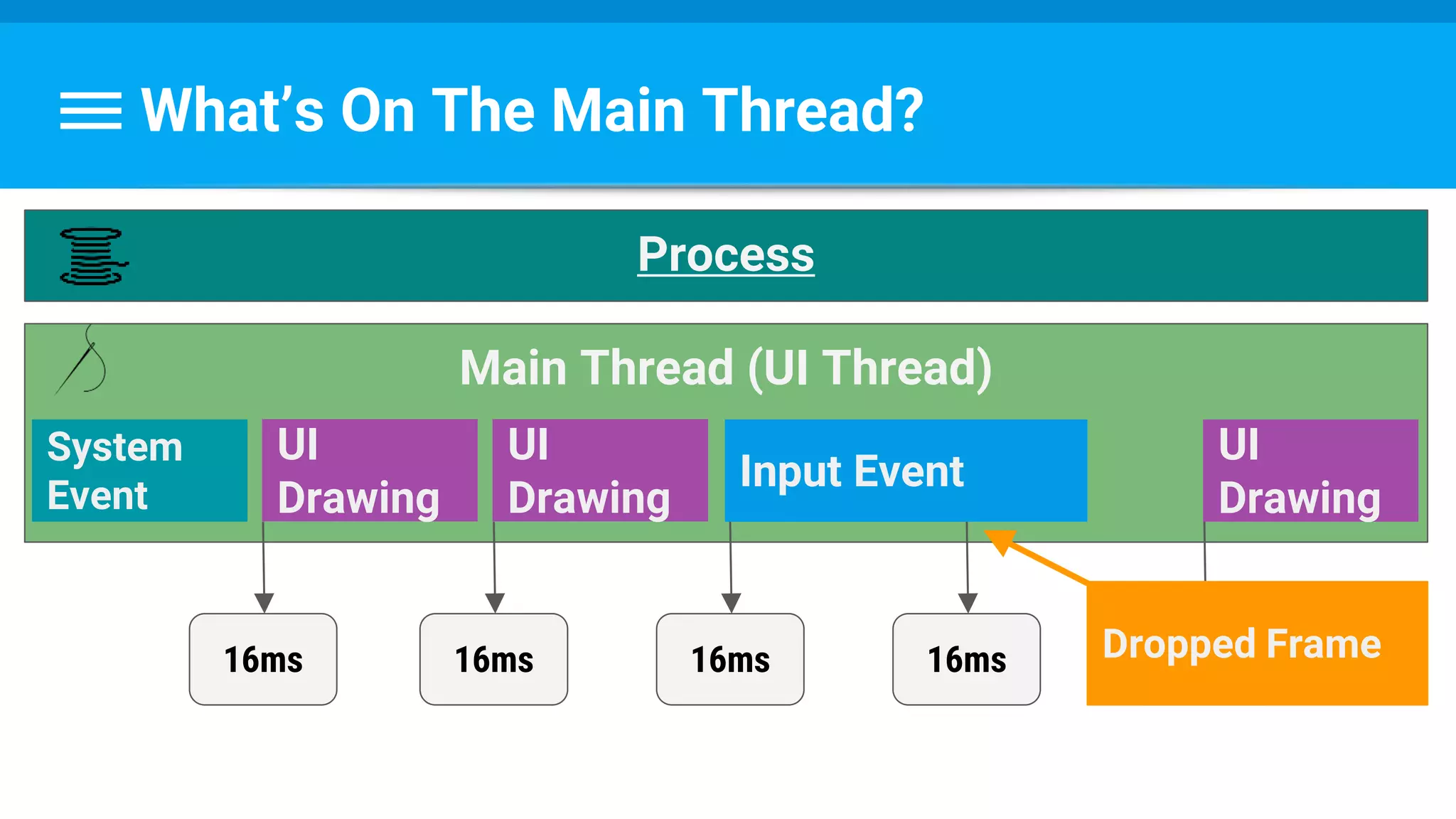
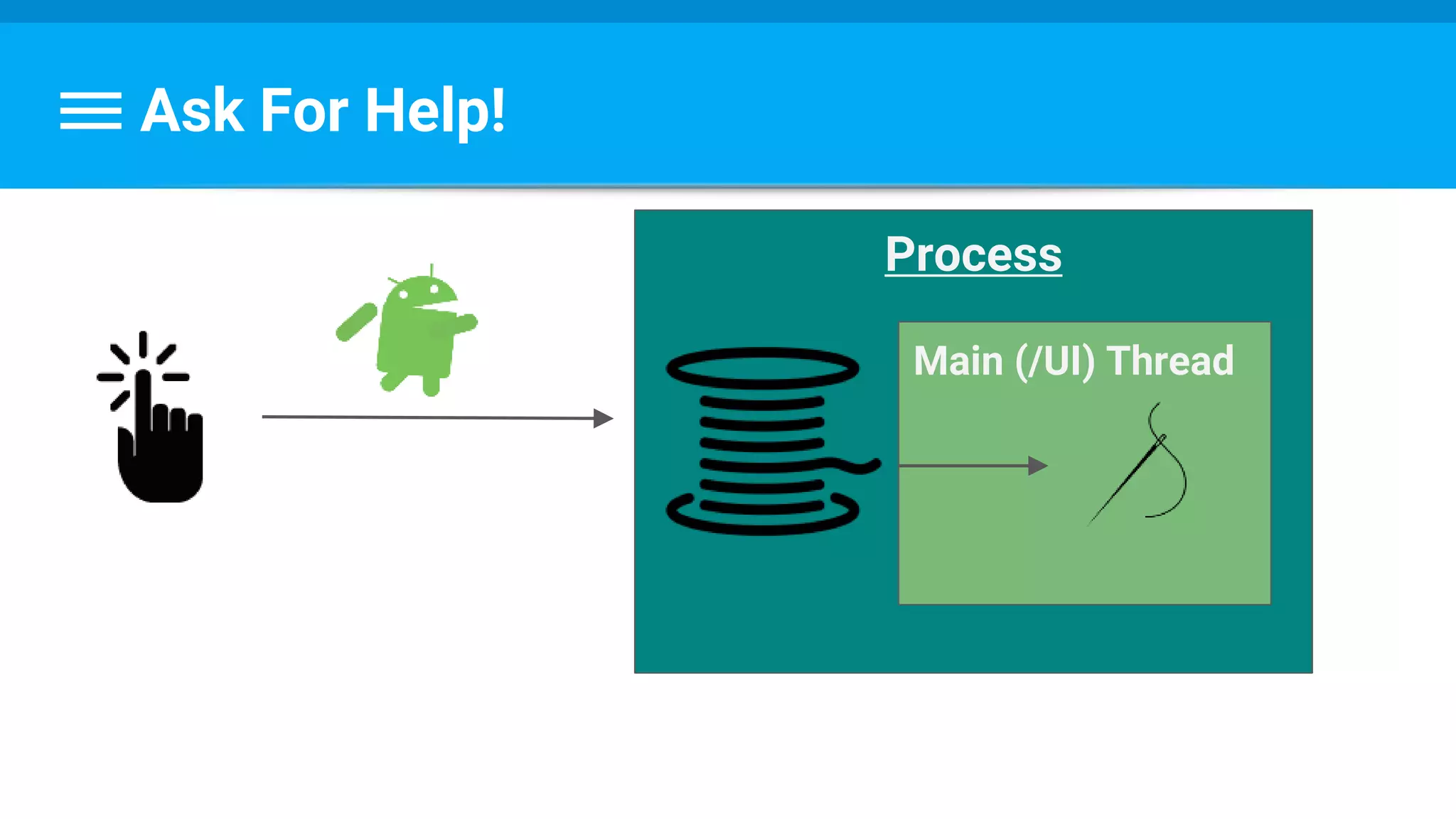
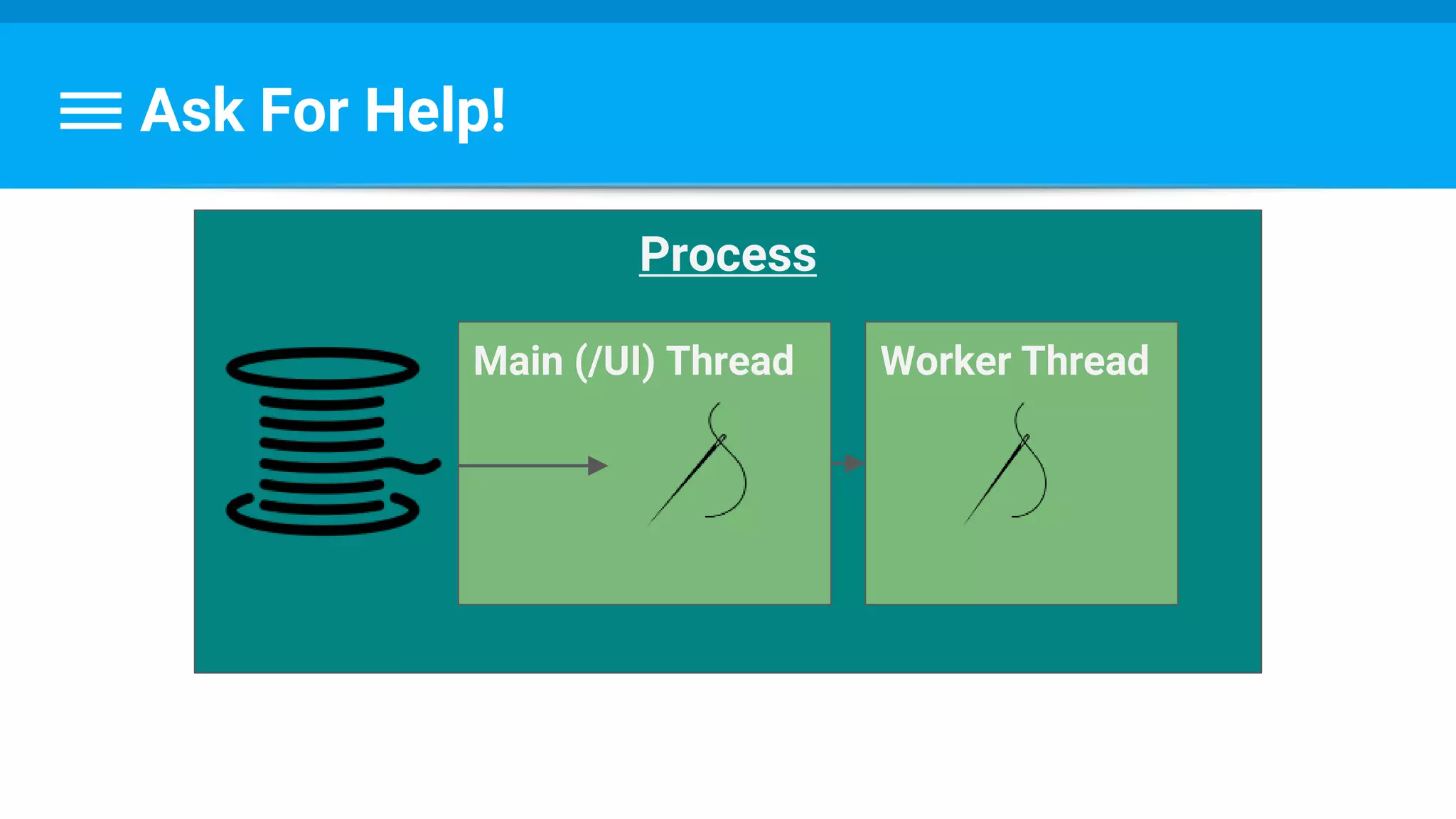
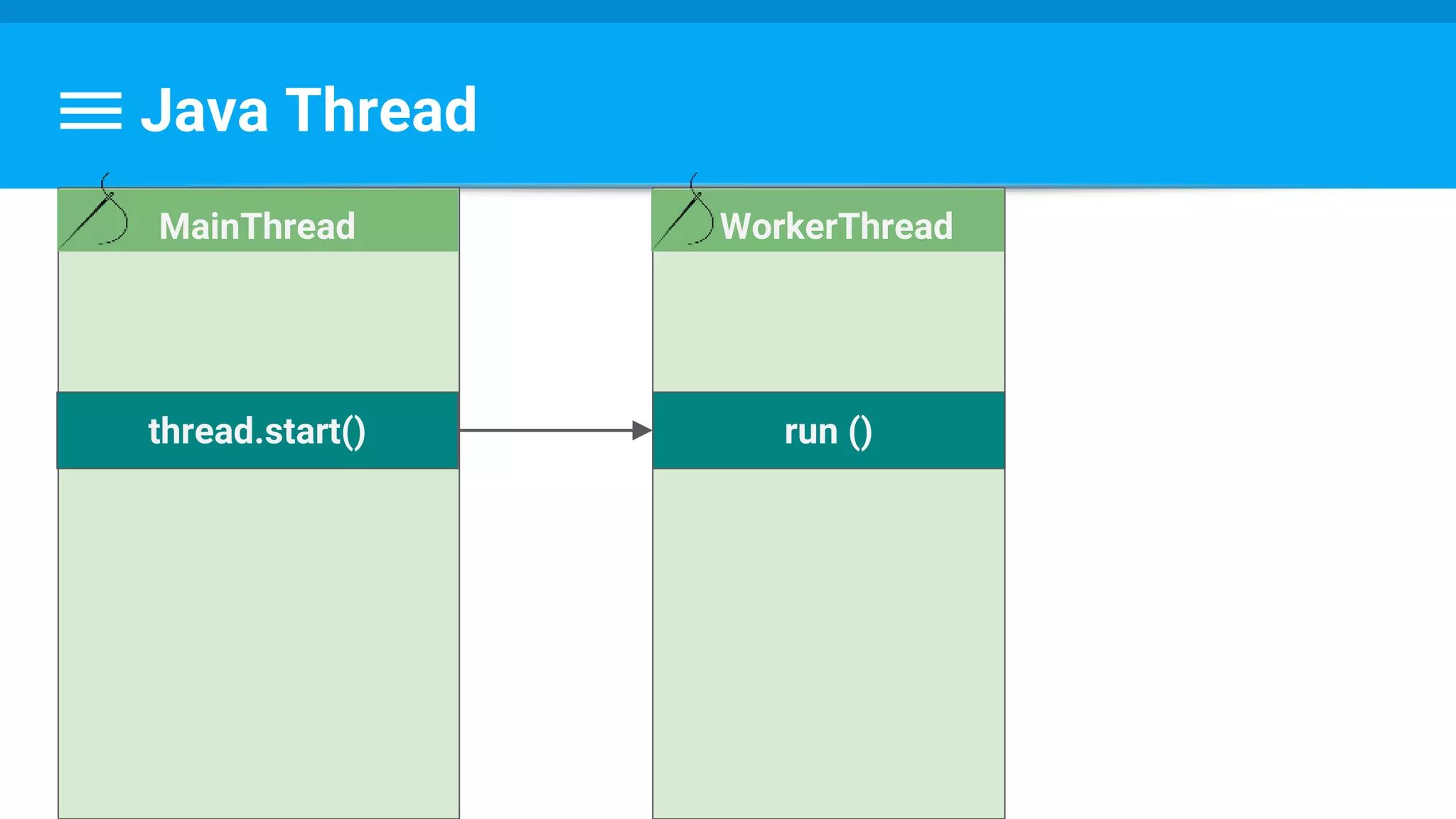
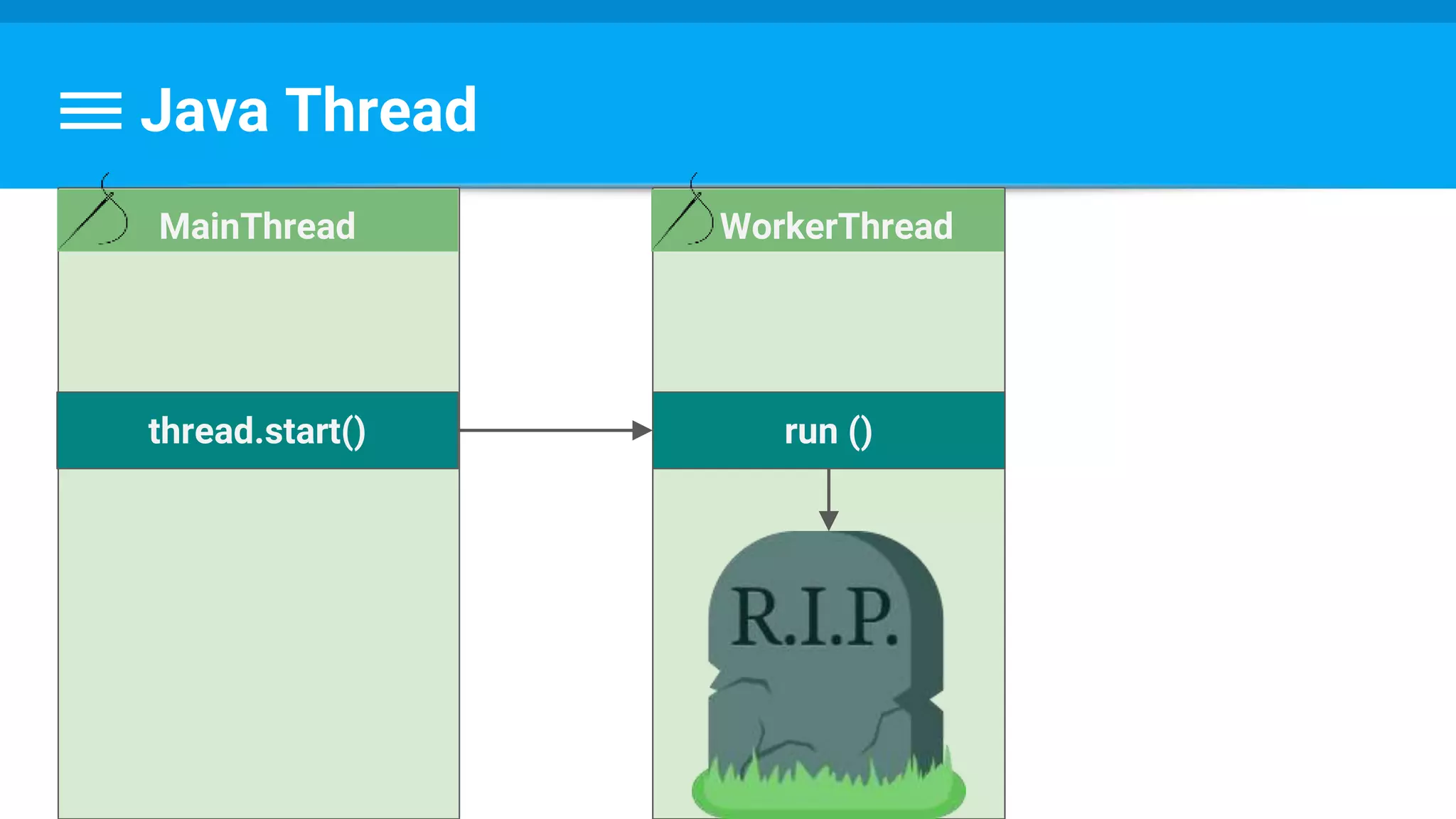
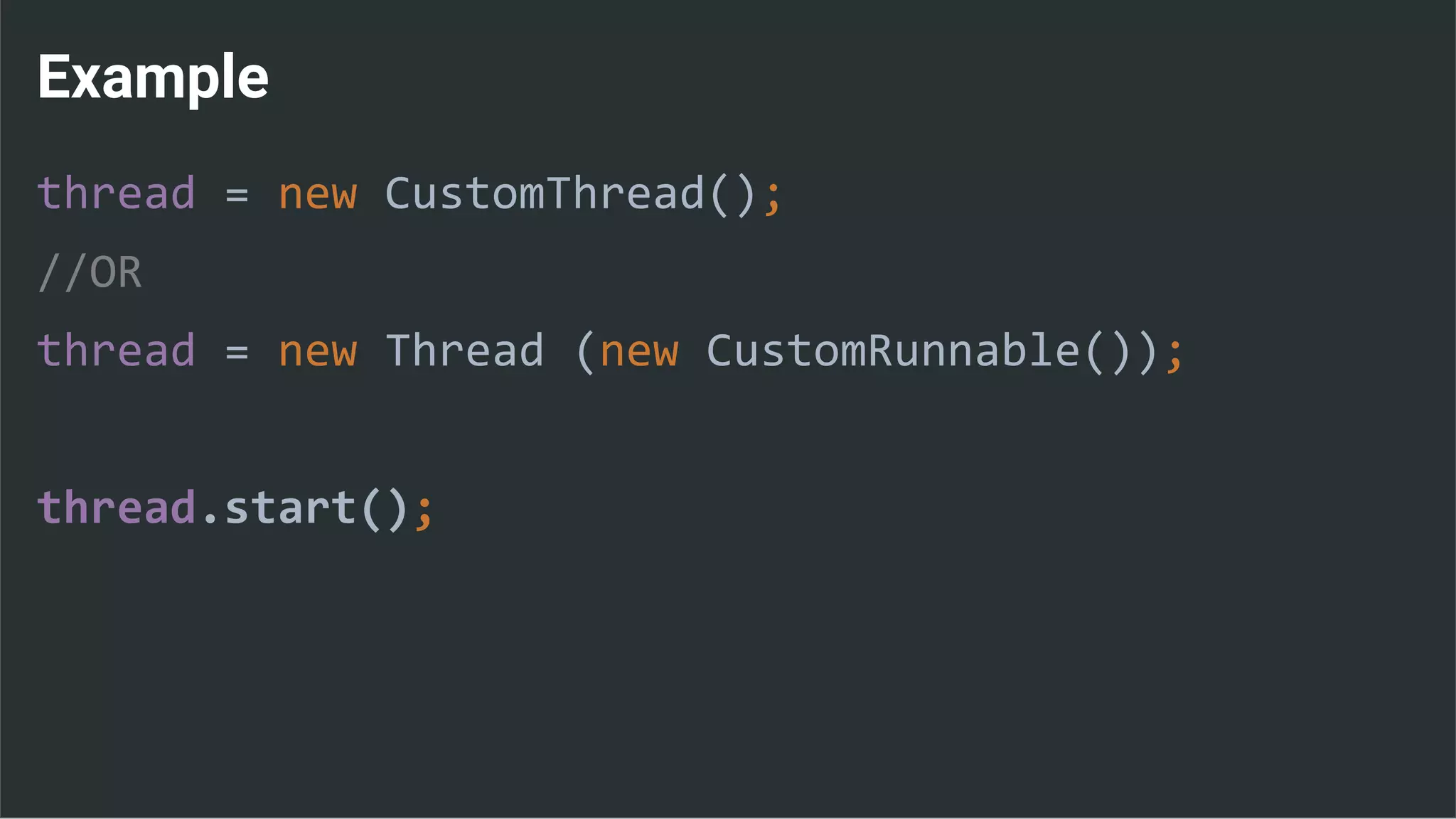
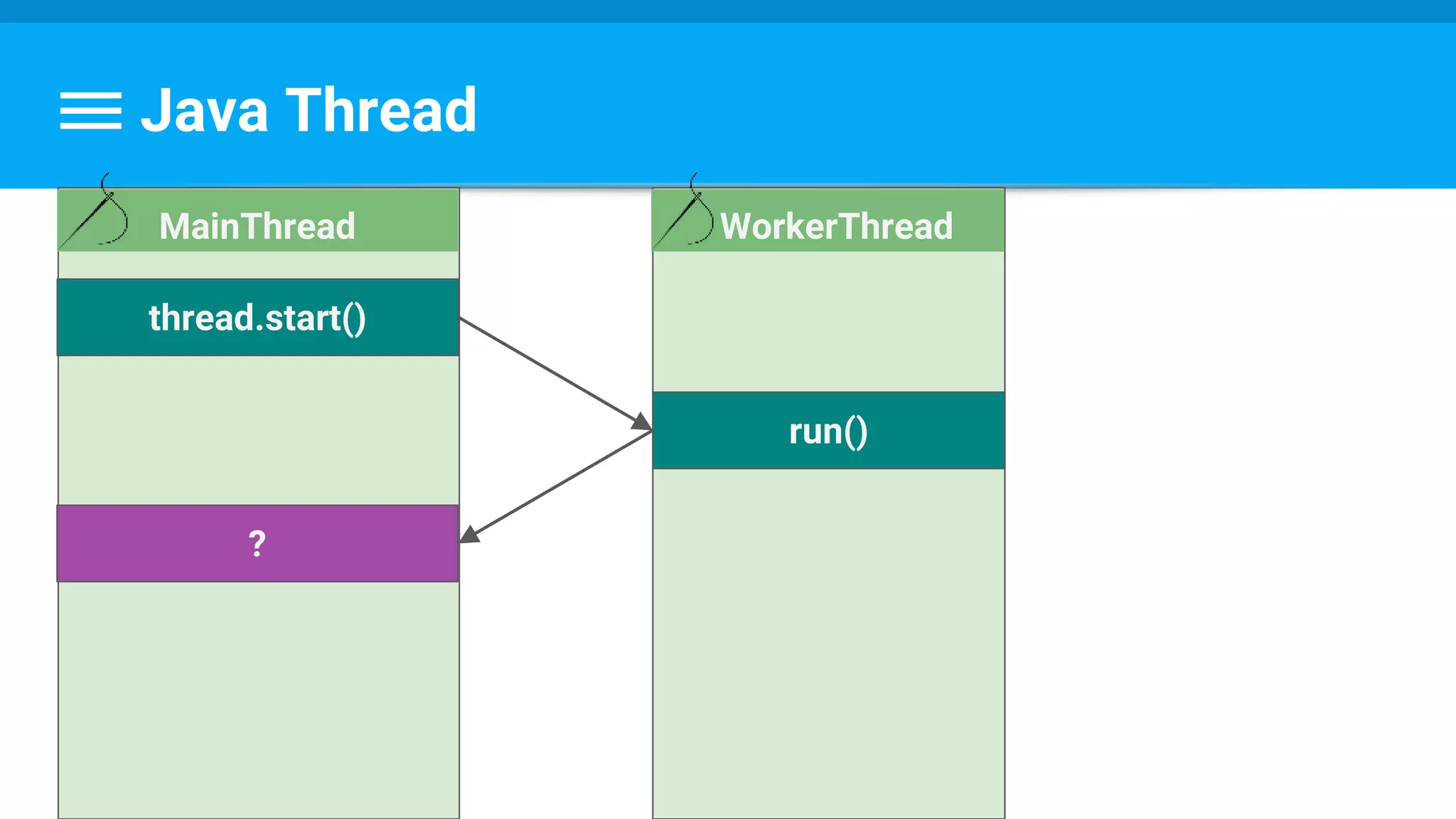
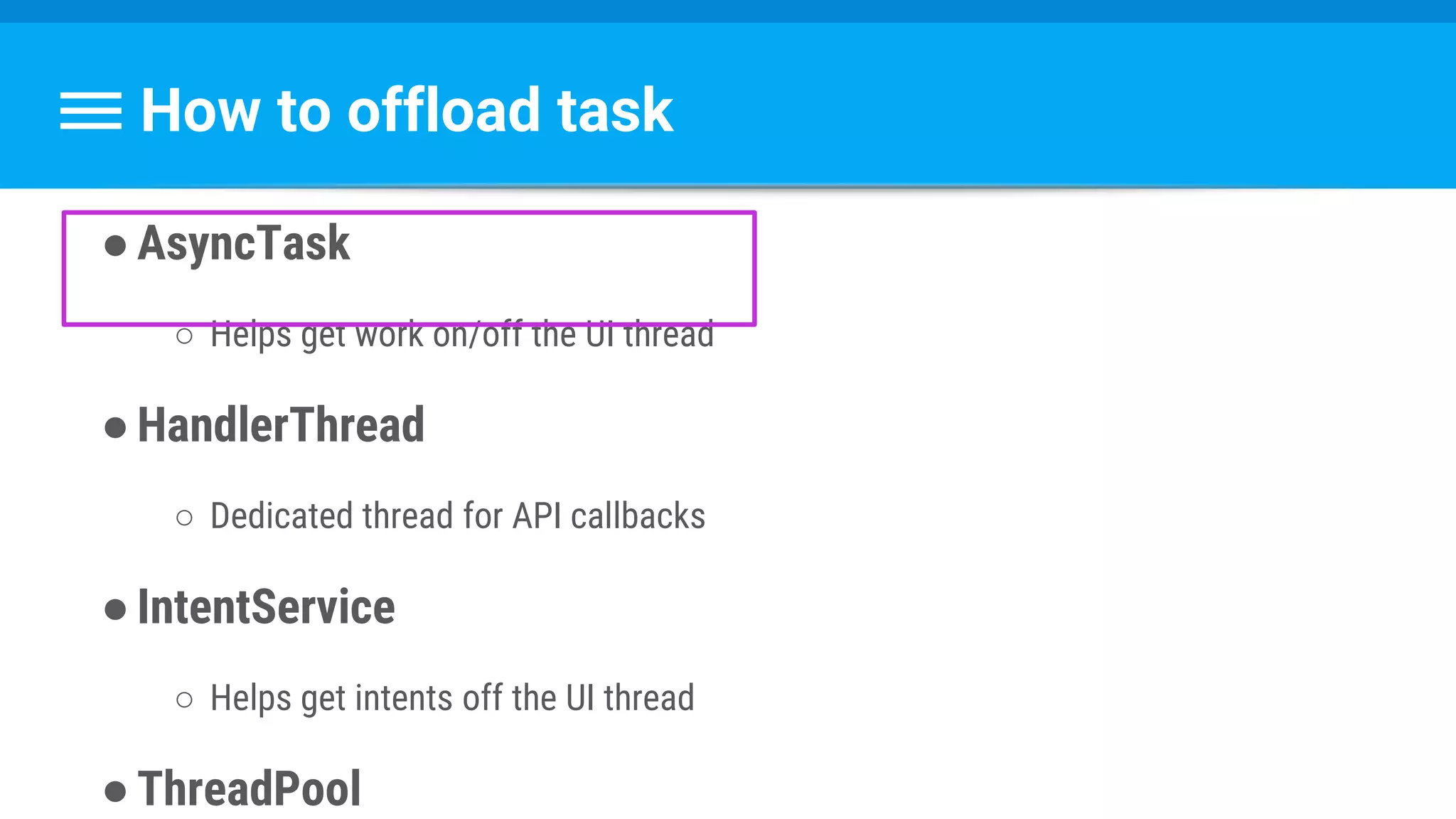
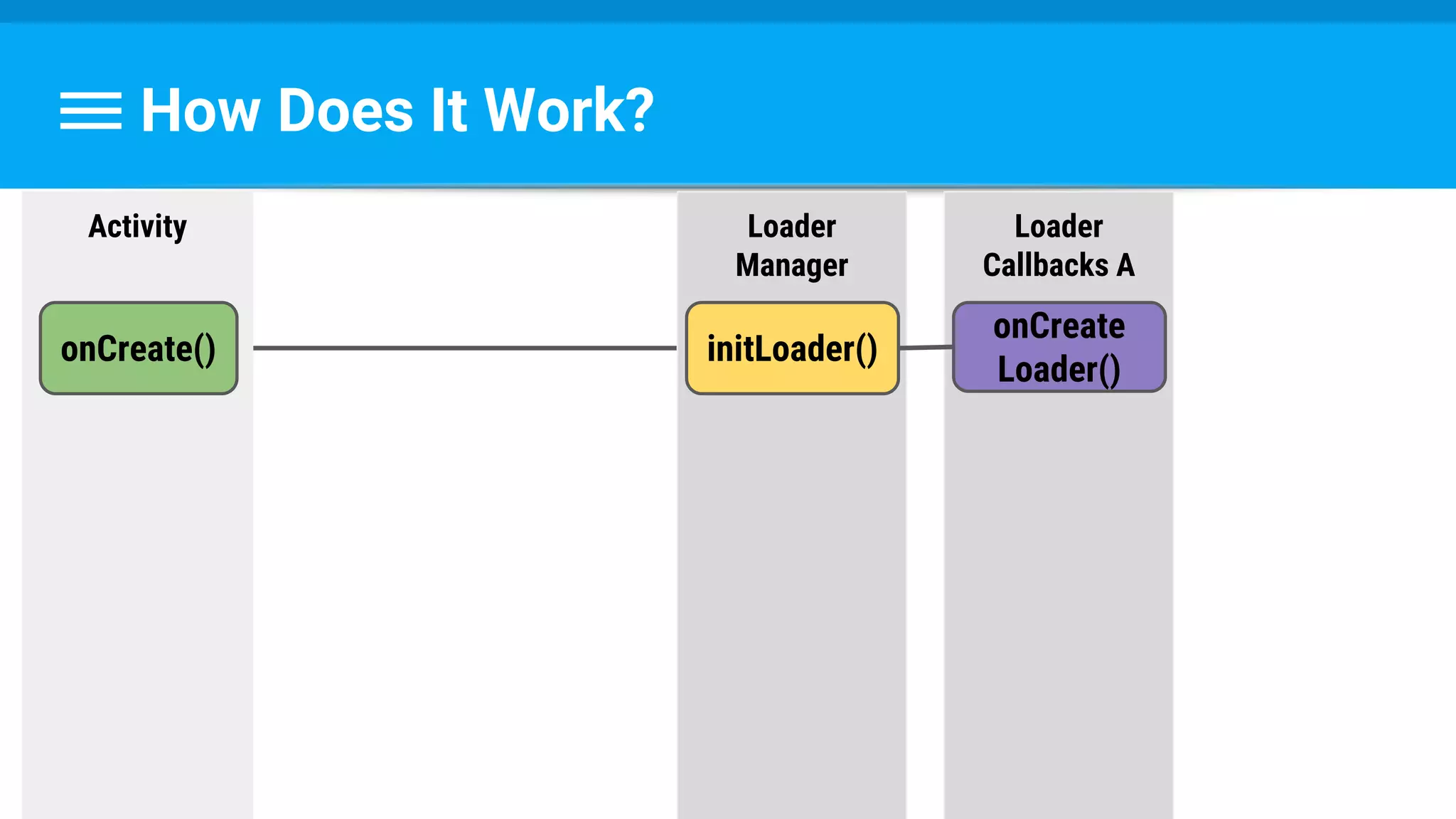
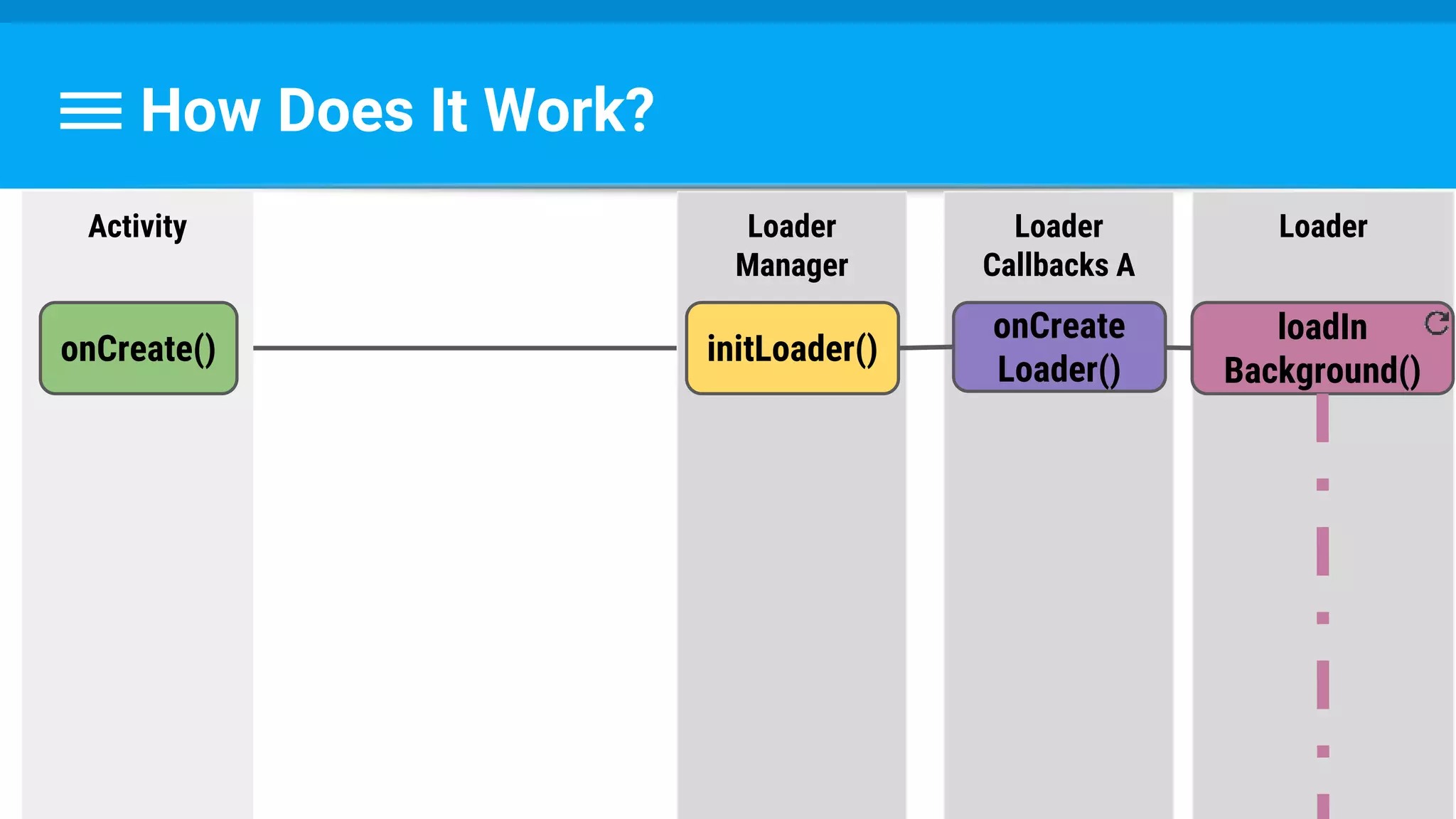
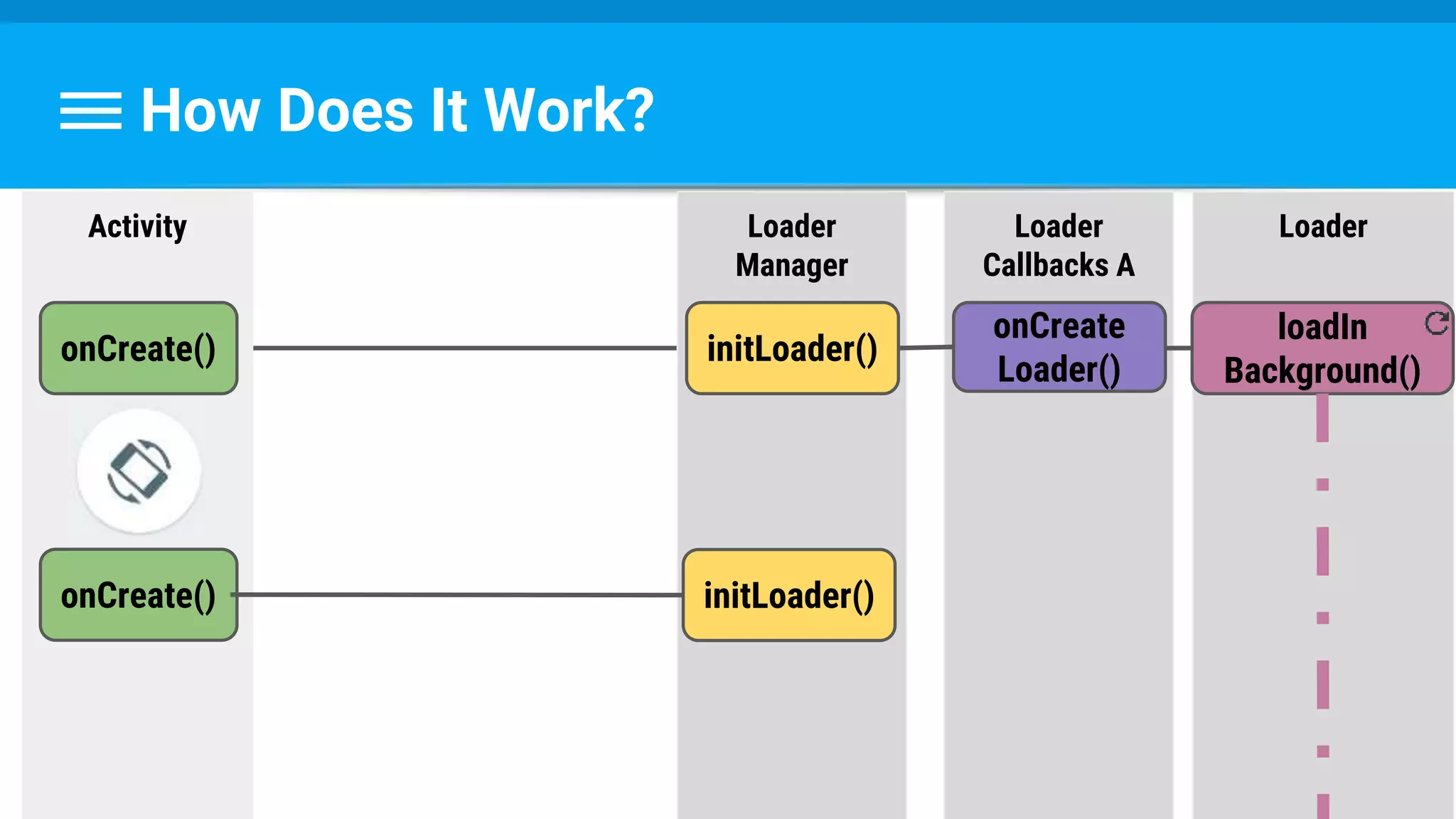
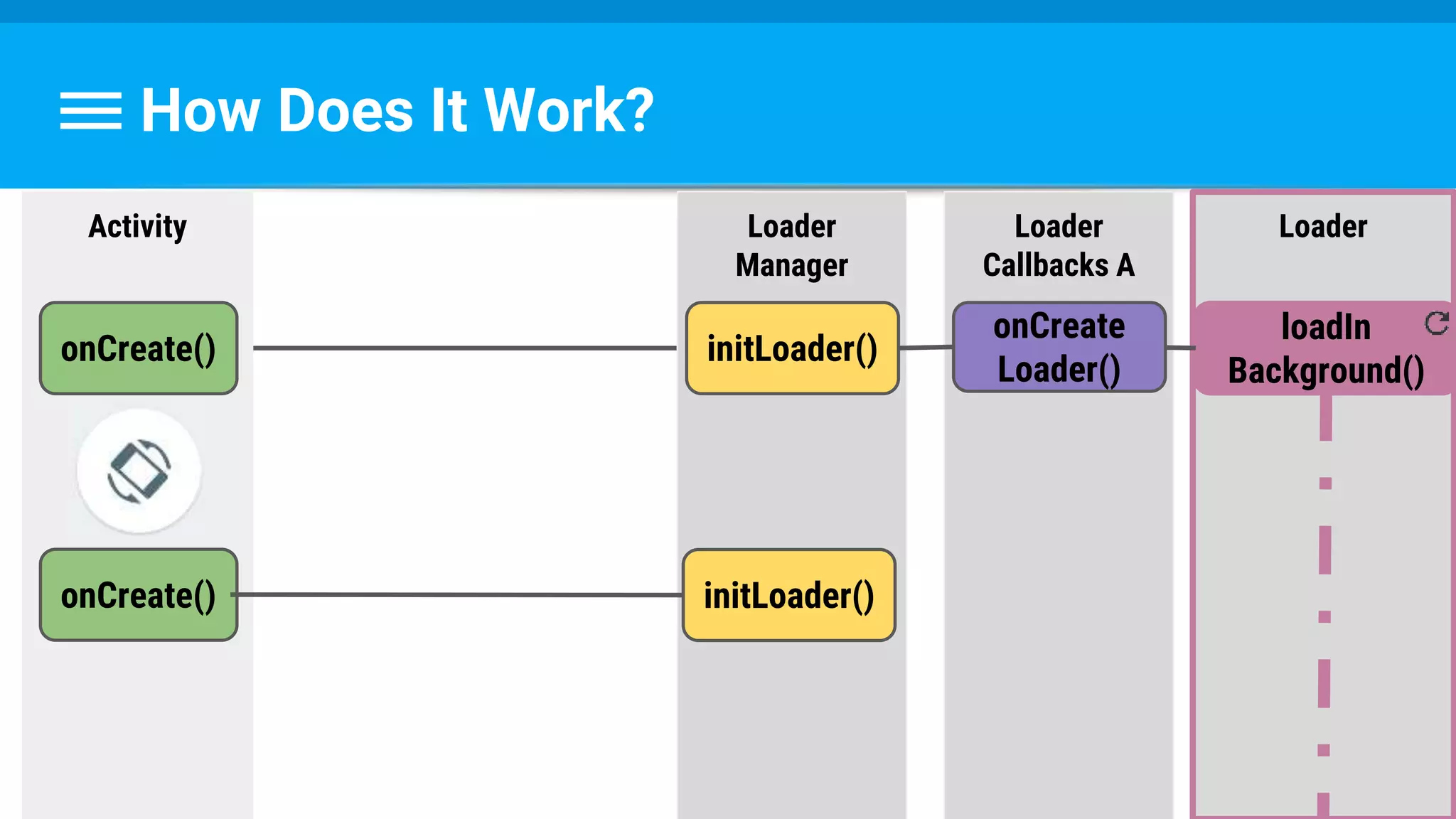
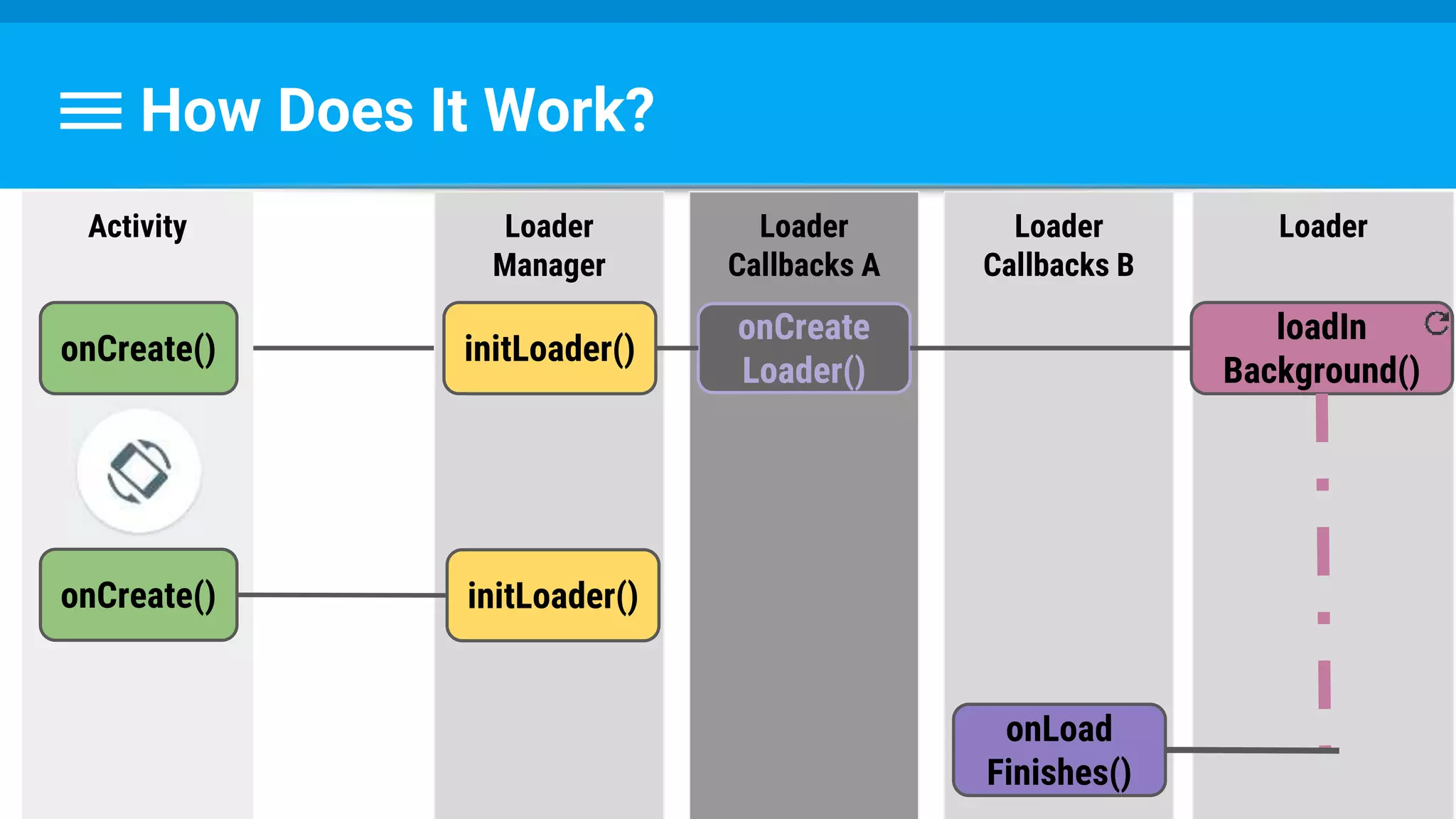
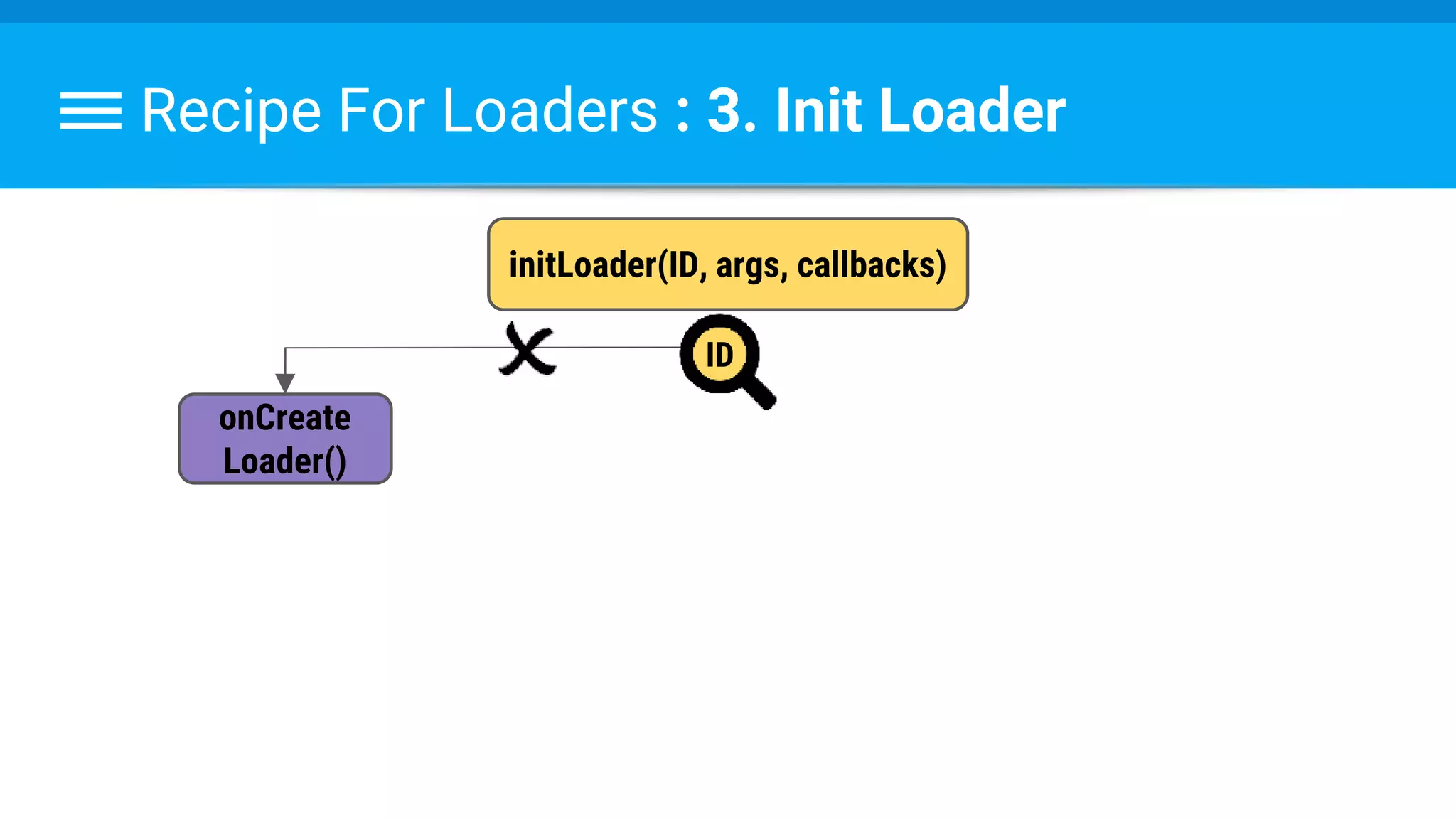
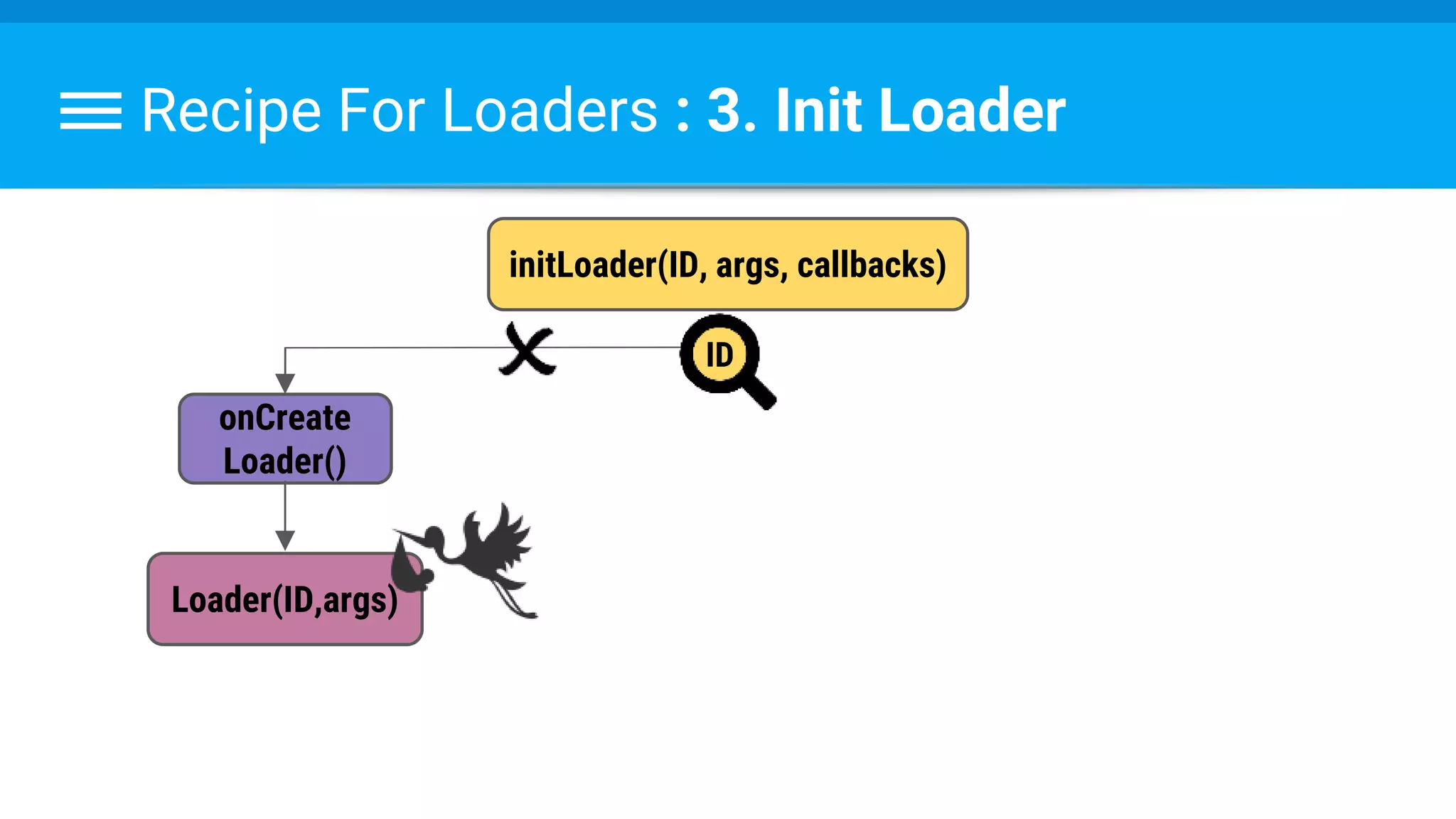
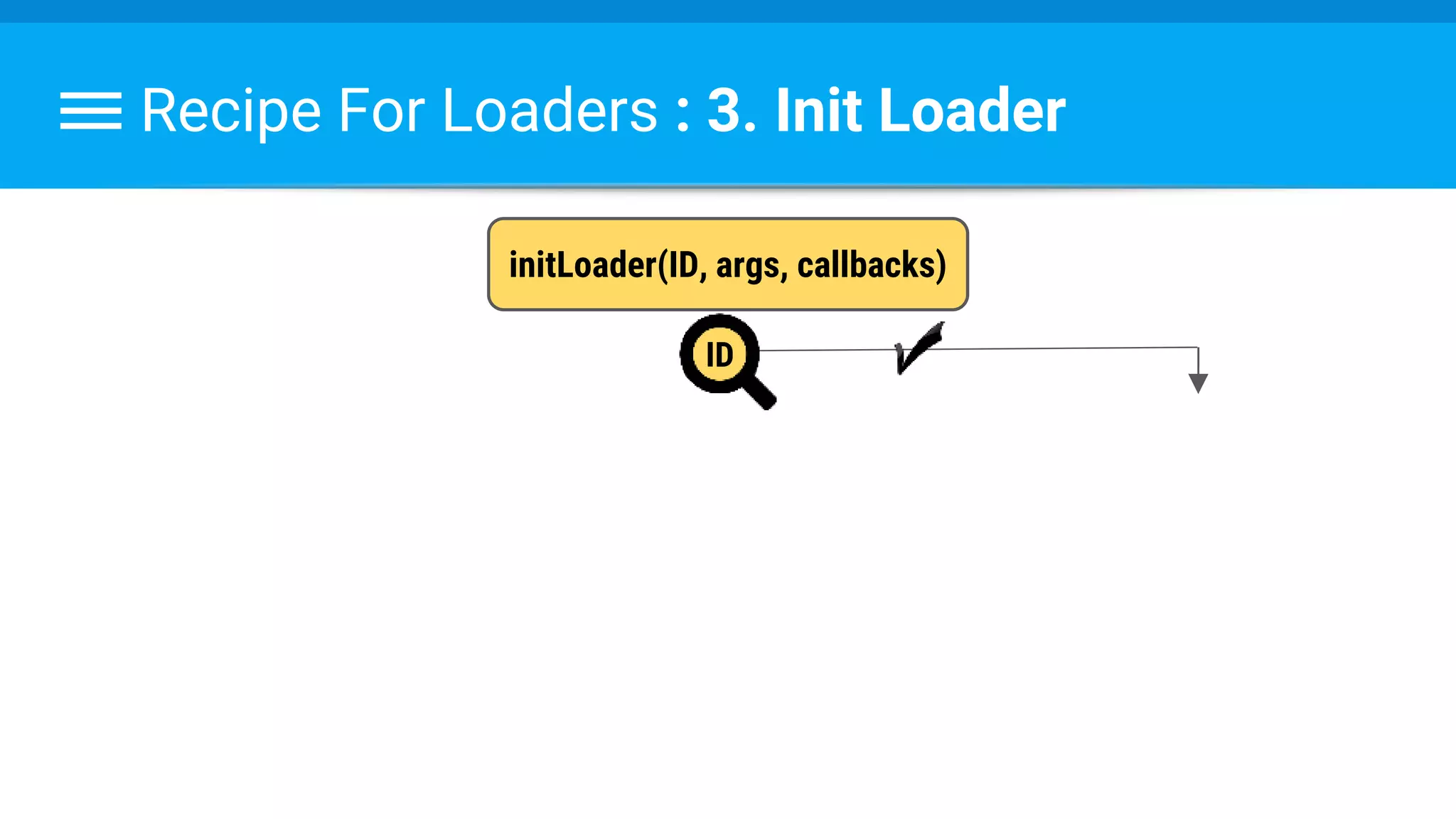
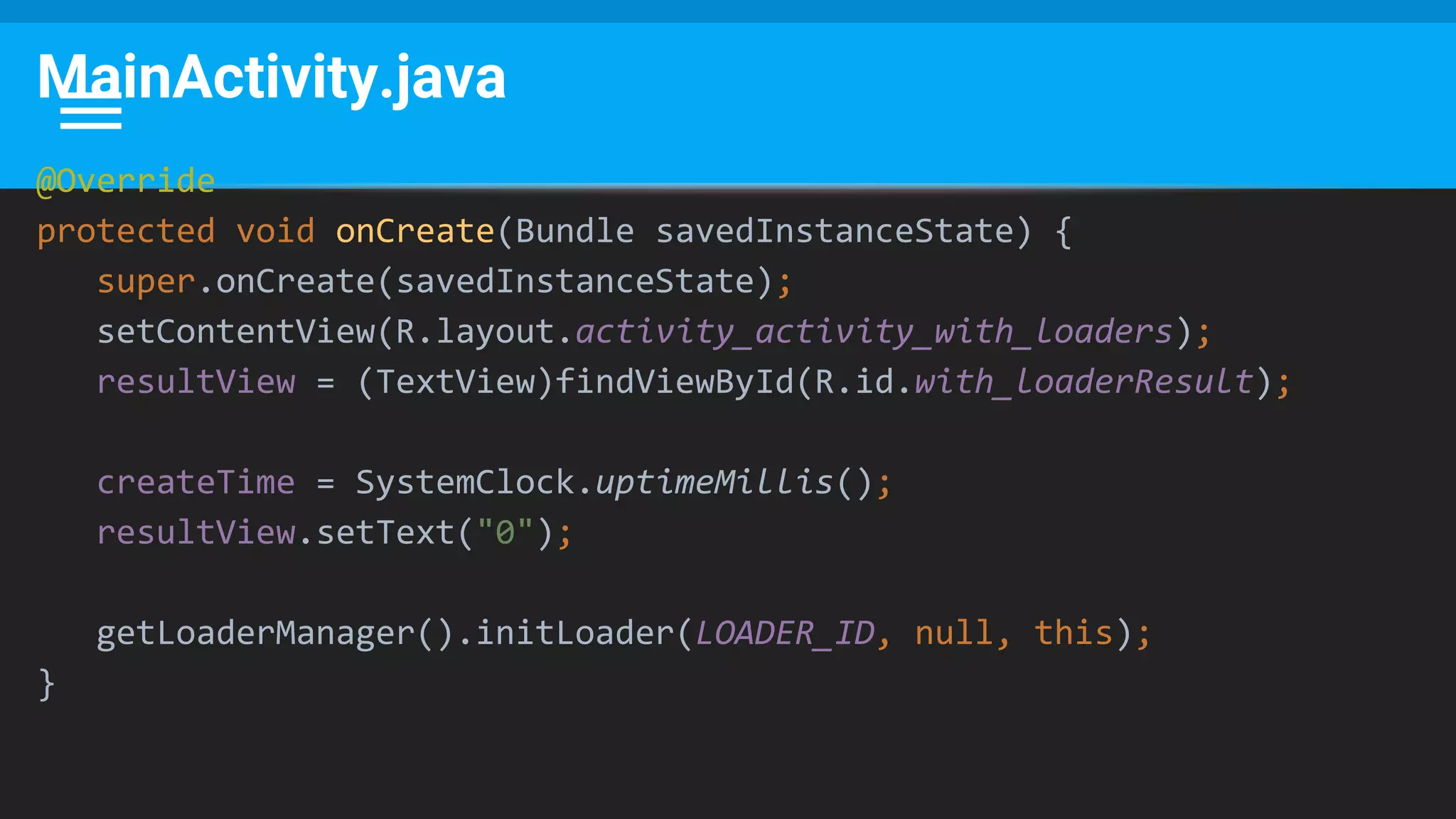
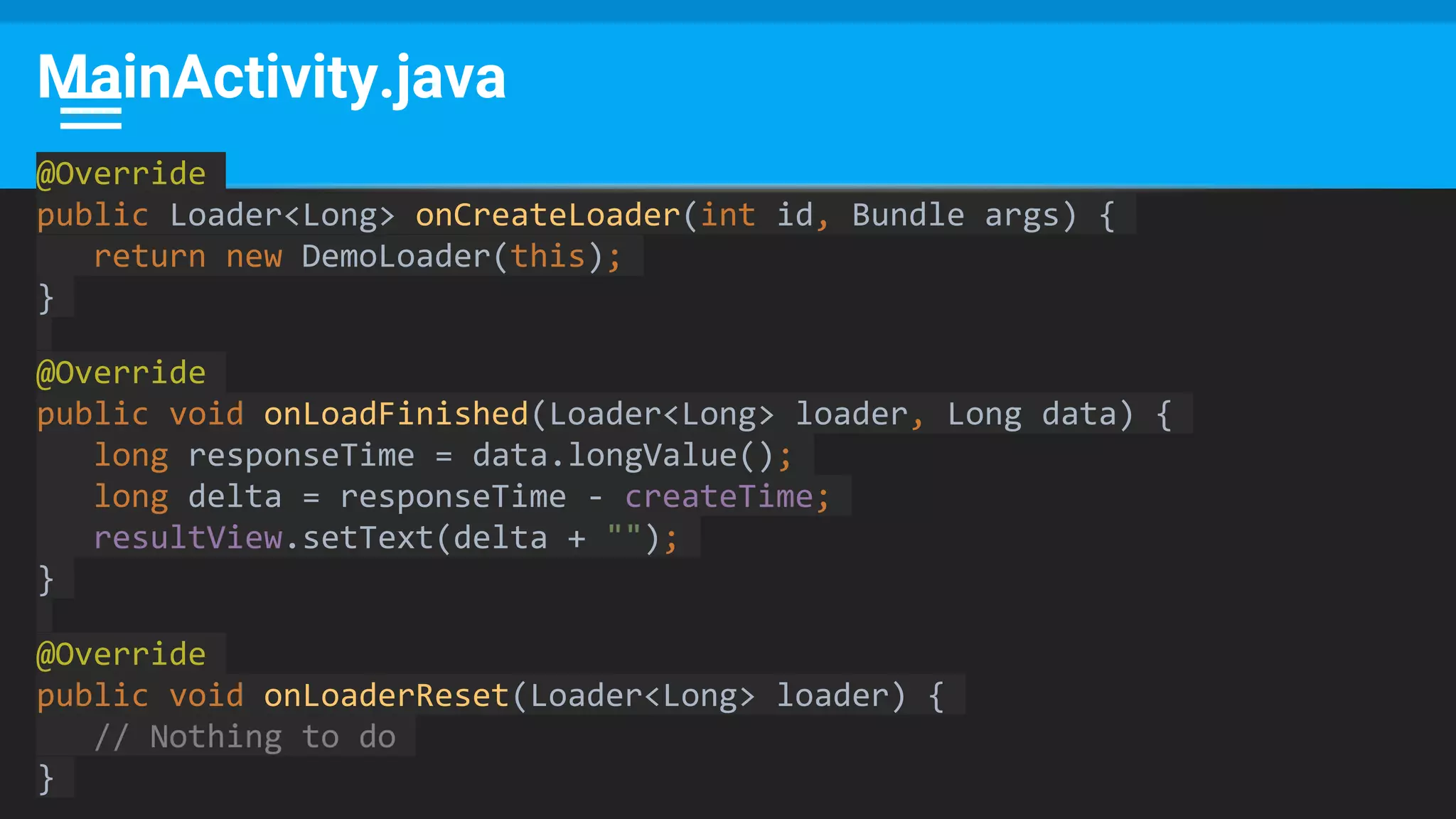
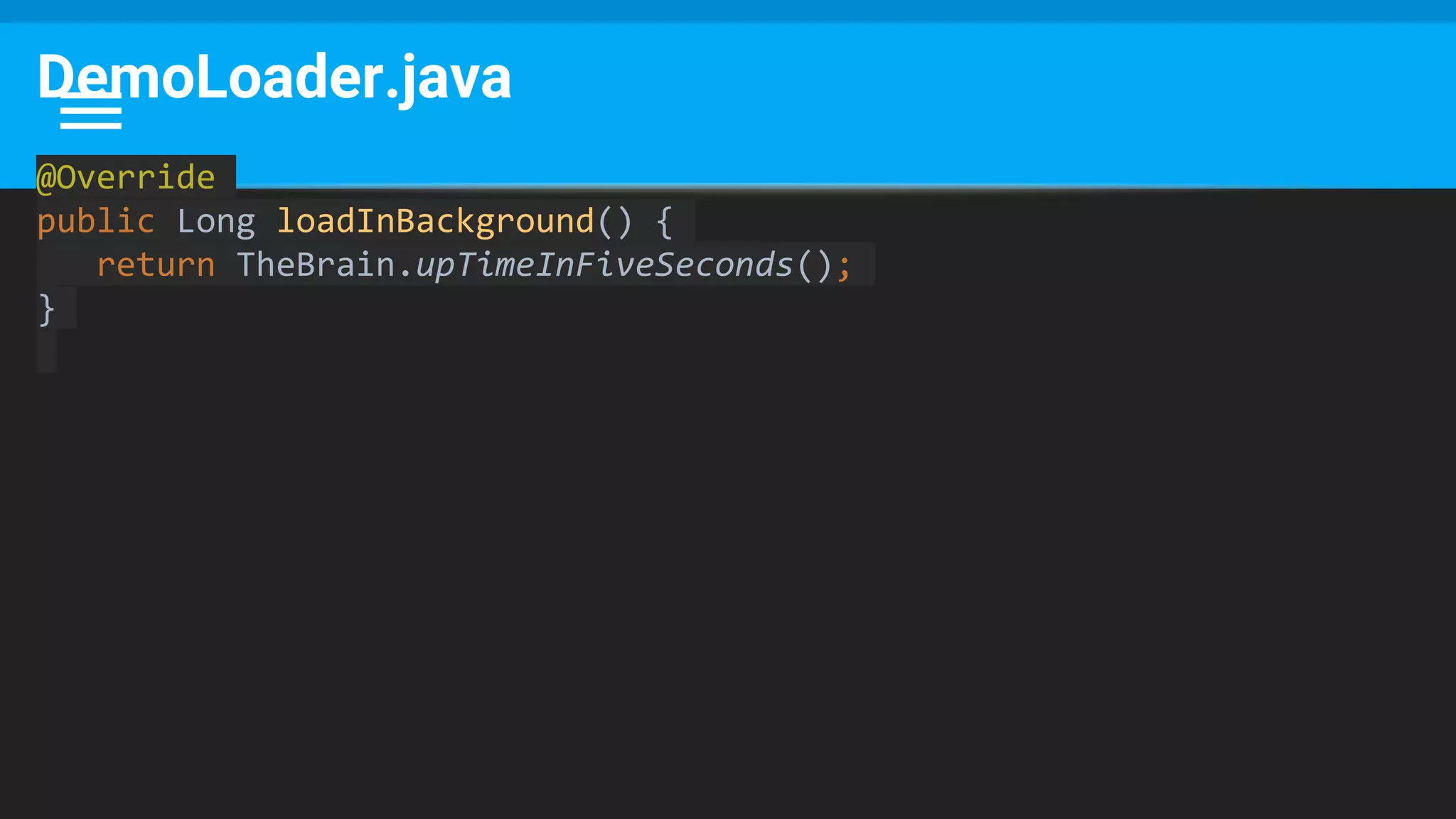
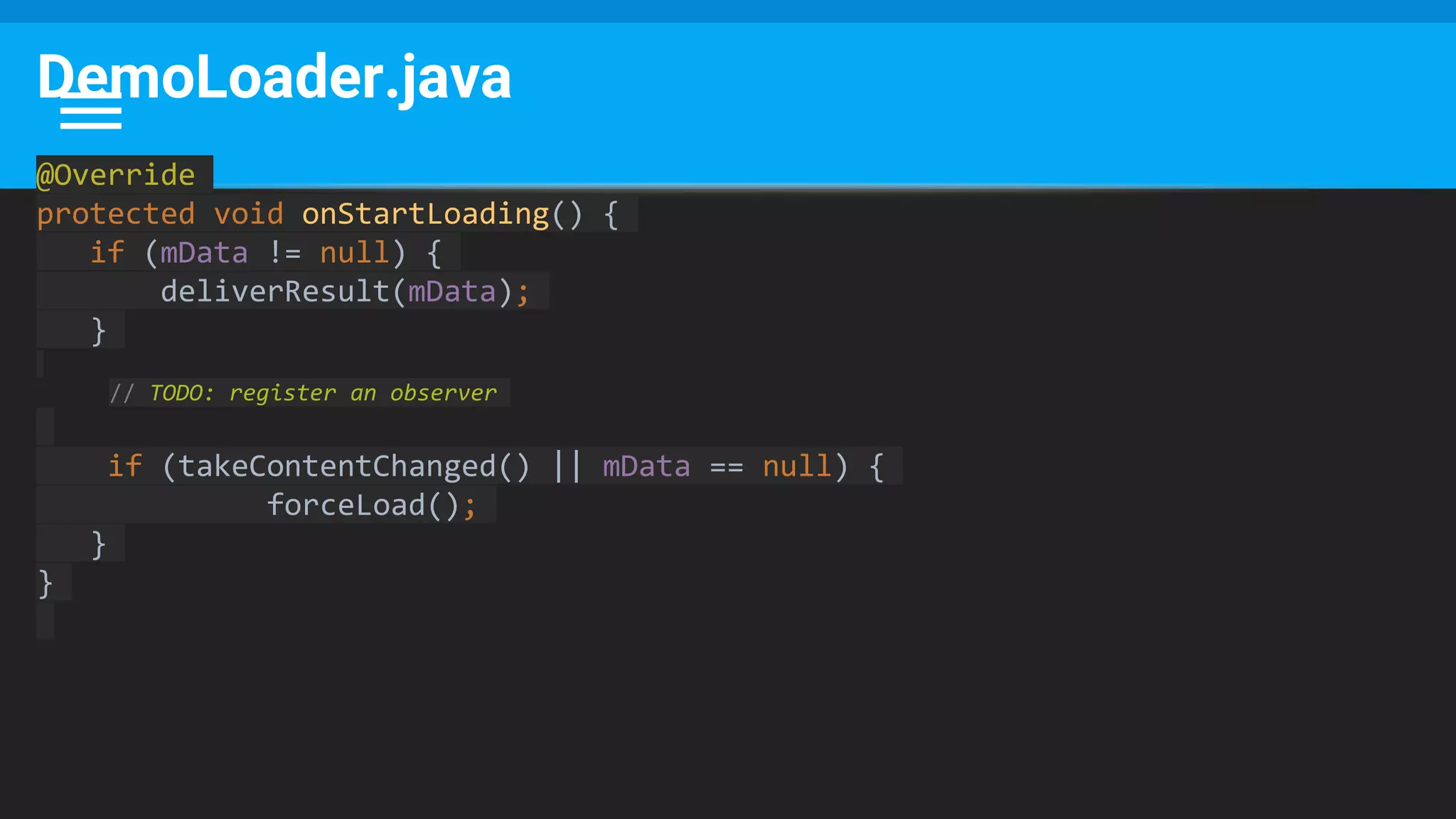
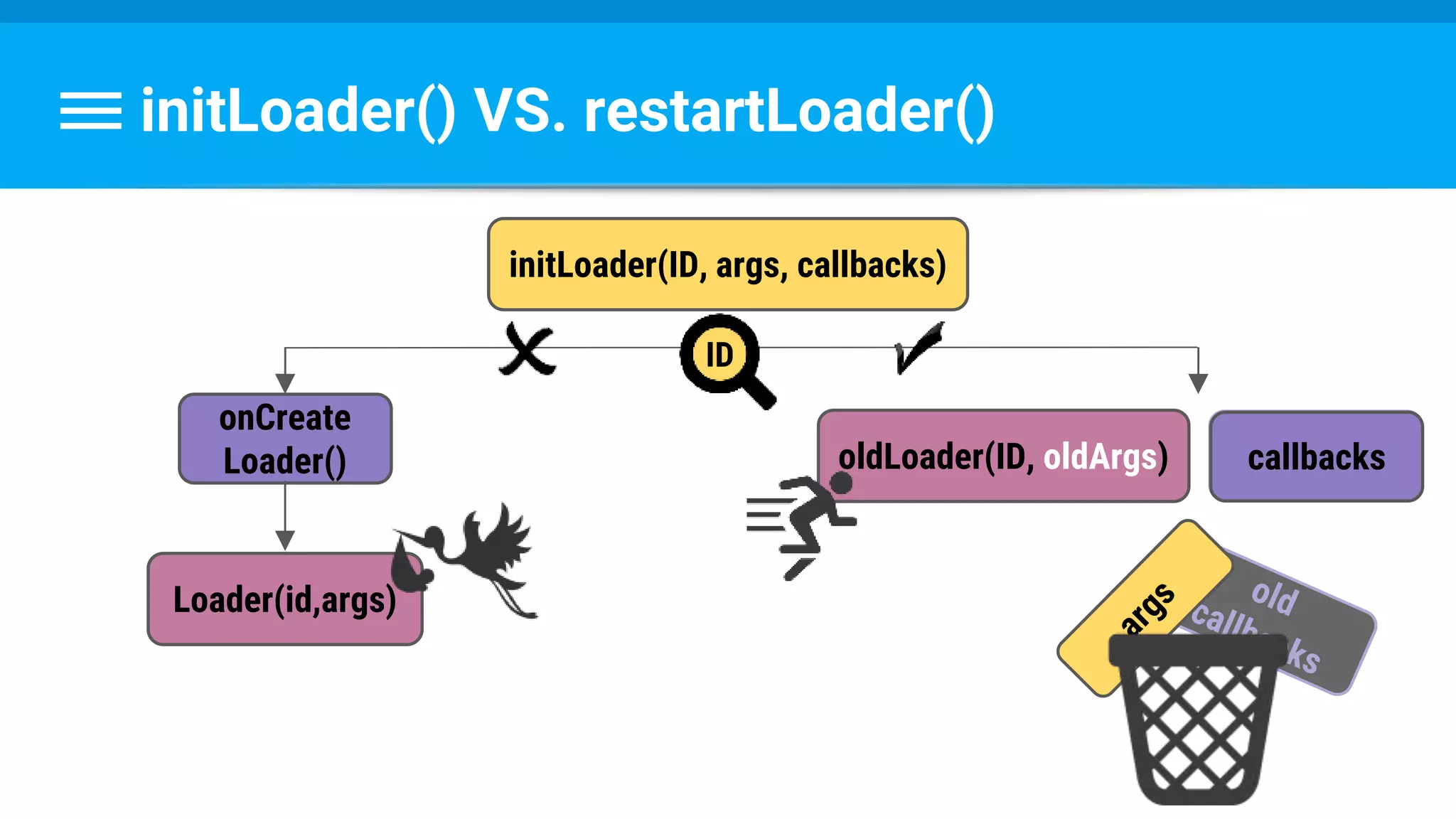
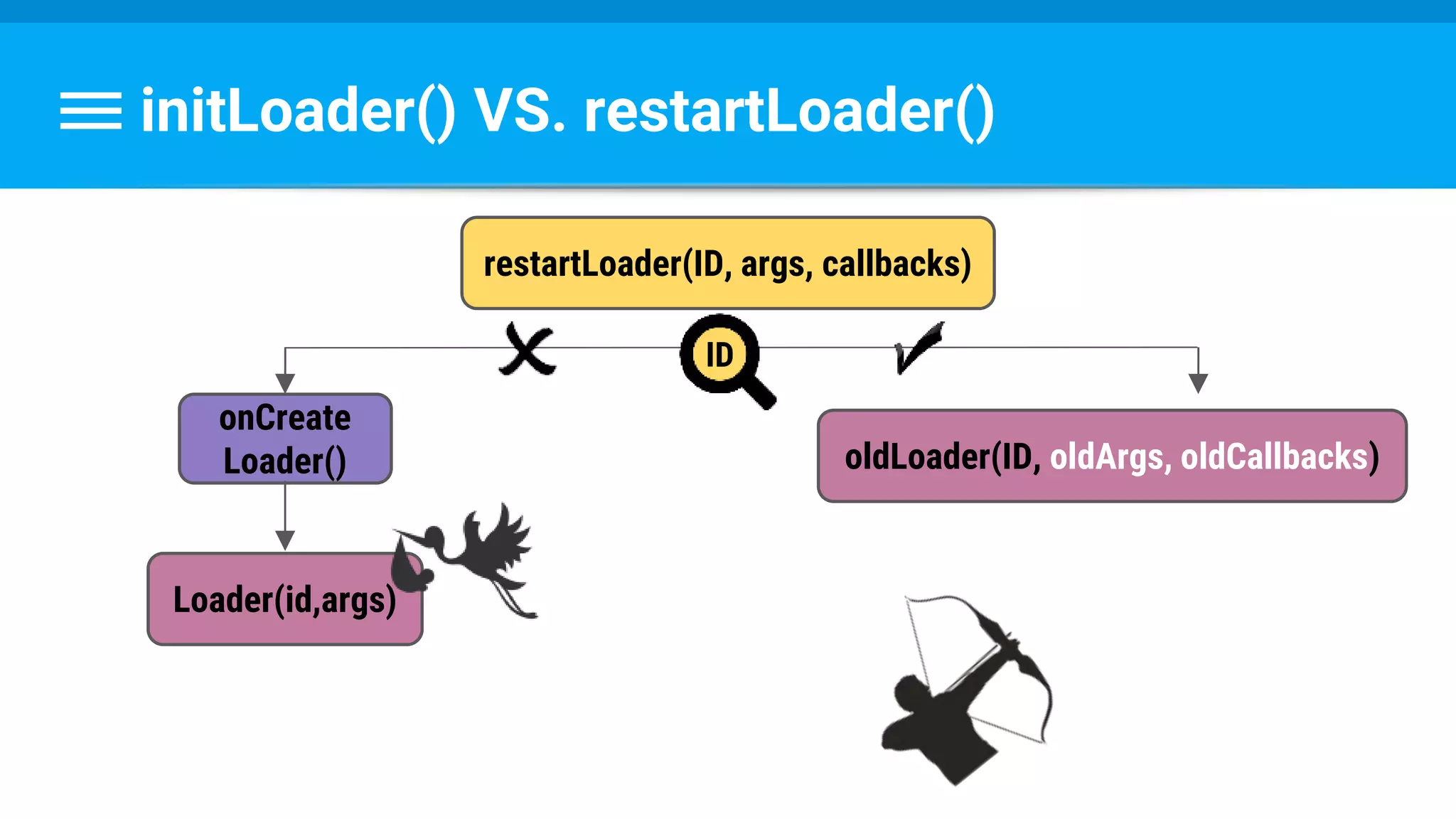
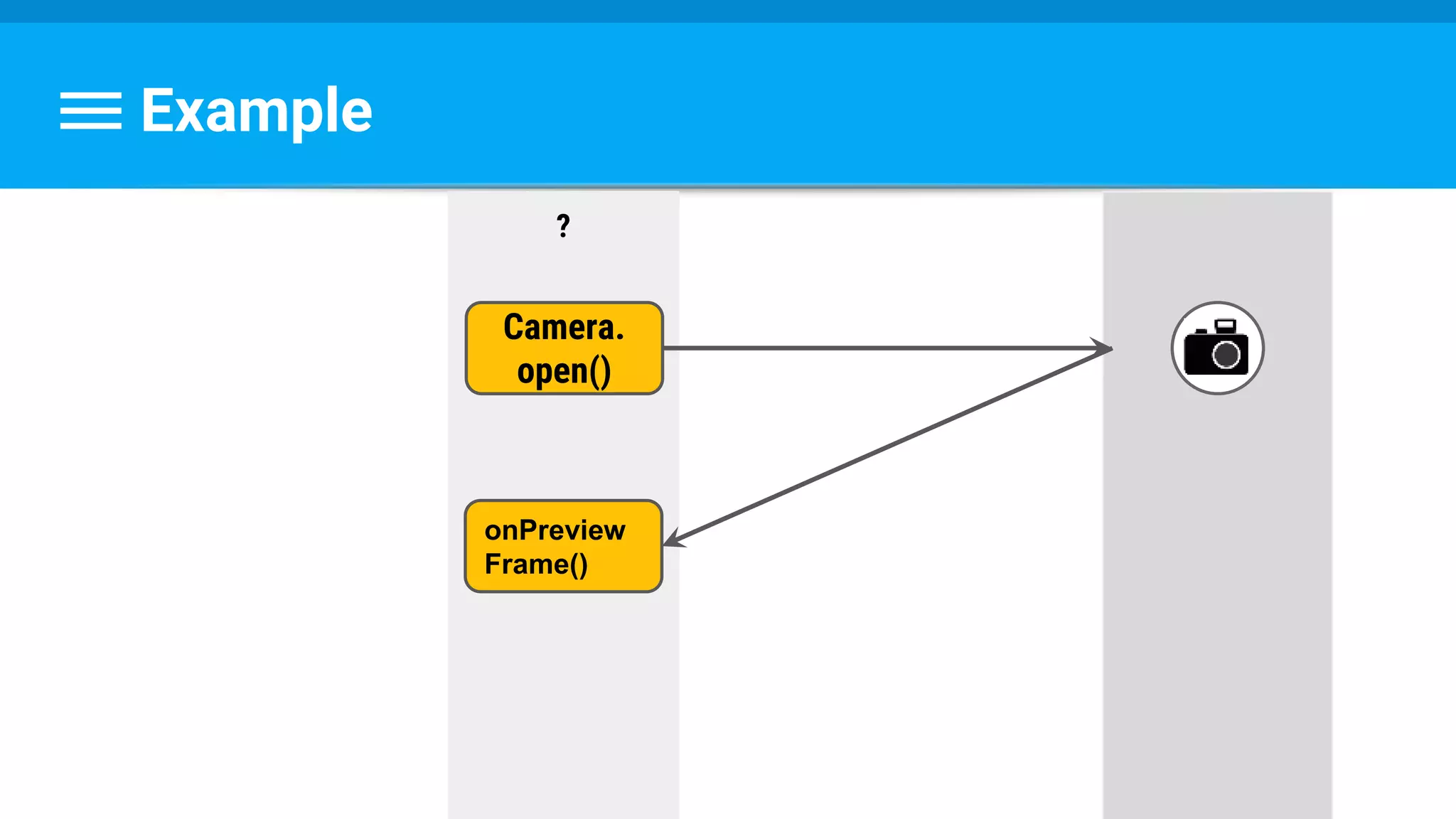
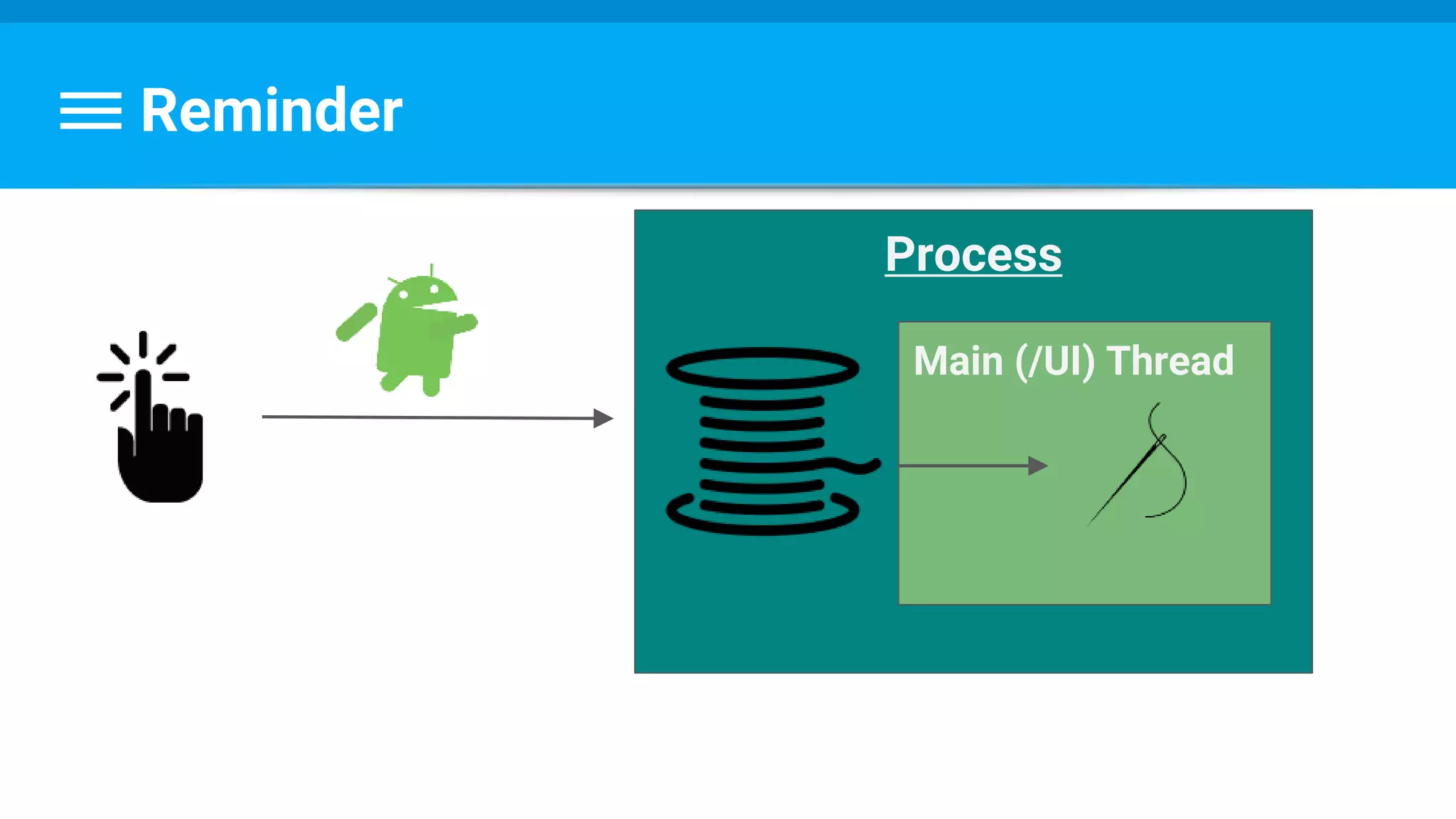
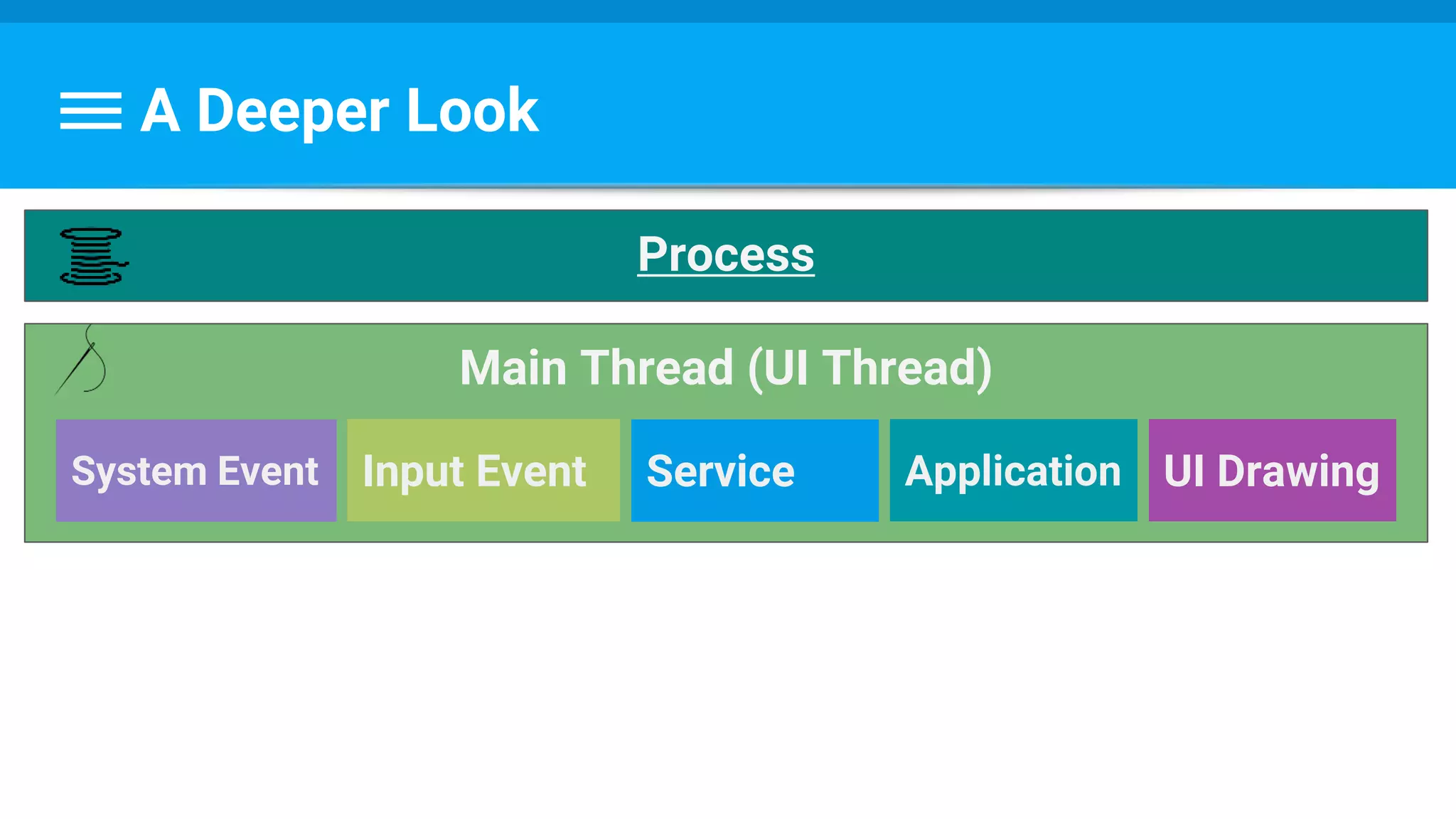
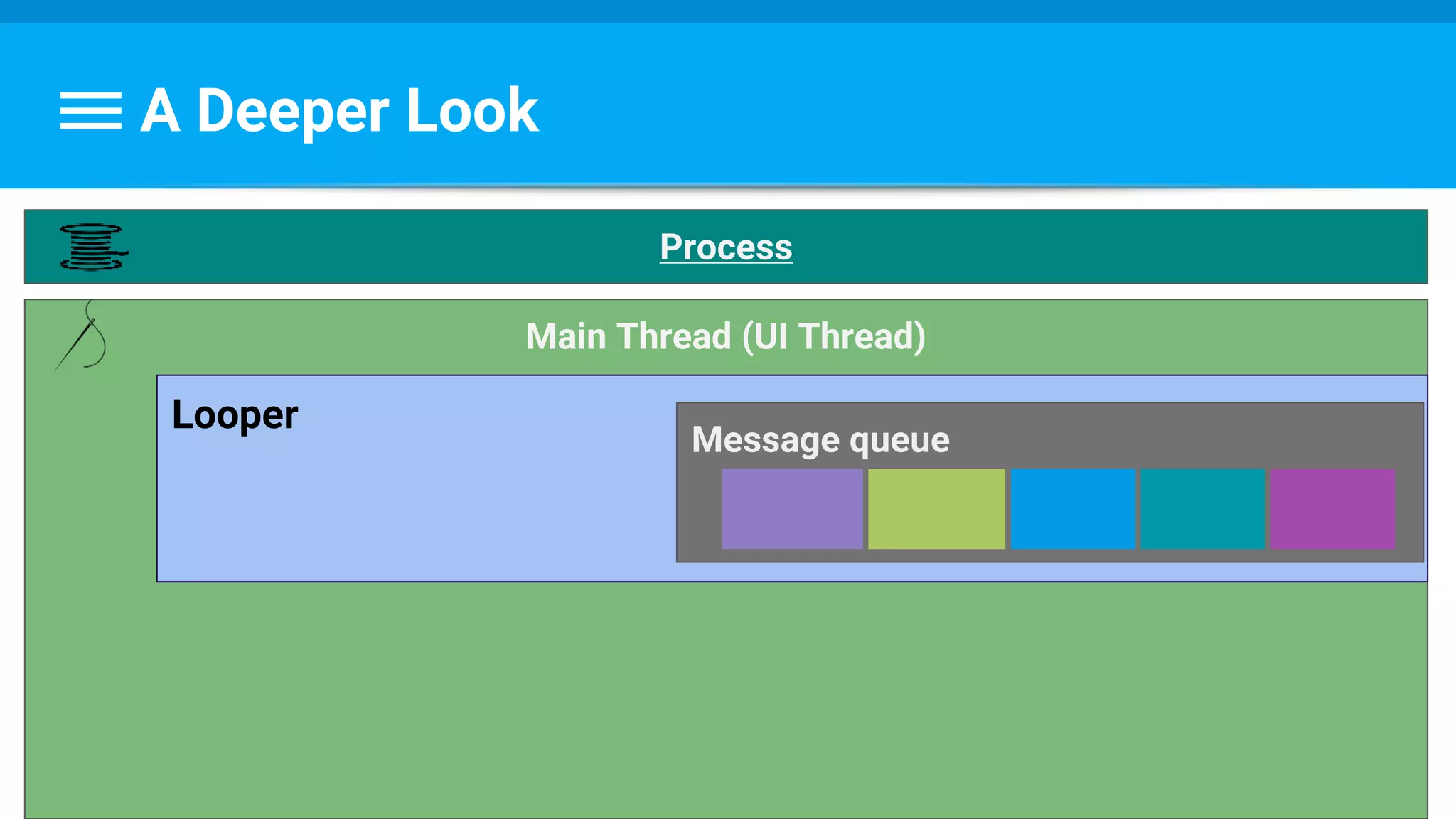
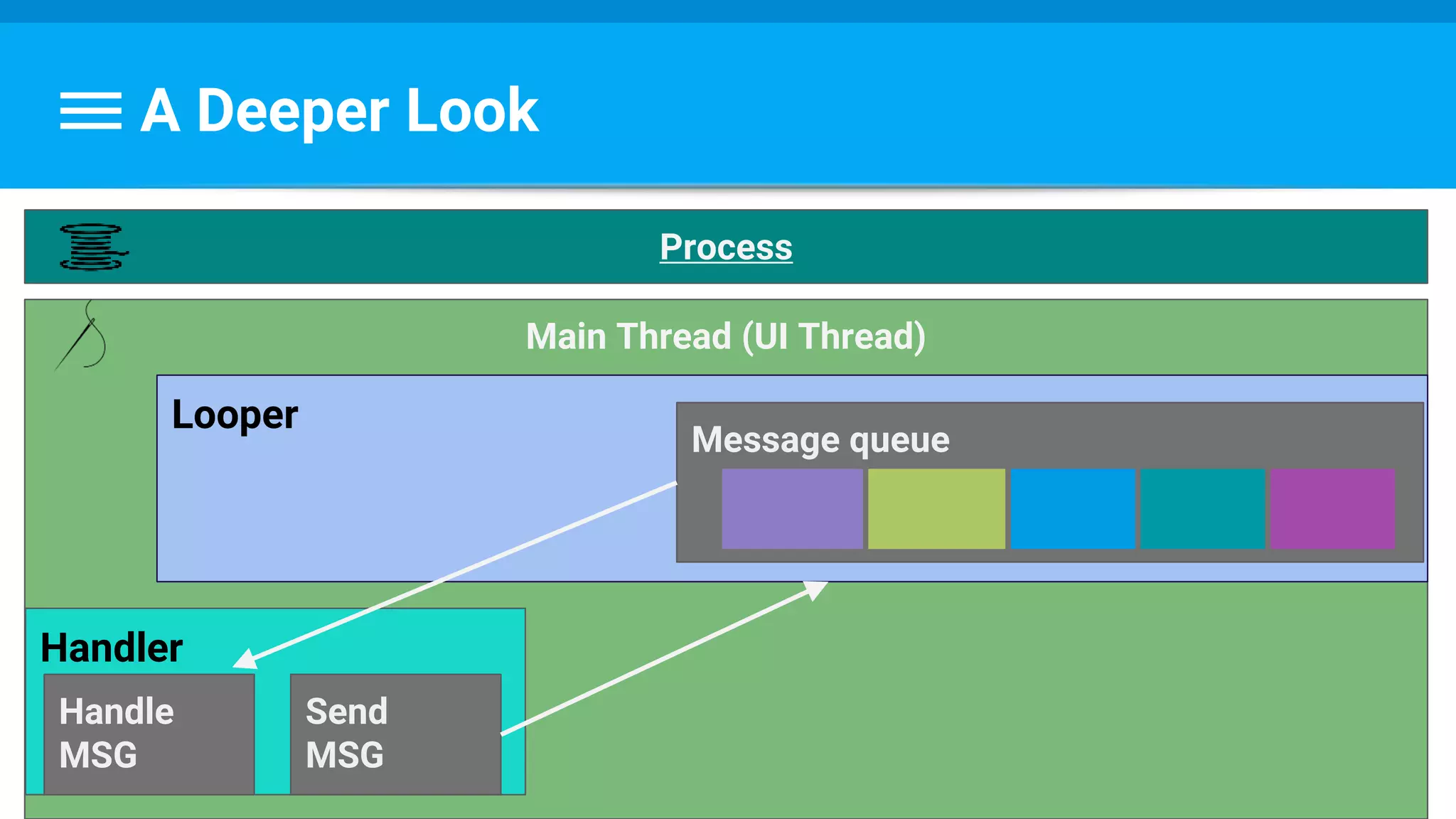
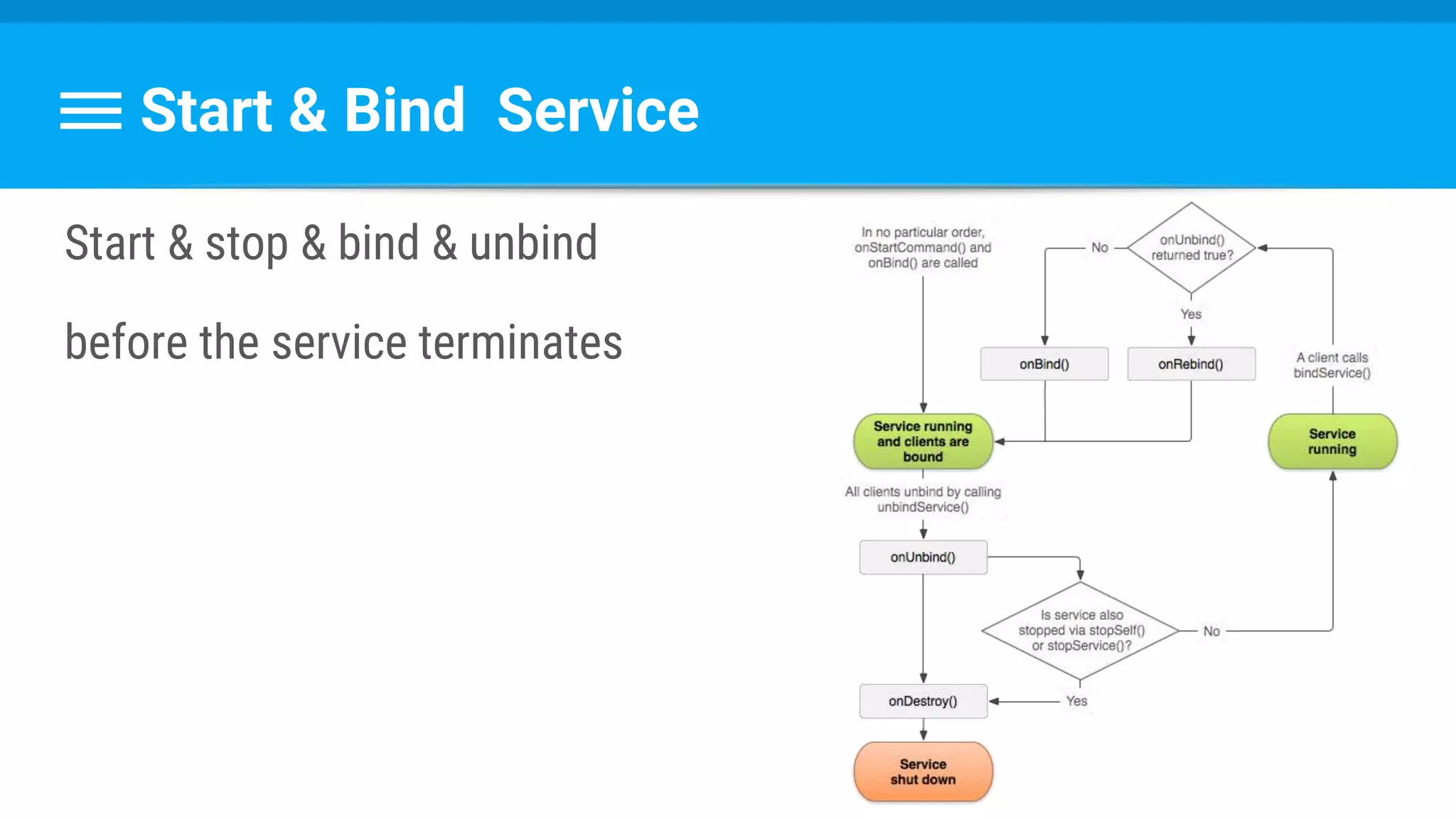
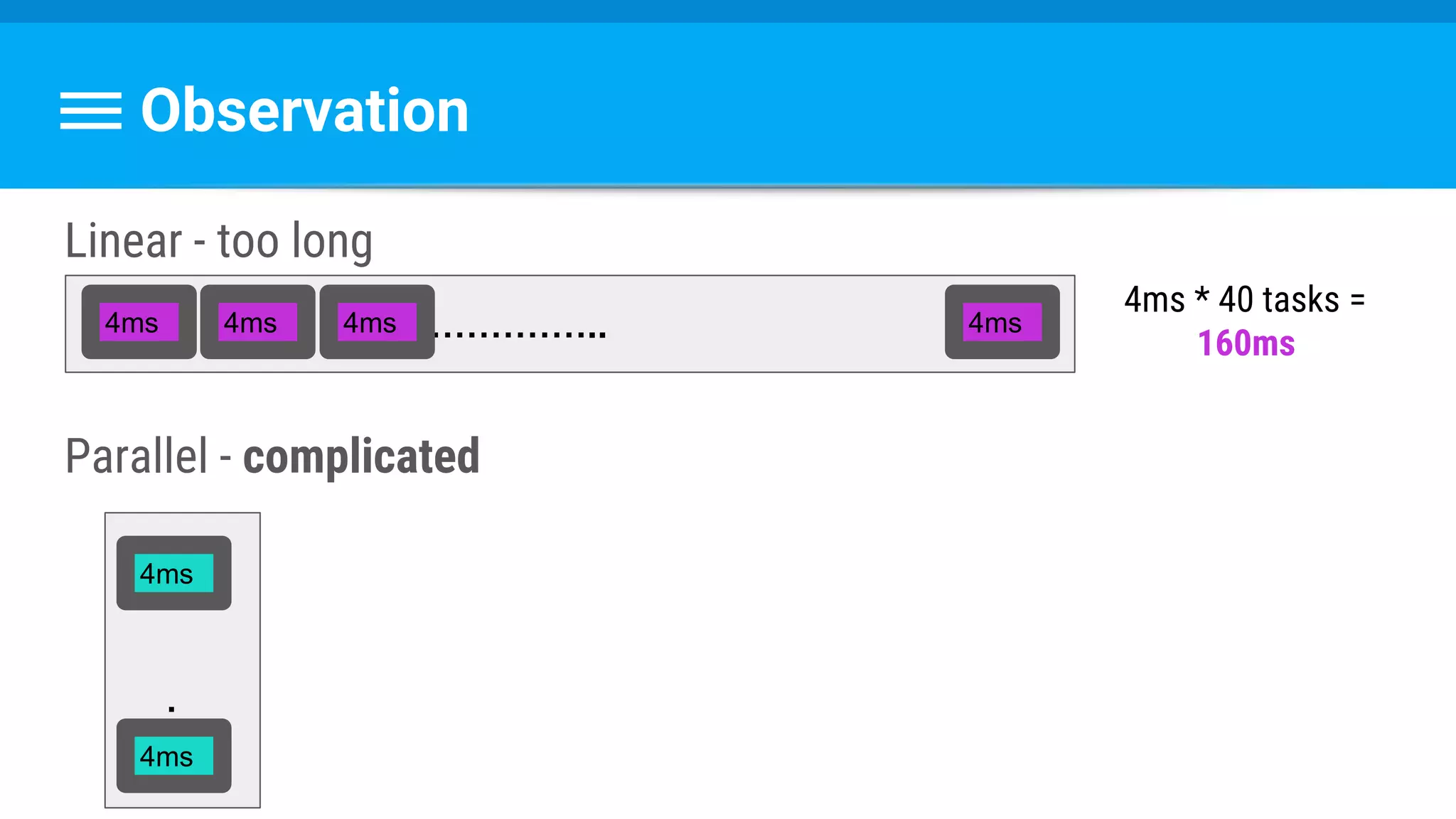
The document discusses threading in Android applications. It begins by explaining that the main or UI thread is responsible for drawing the user interface and handling input/output events. Any blocking operations on this thread can cause the application to become unresponsive. The document then discusses various approaches for offloading work from the main thread including using AsyncTask, HandlerThread, IntentService, and ThreadPoolExecutor. It provides examples and best practices for implementing each approach to avoid blocking the main thread and ensure responsive user experiences.
















![Example
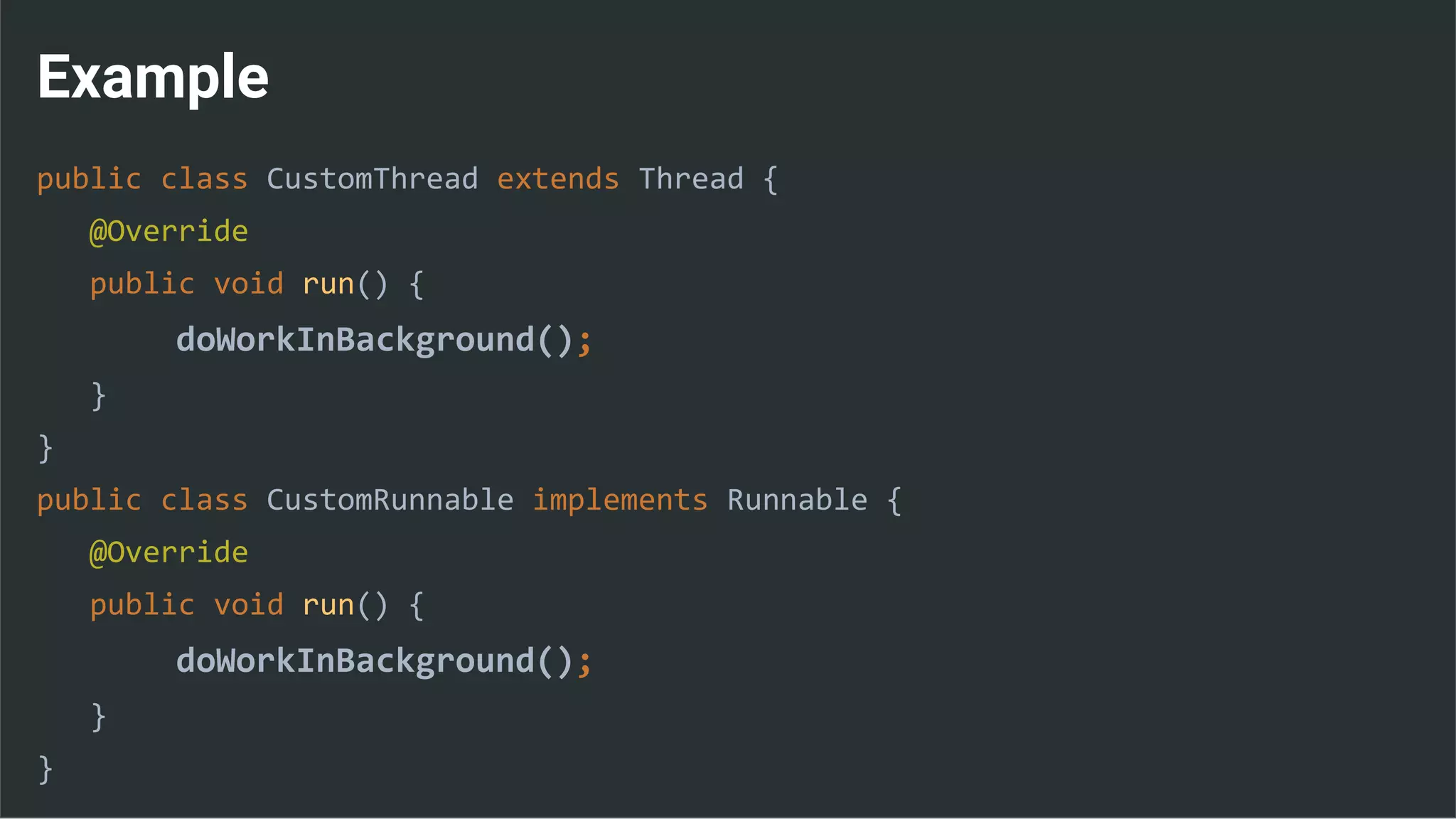
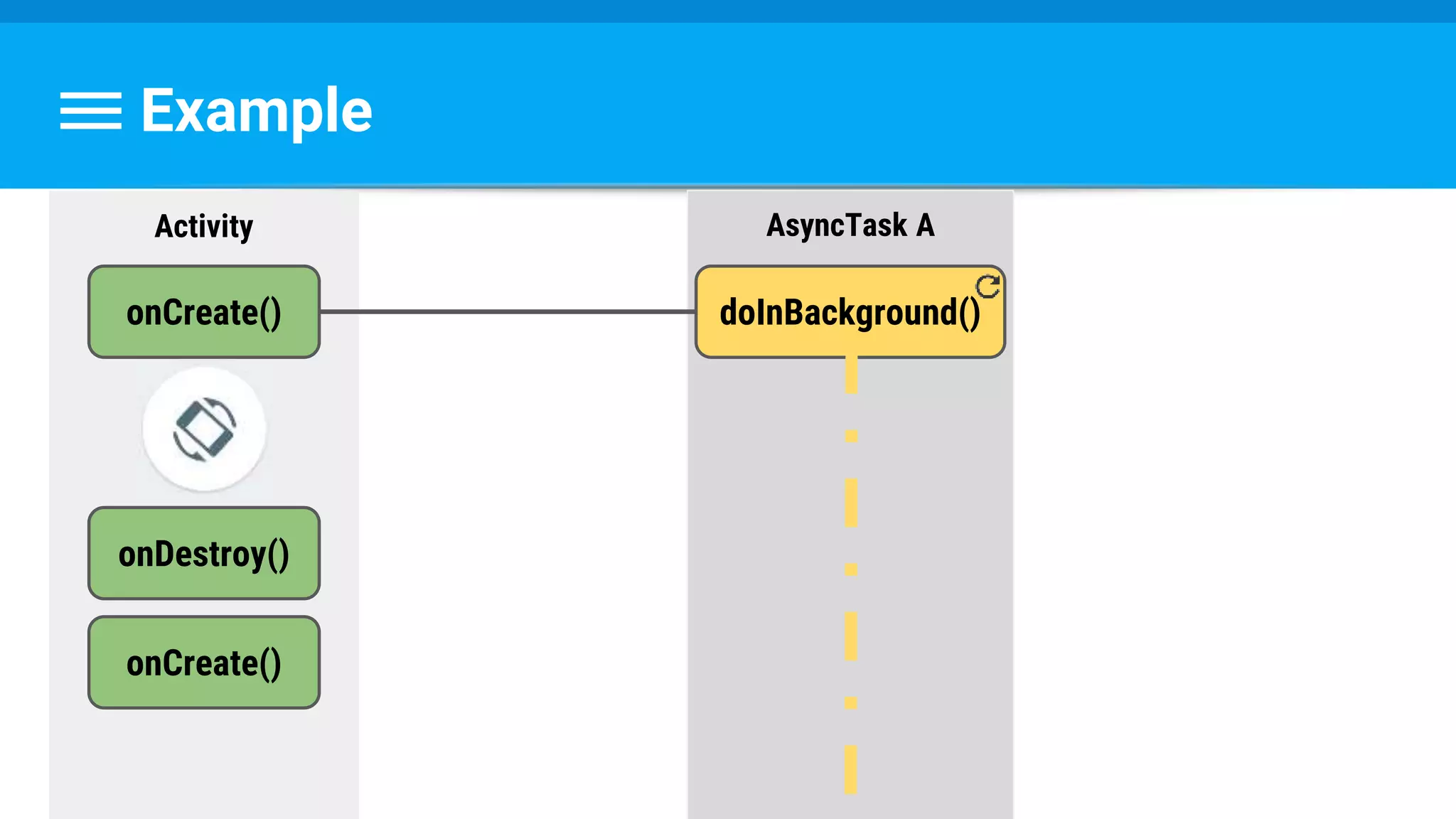
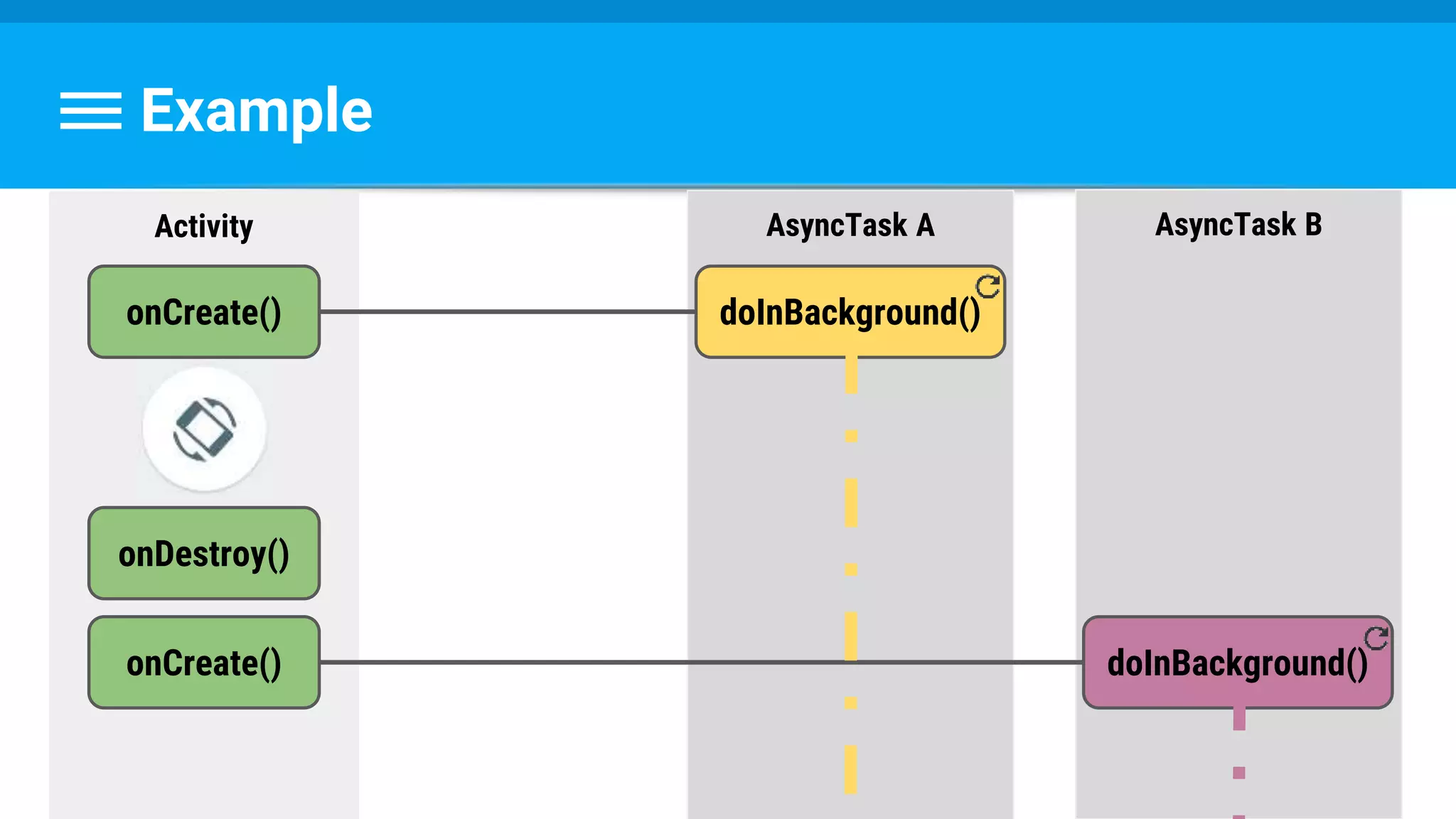
public class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
}
return totalSize;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performance6-threading-160915191218/75/Performance-6-threading-35-2048.jpg)
![Example
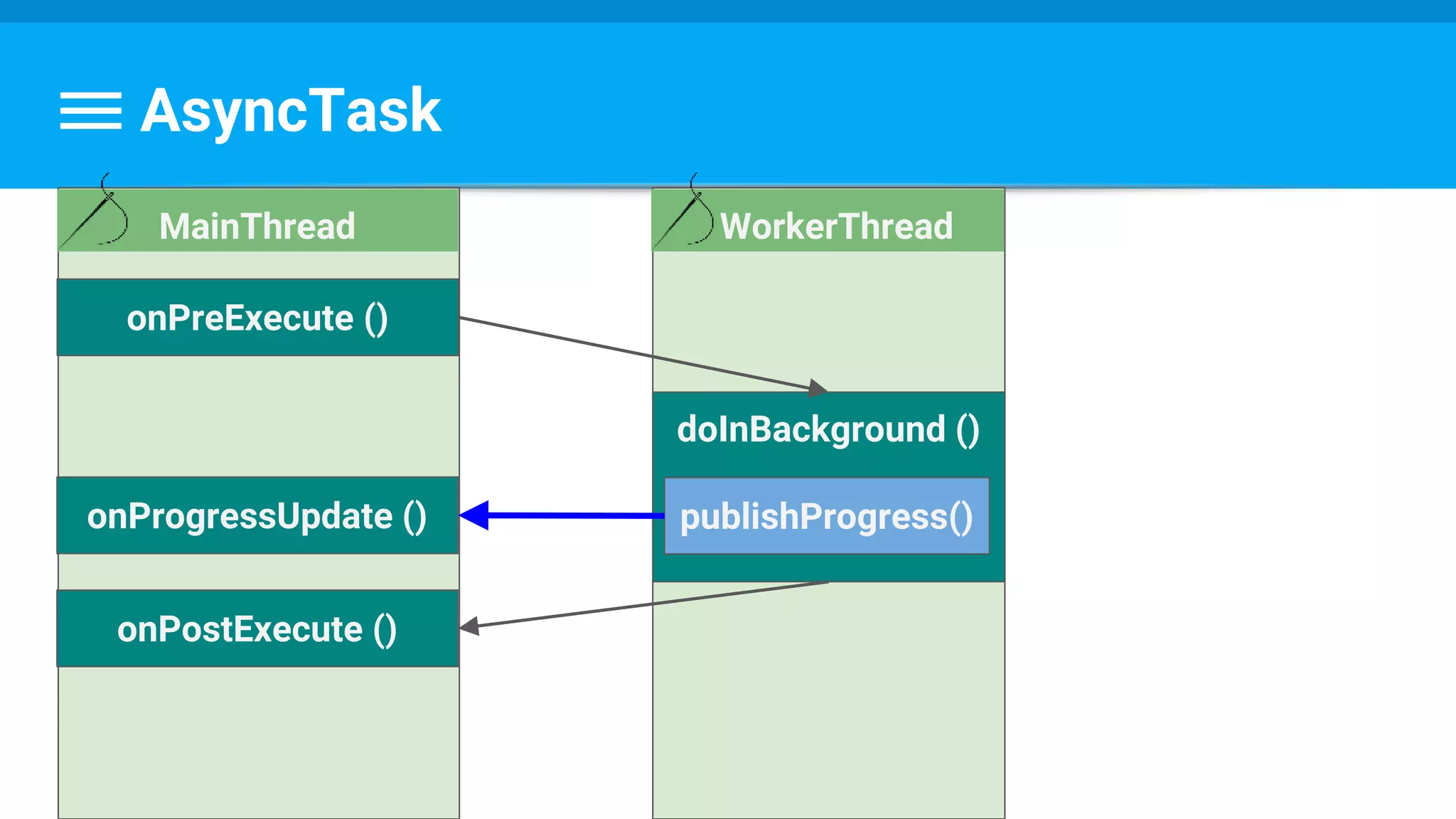
public class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
// ...
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
setProgressPercent(progress[0]);
}
protected void onPostExecute(Long result) {
showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performance6-threading-160915191218/75/Performance-6-threading-36-2048.jpg)
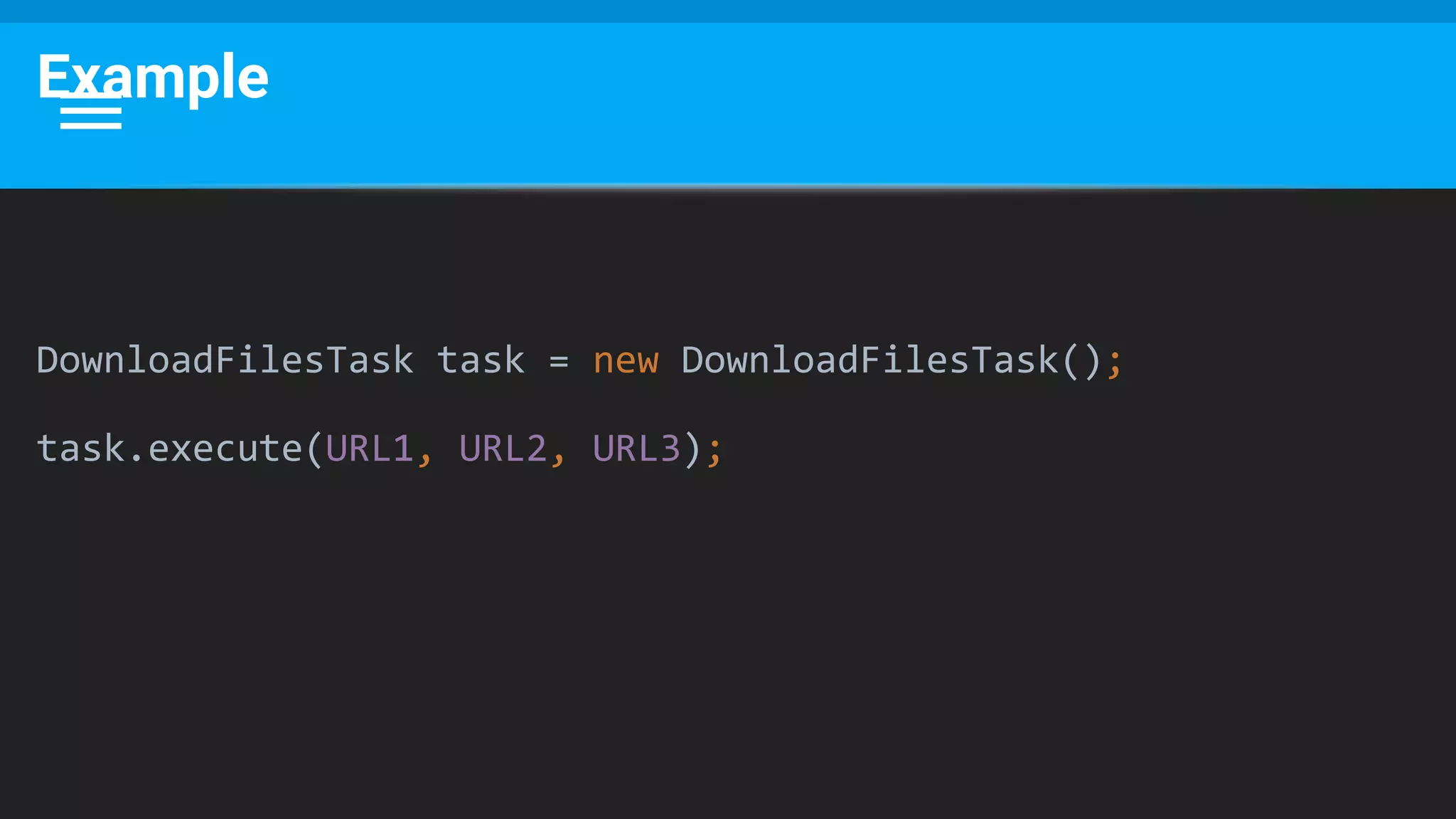
![This Would Also Work
DownloadFilesTask task = new DownloadFilesTask(URL1, URL2, URL3);
task.execute();
public class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Integer, Long> {
private URL[] urls;
public DownloadFilesTask(URL... urls) {
this.urls = urls;
}
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performance6-threading-160915191218/75/Performance-6-threading-38-2048.jpg)
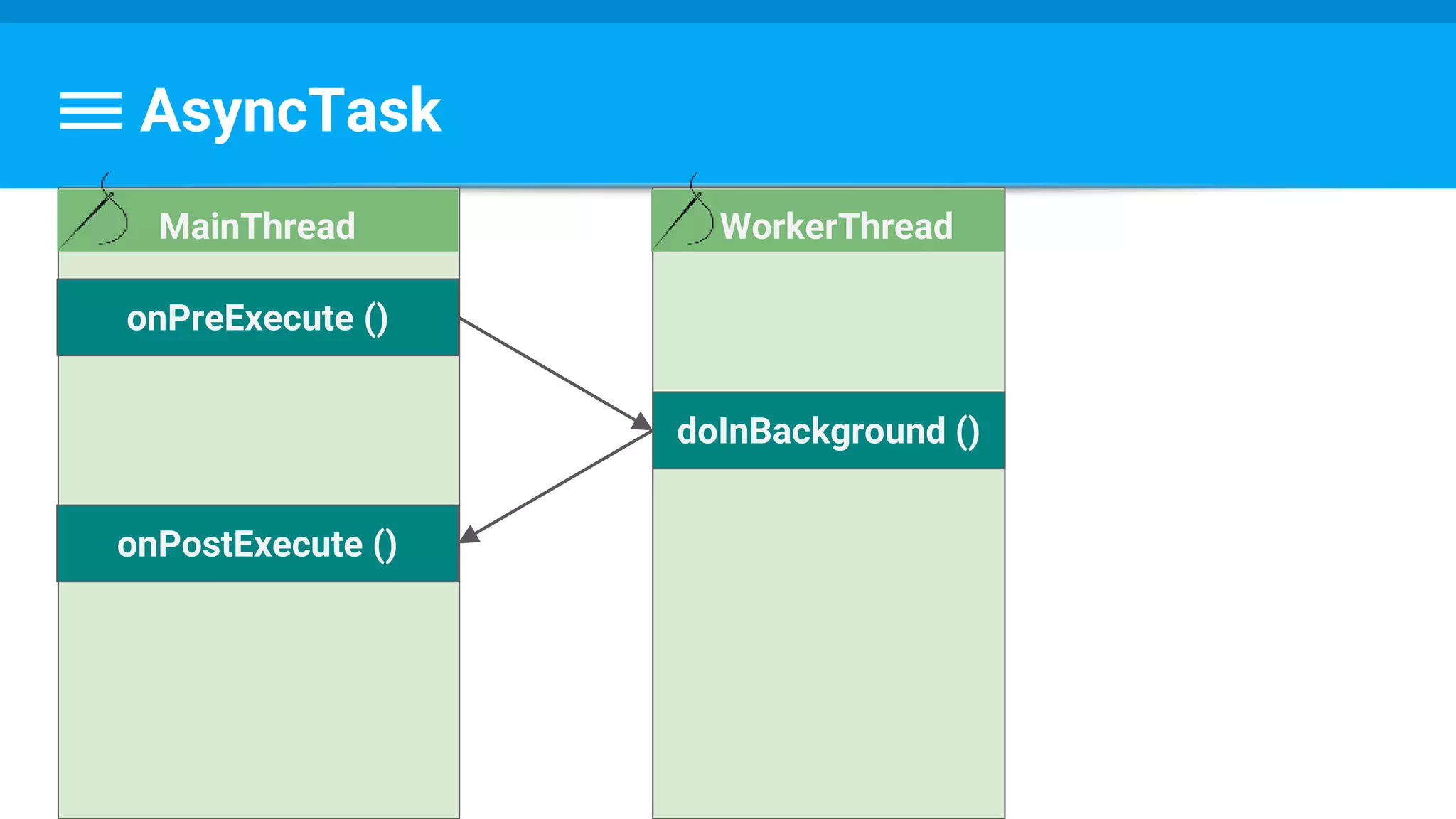
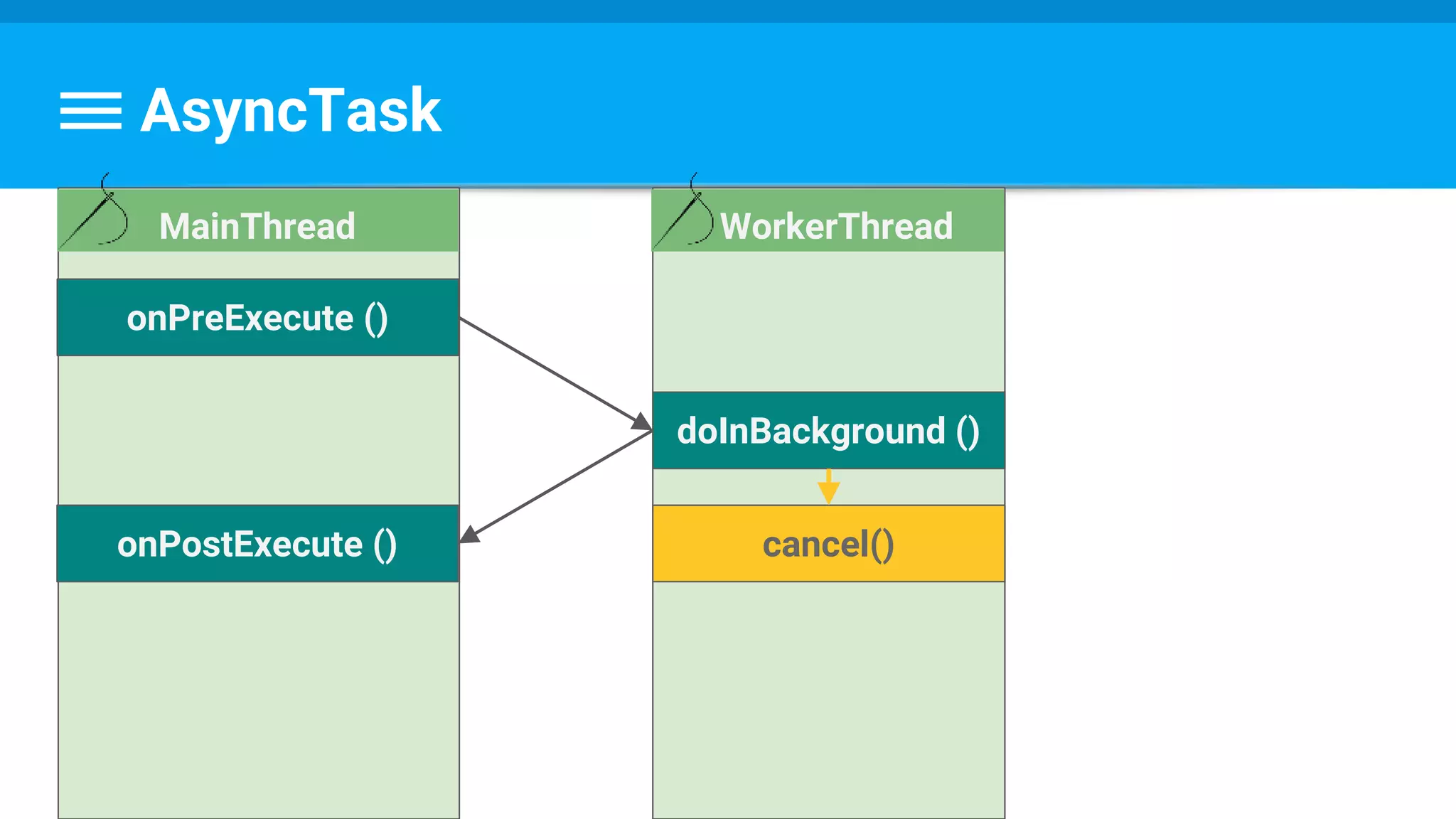
![Example
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
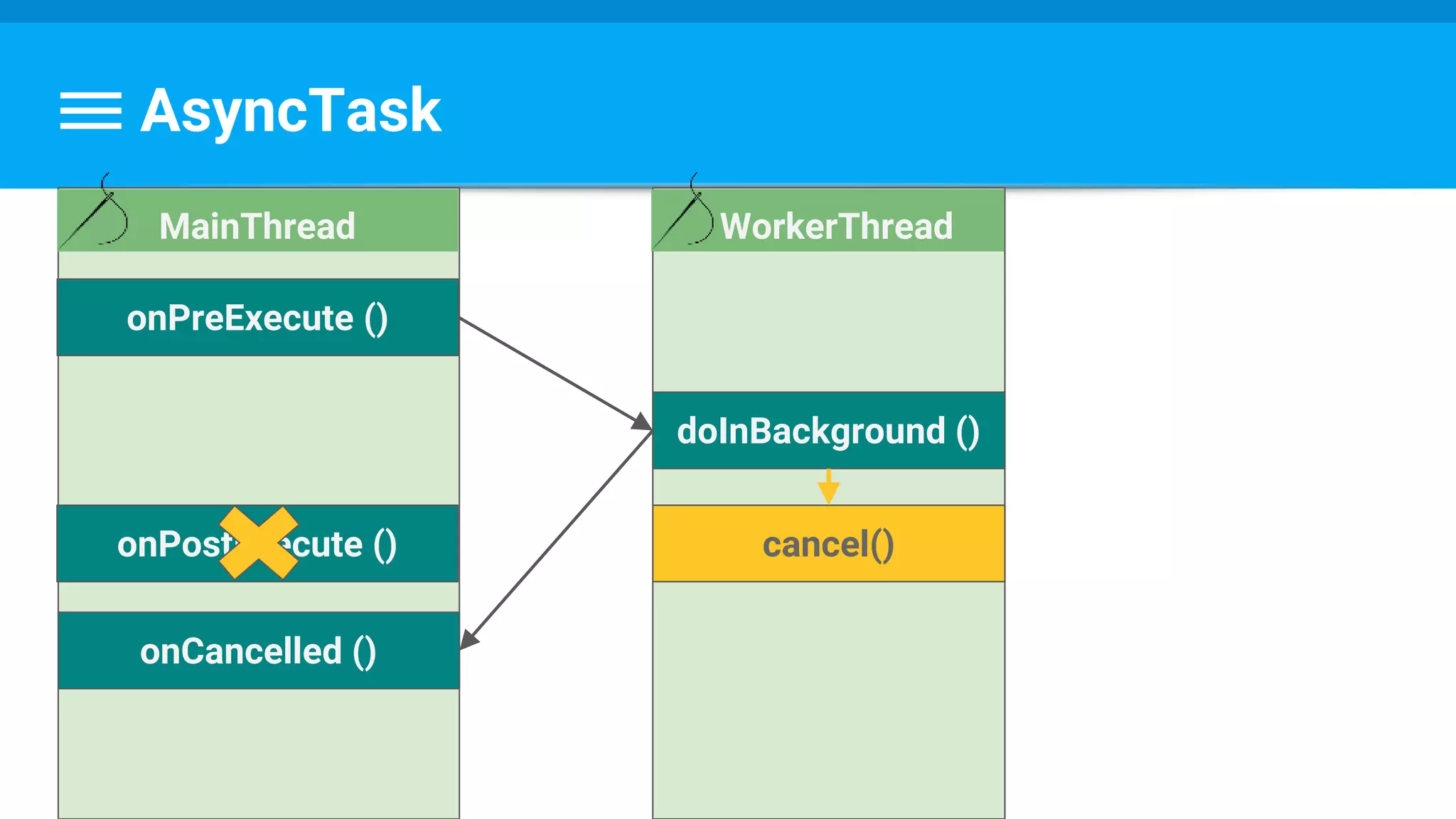
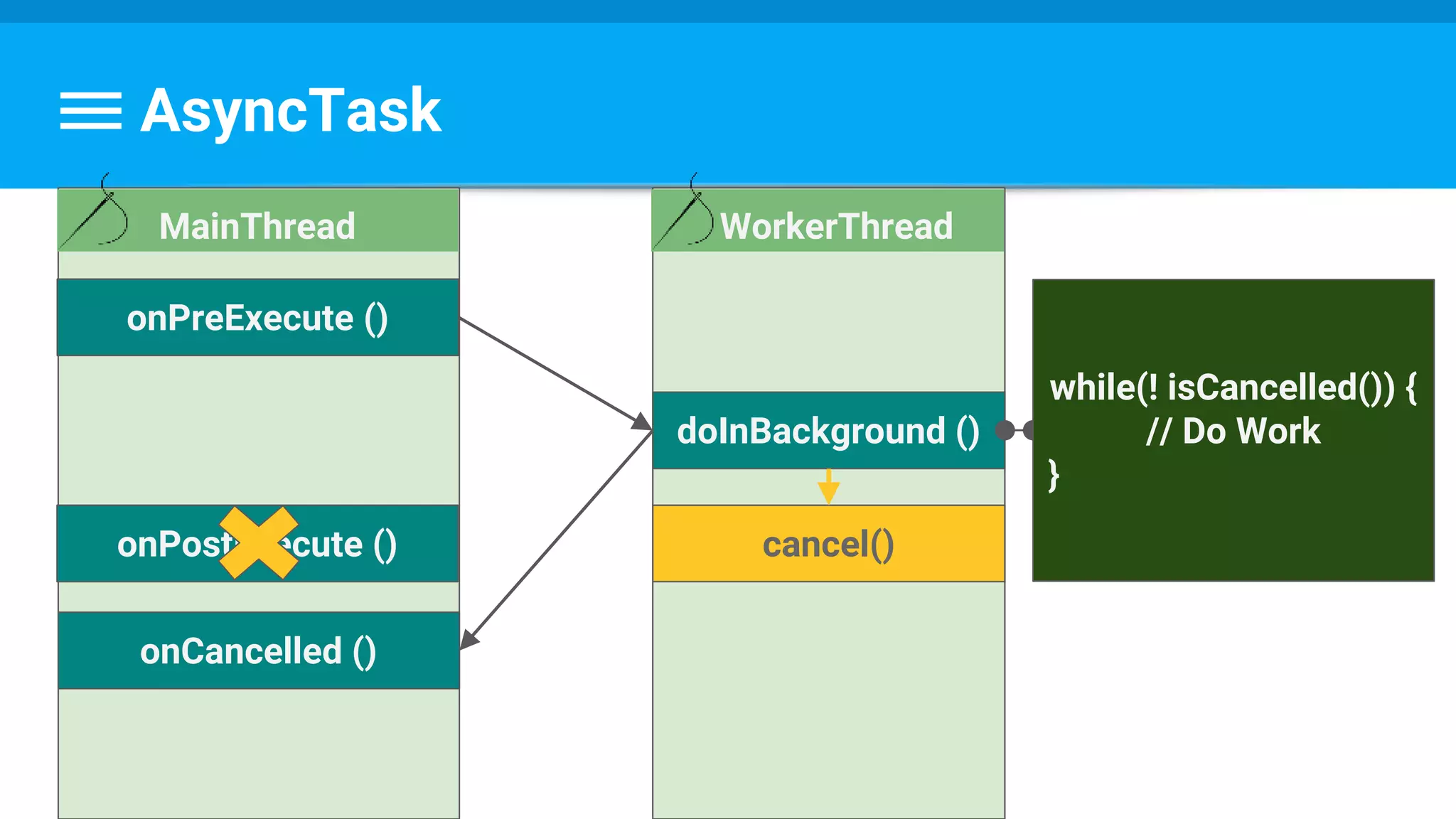
// Escape early if cancel() is called
if (isCancelled()) break;
}
return totalSize;
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled(Long result) {
showDialog("Downloaded was cancelled after " + result + " bytes");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performance6-threading-160915191218/75/Performance-6-threading-44-2048.jpg)












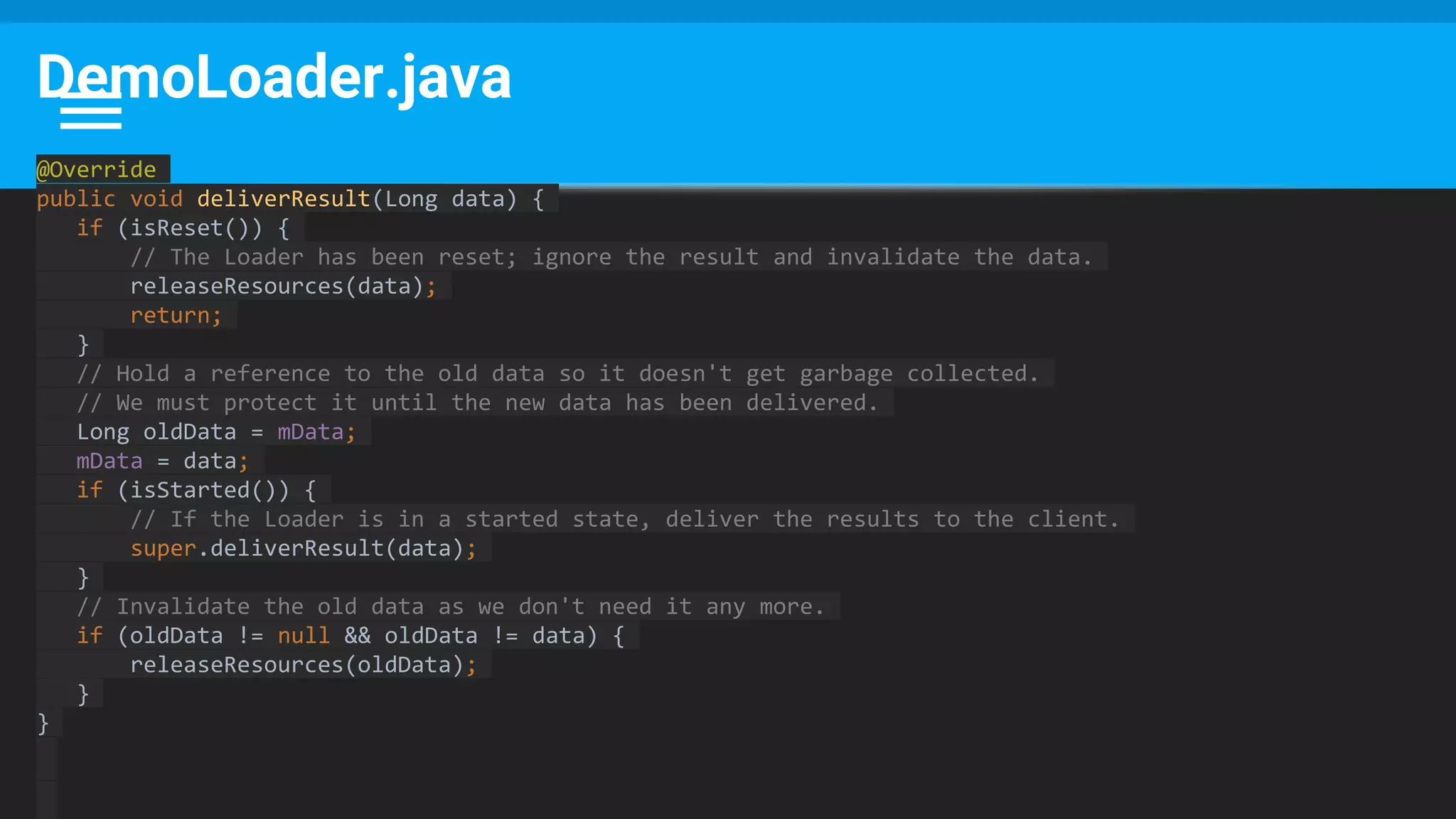

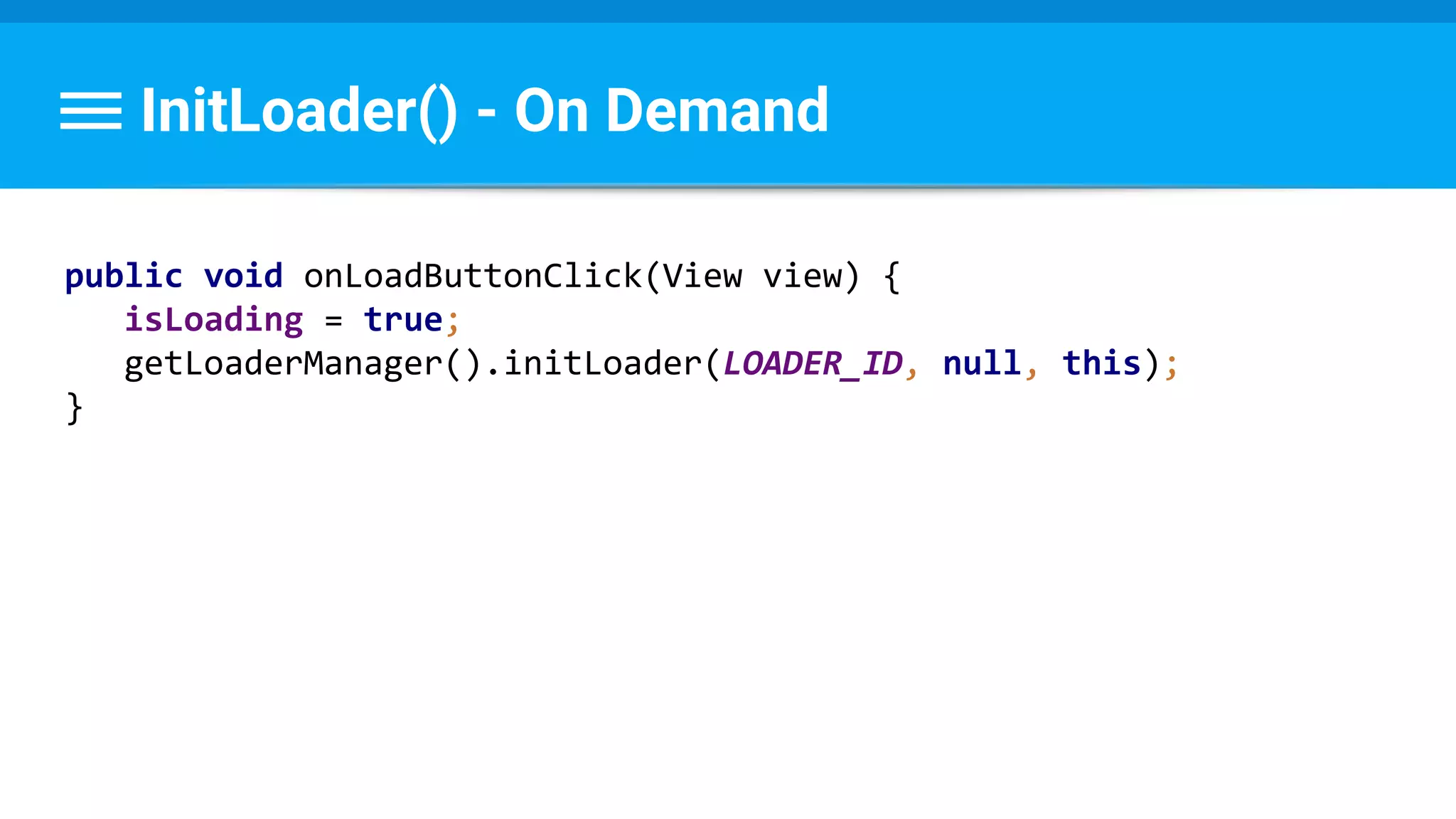
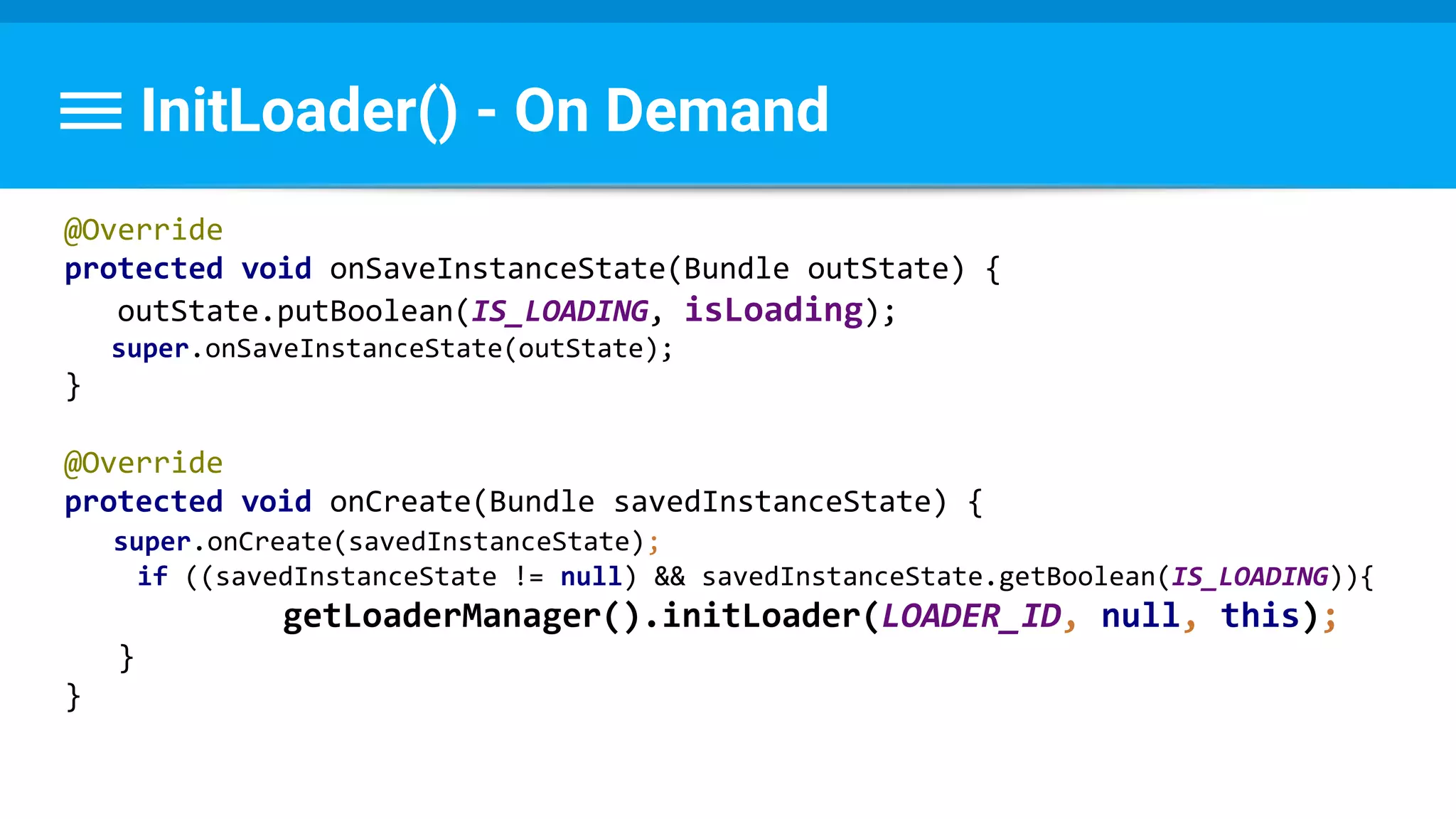
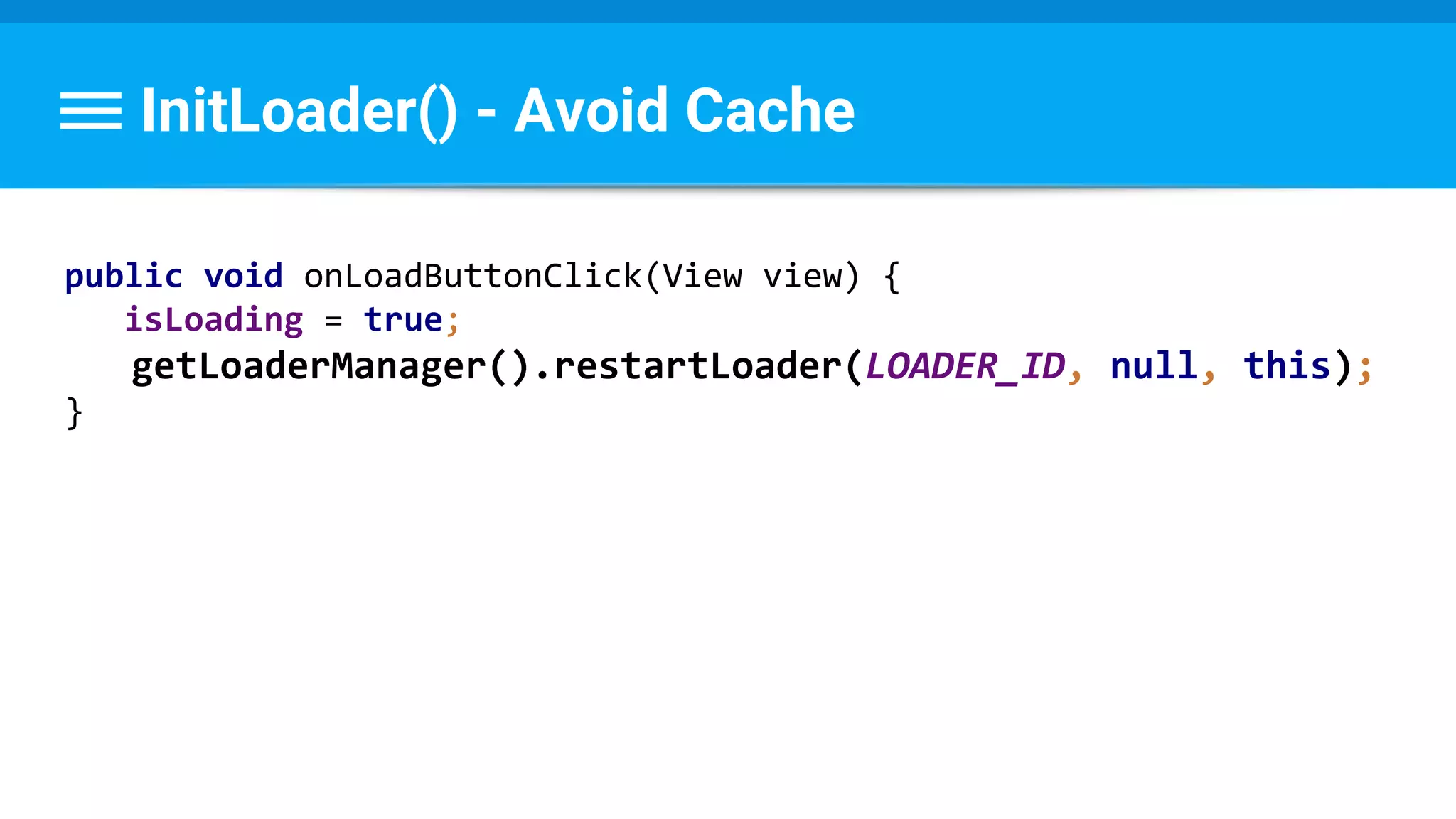





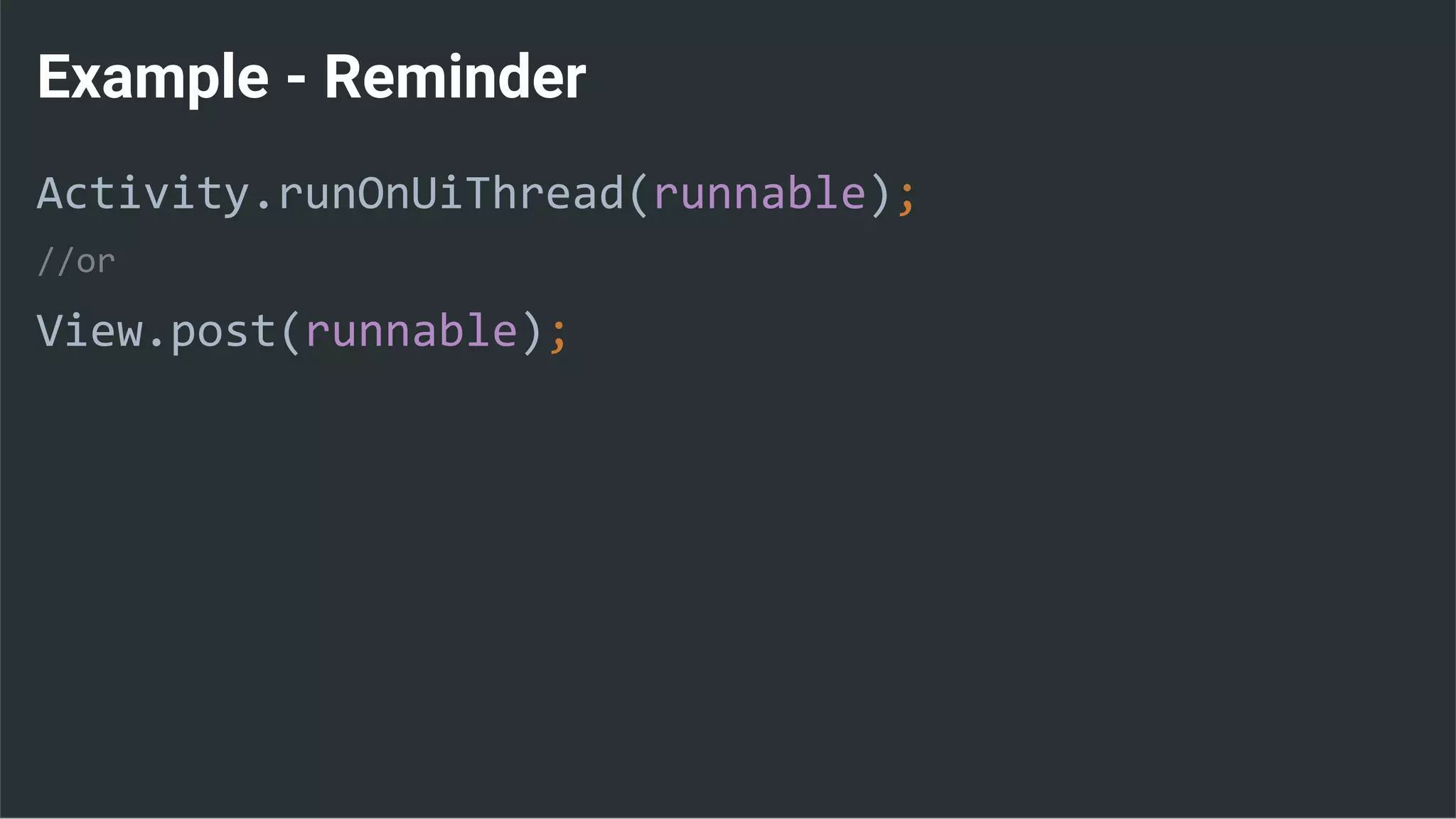


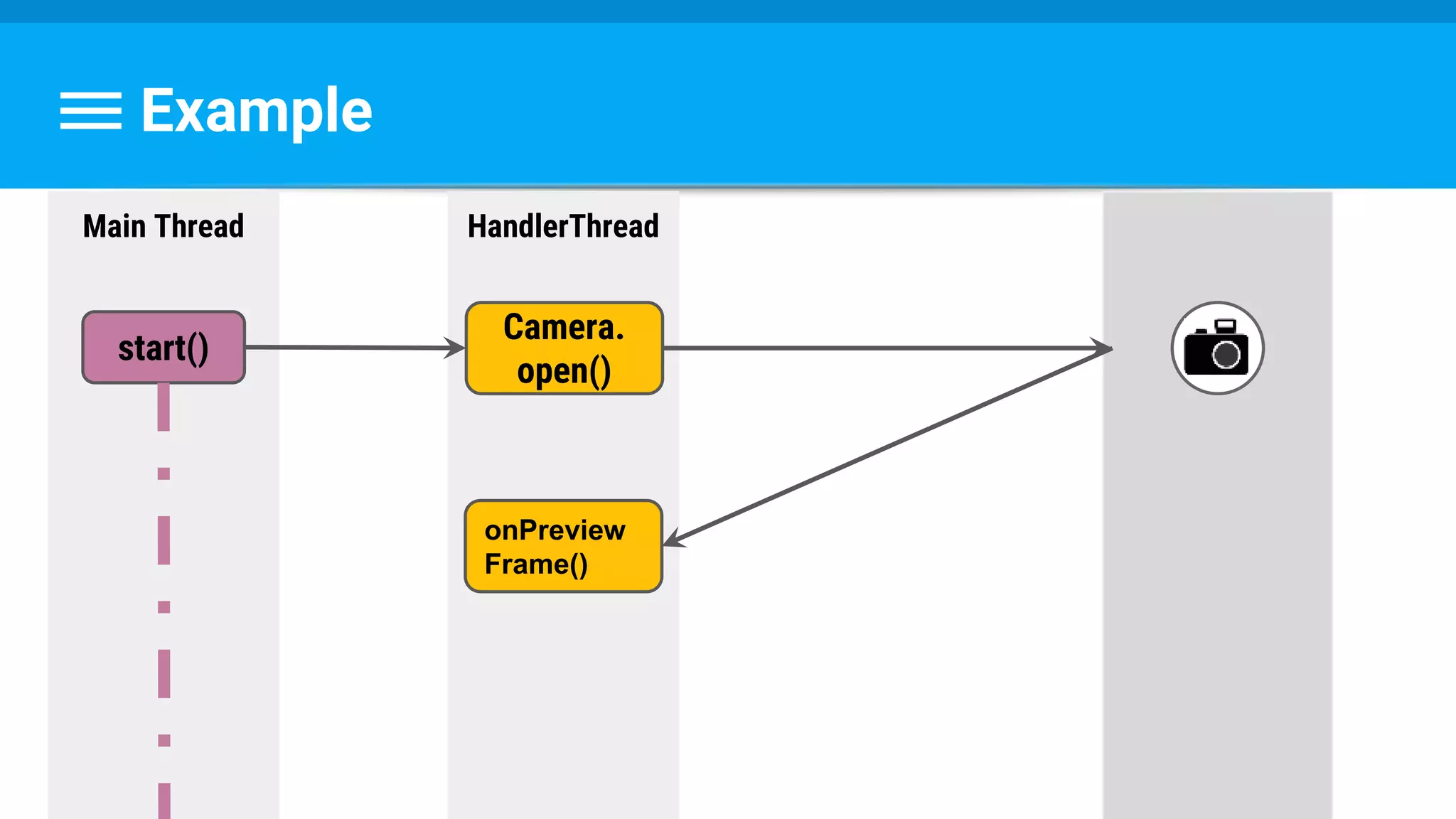

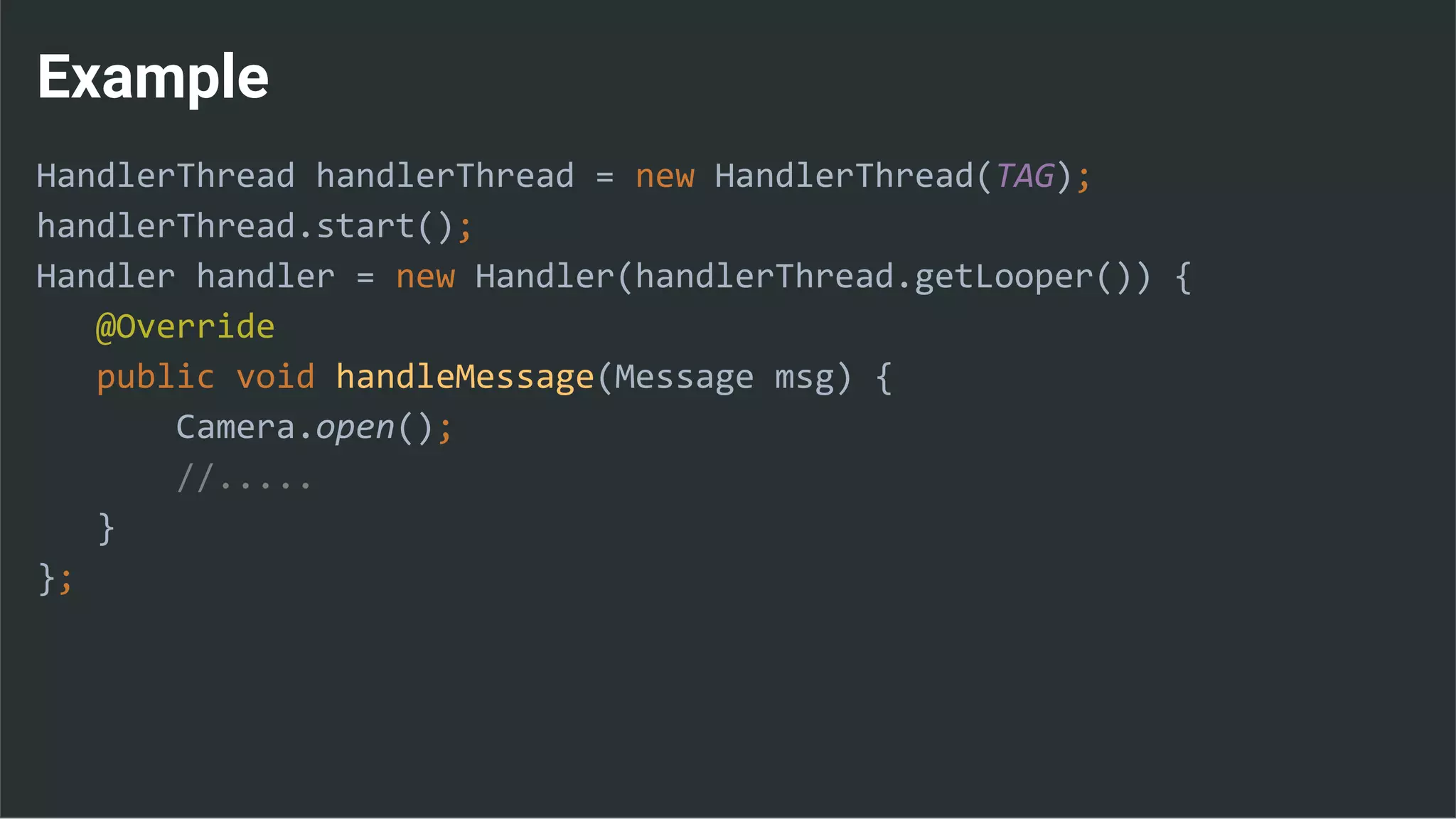




















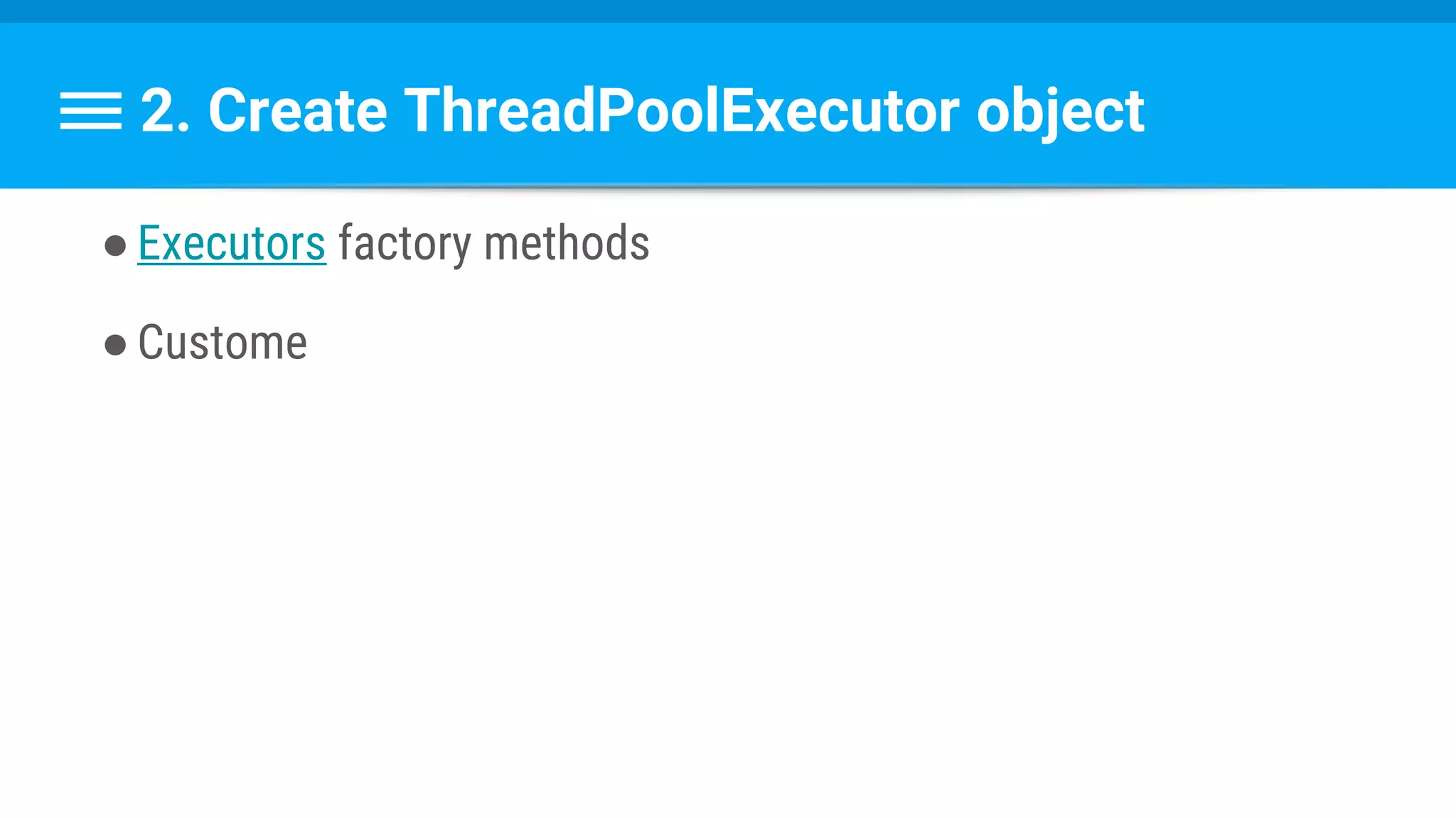


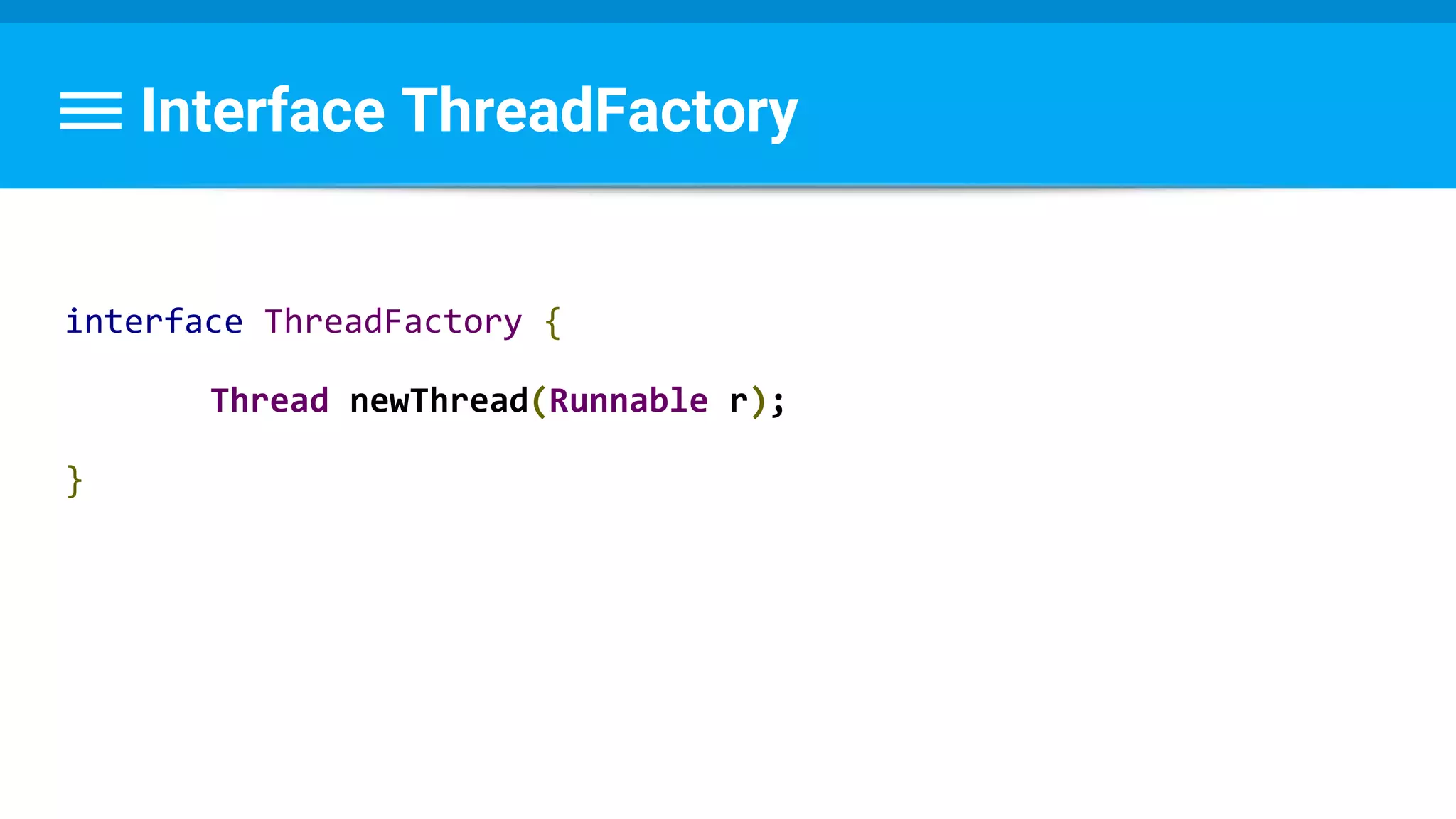
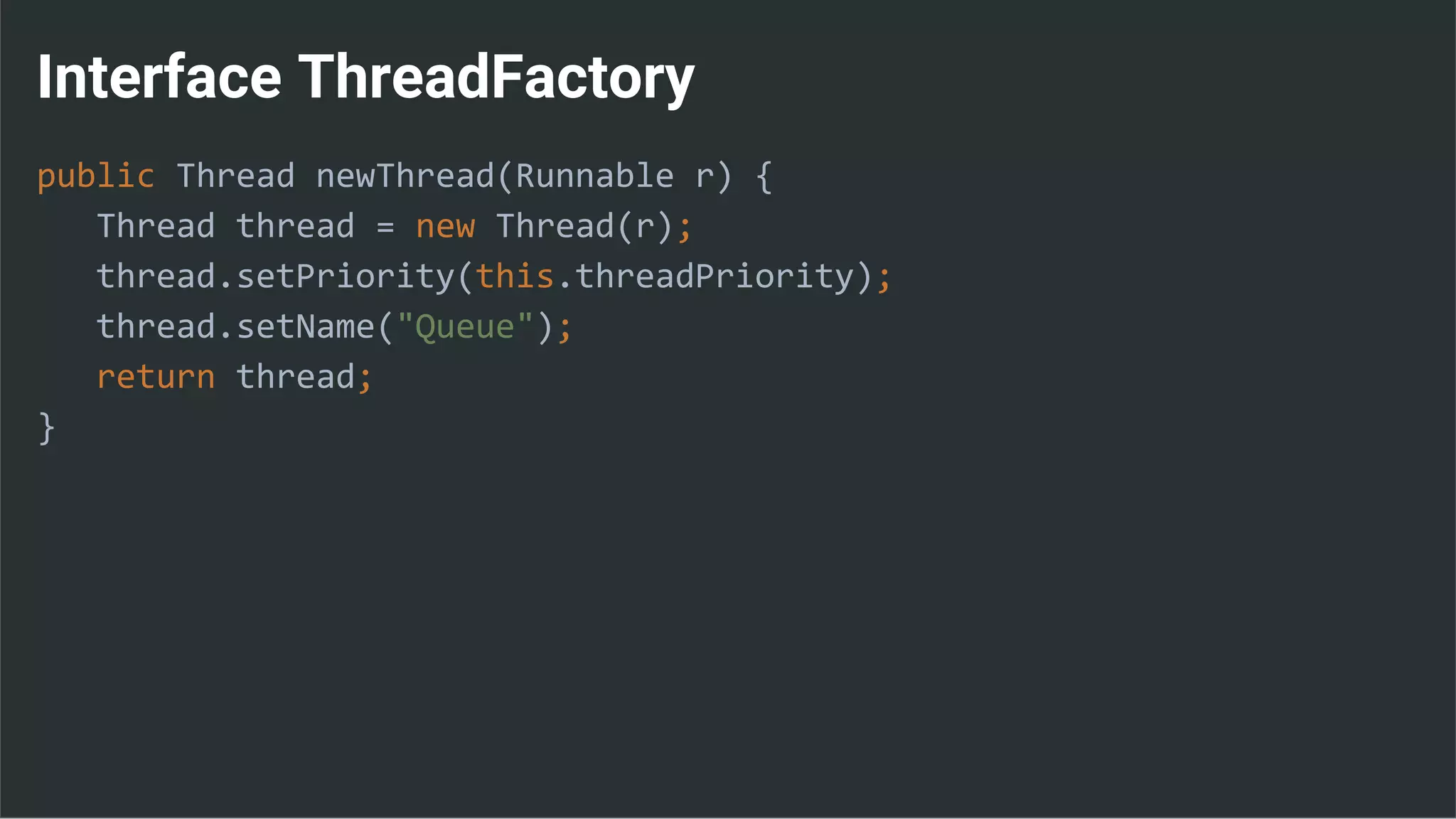




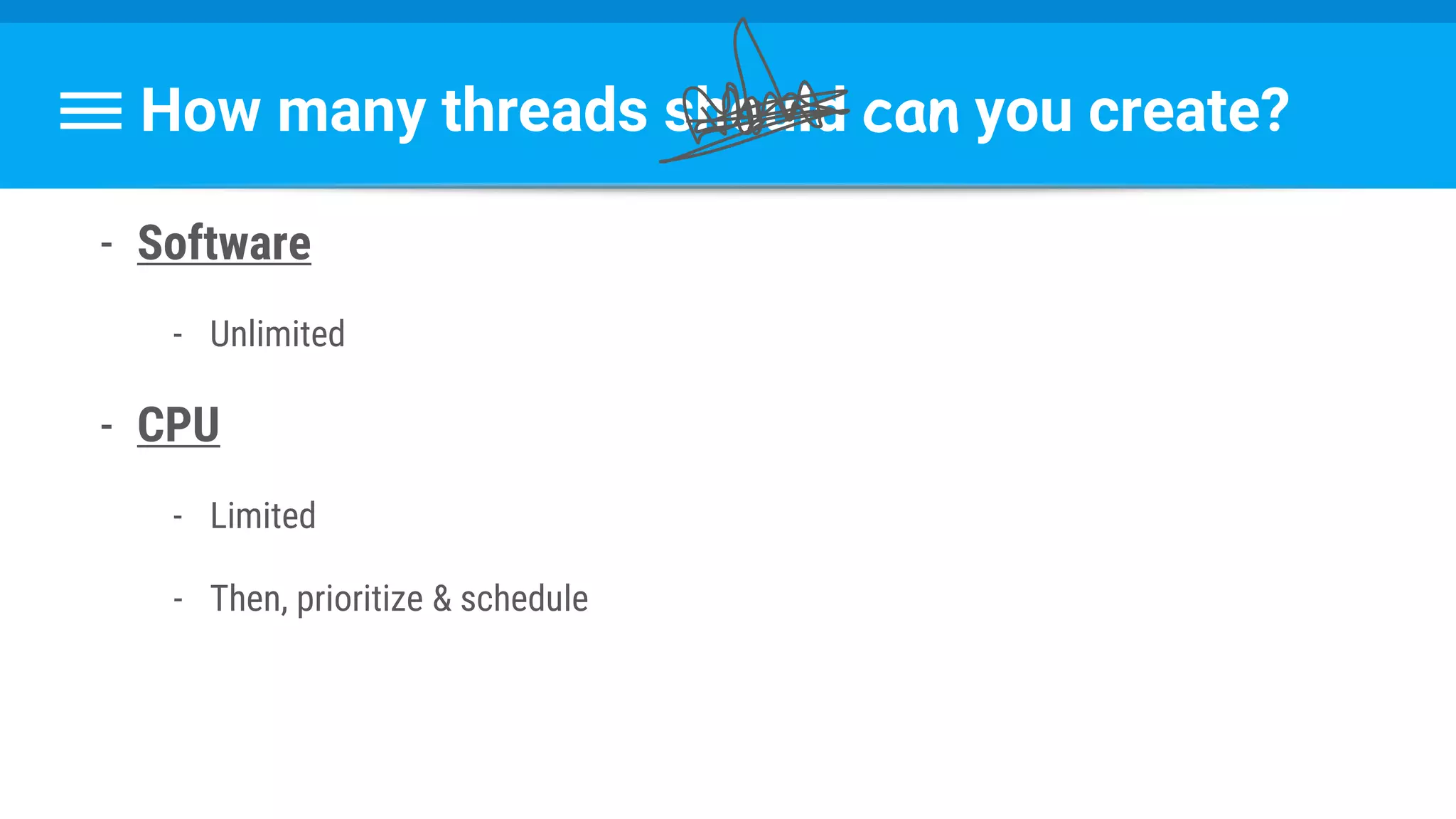
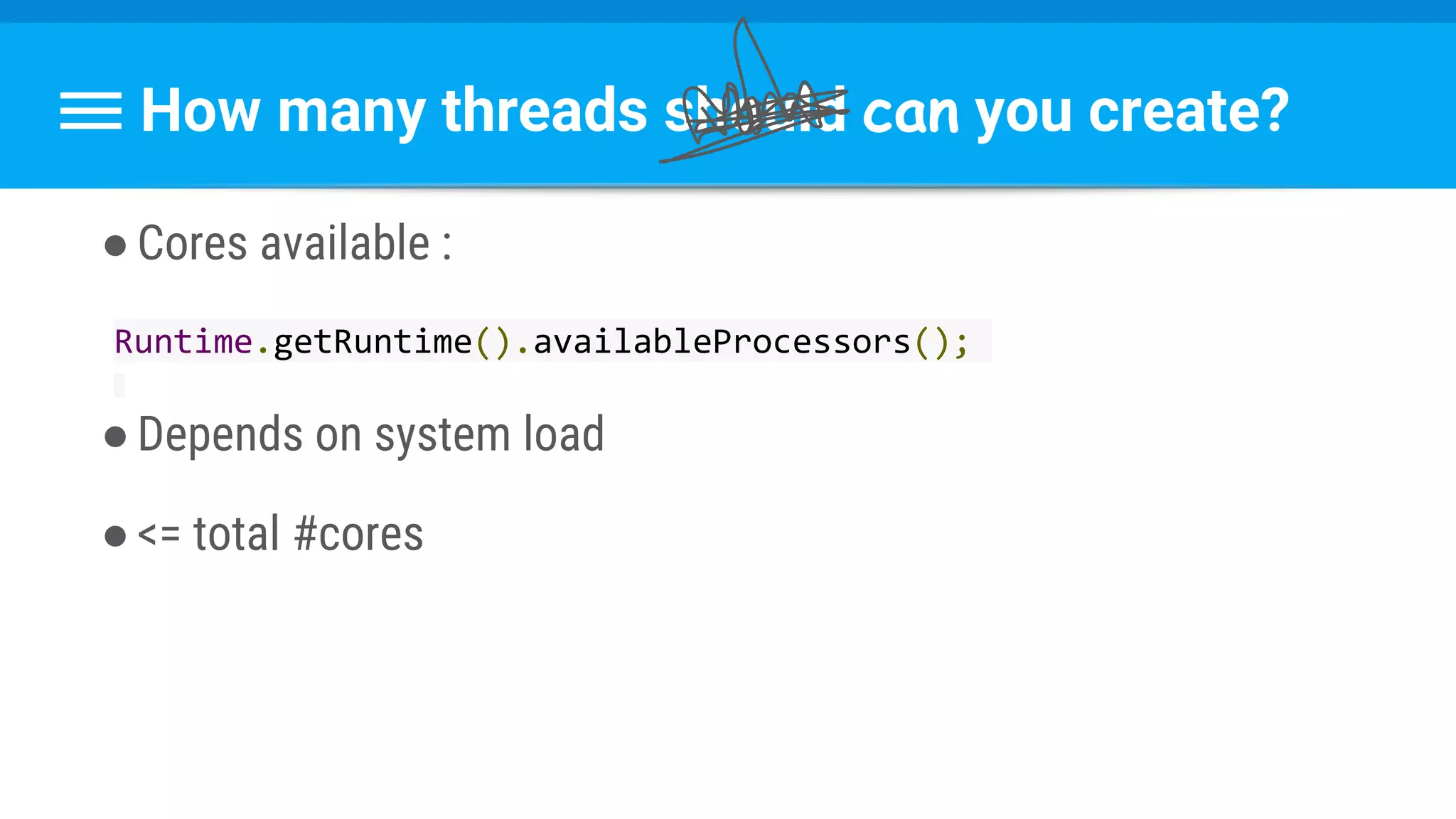

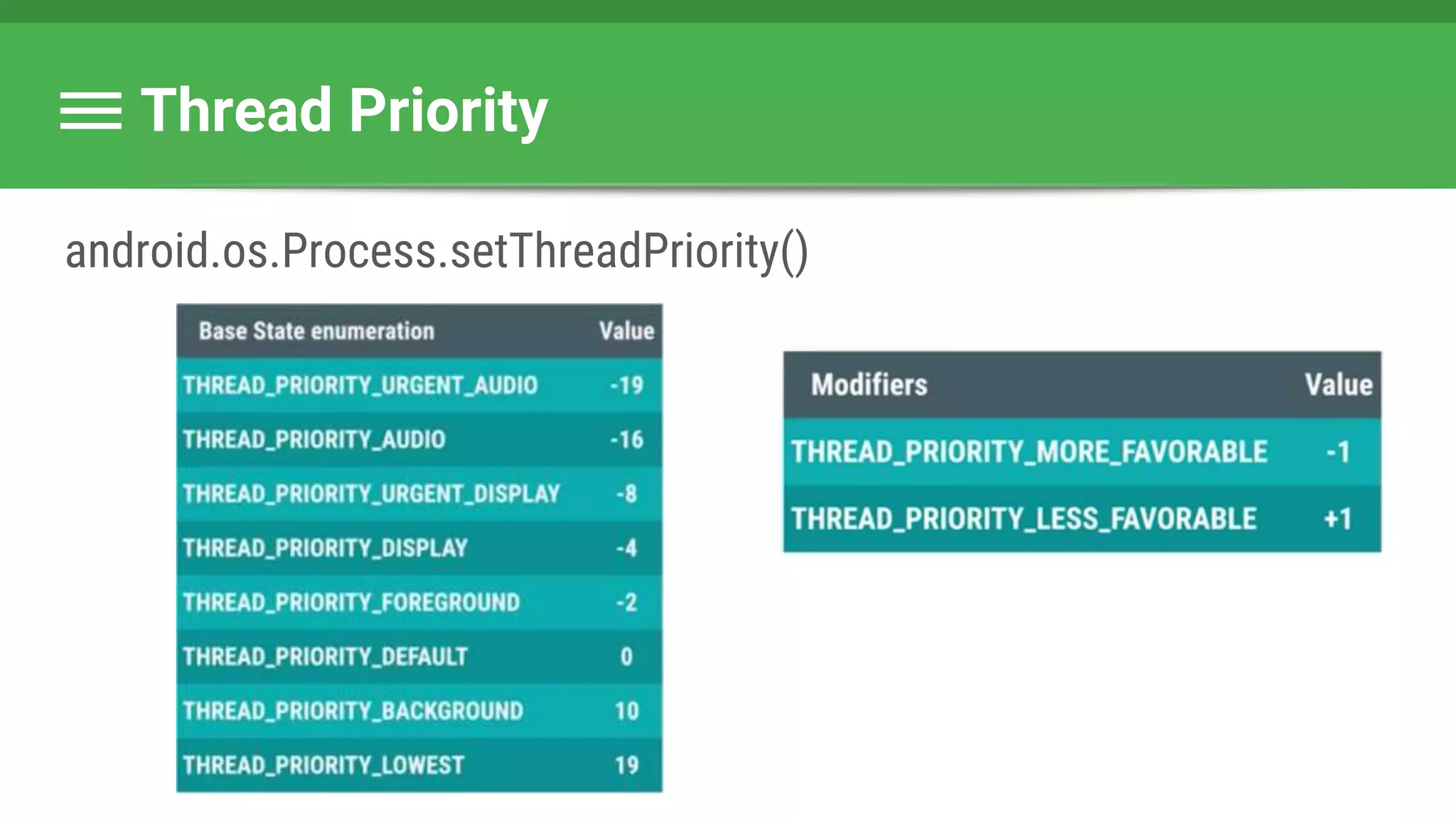
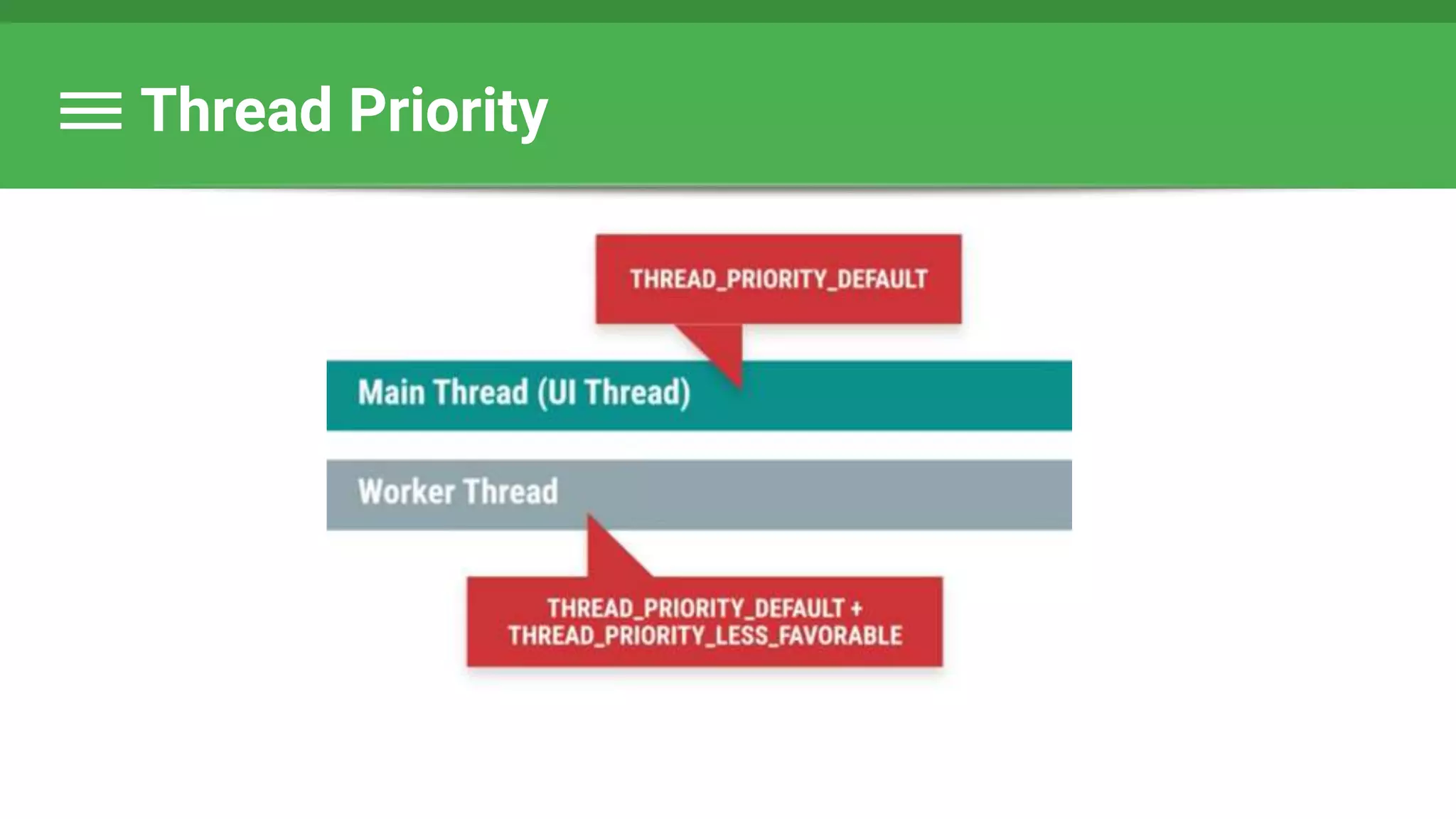
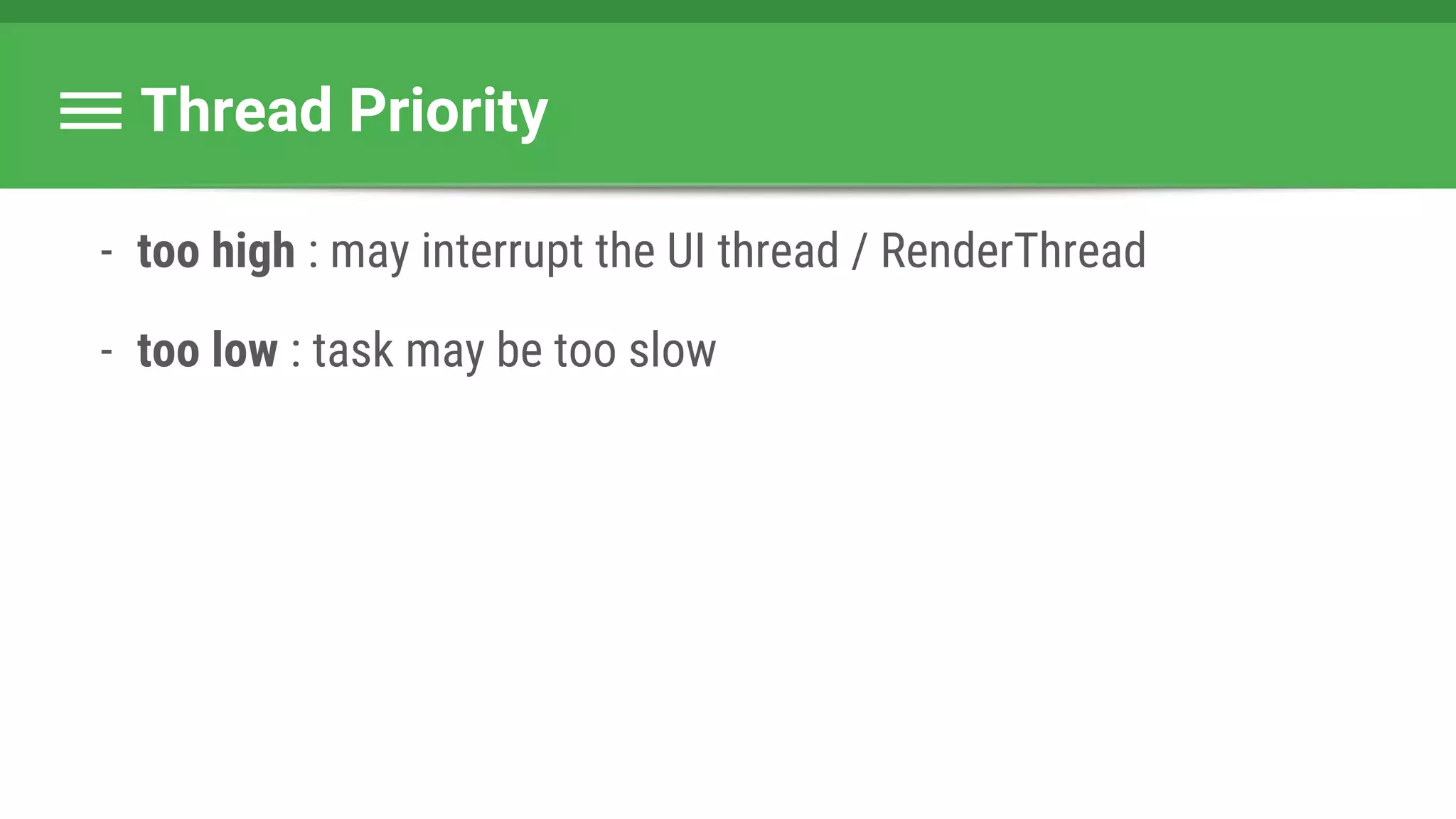




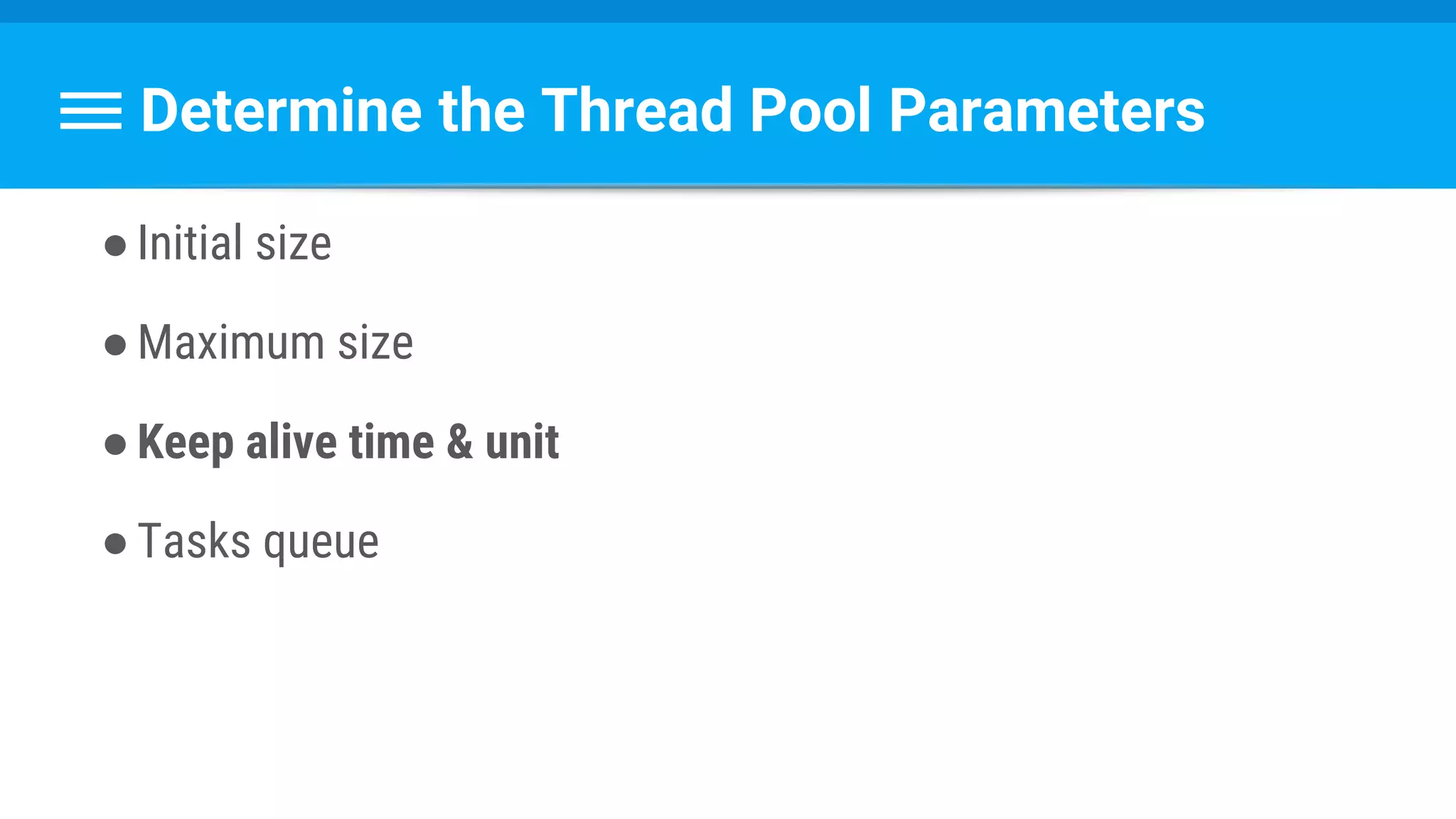



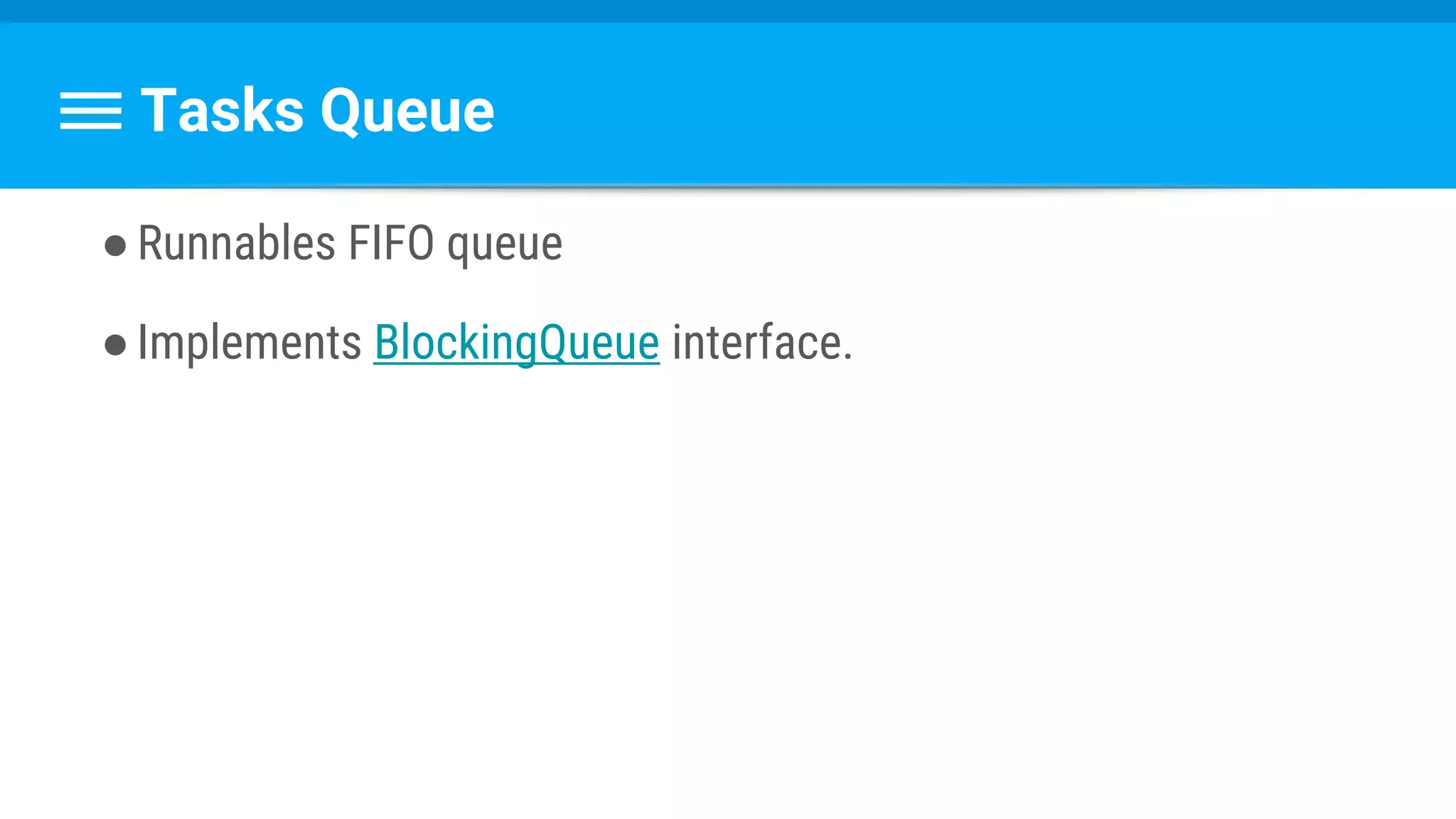
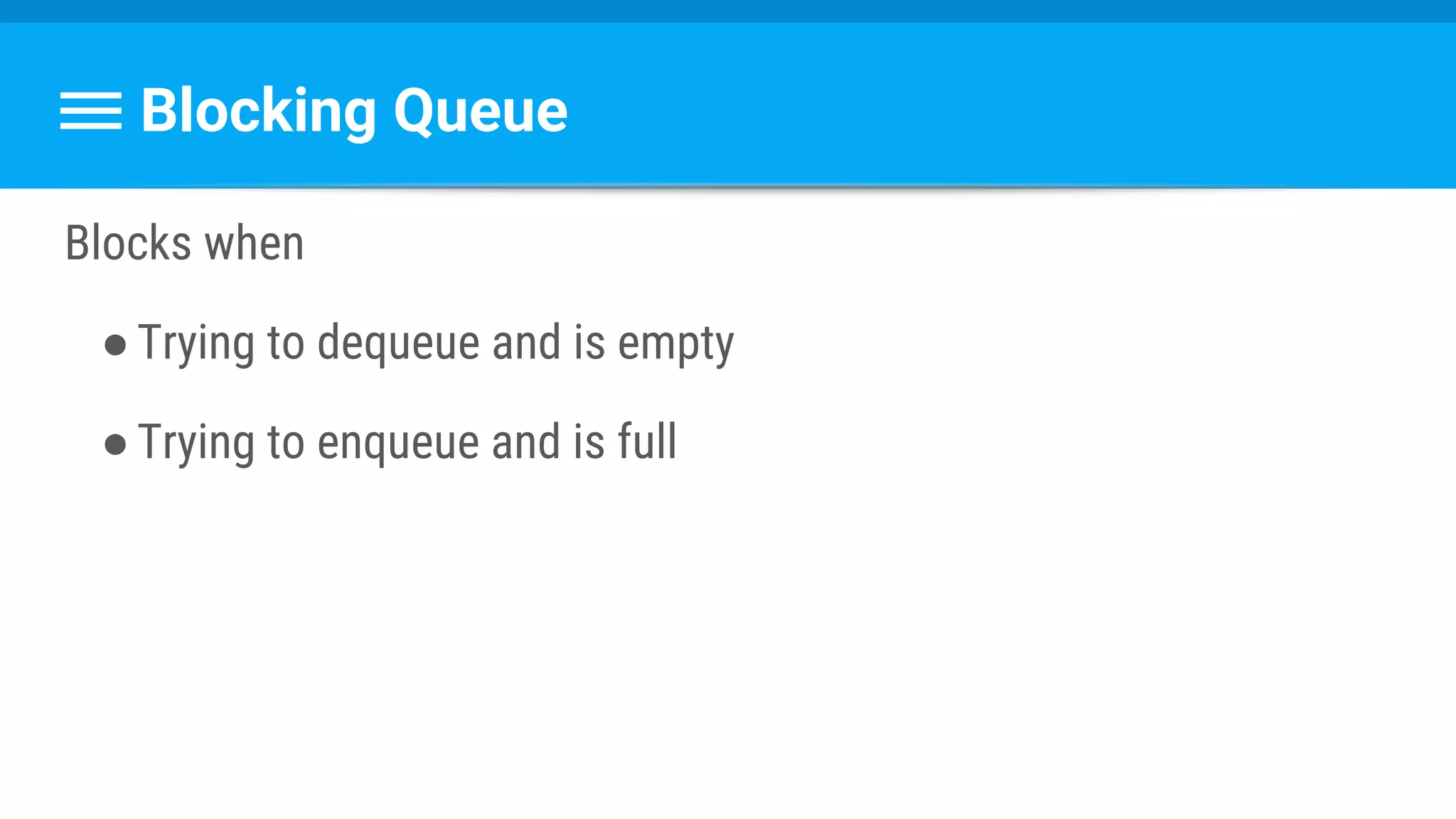

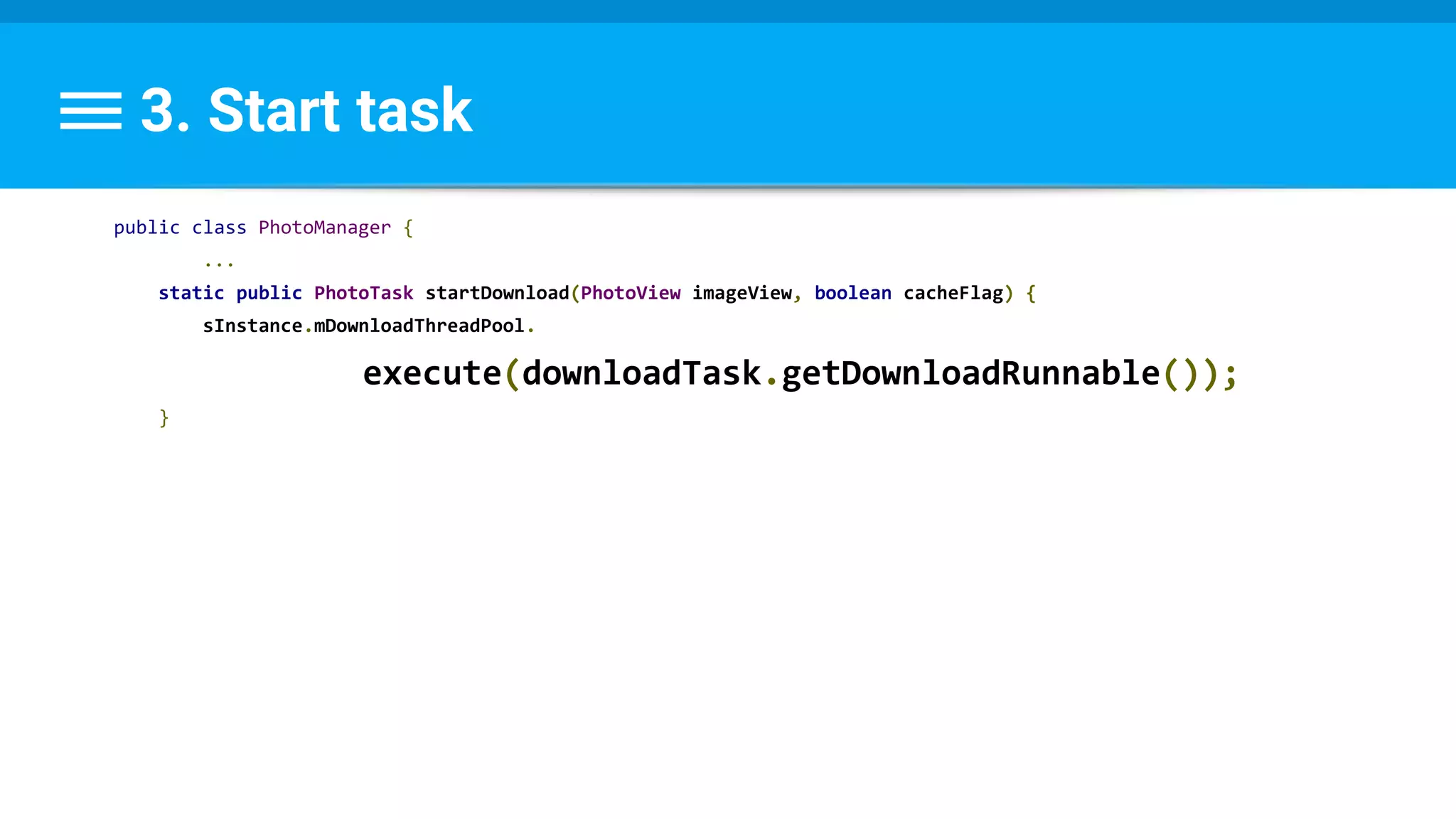

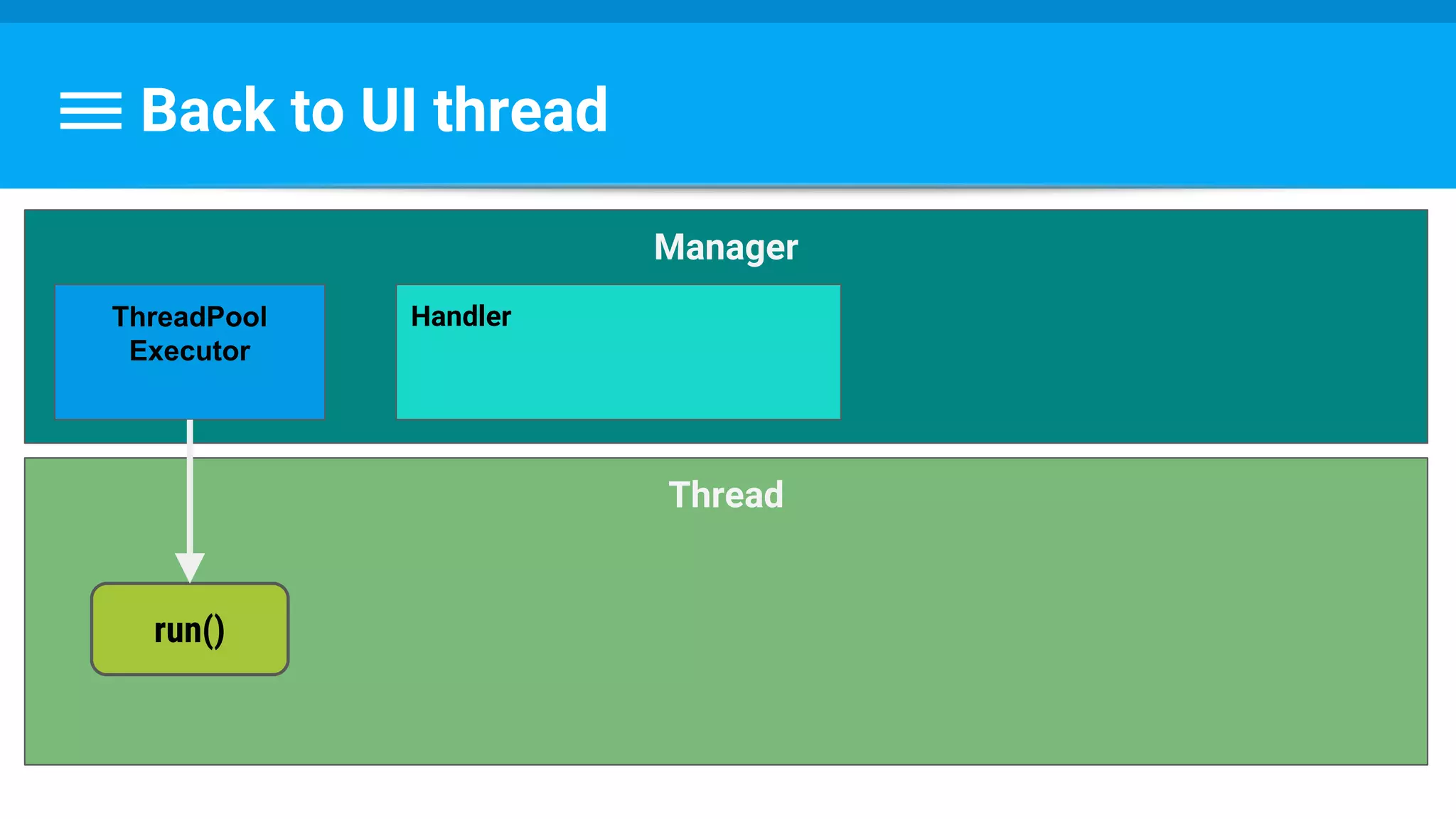

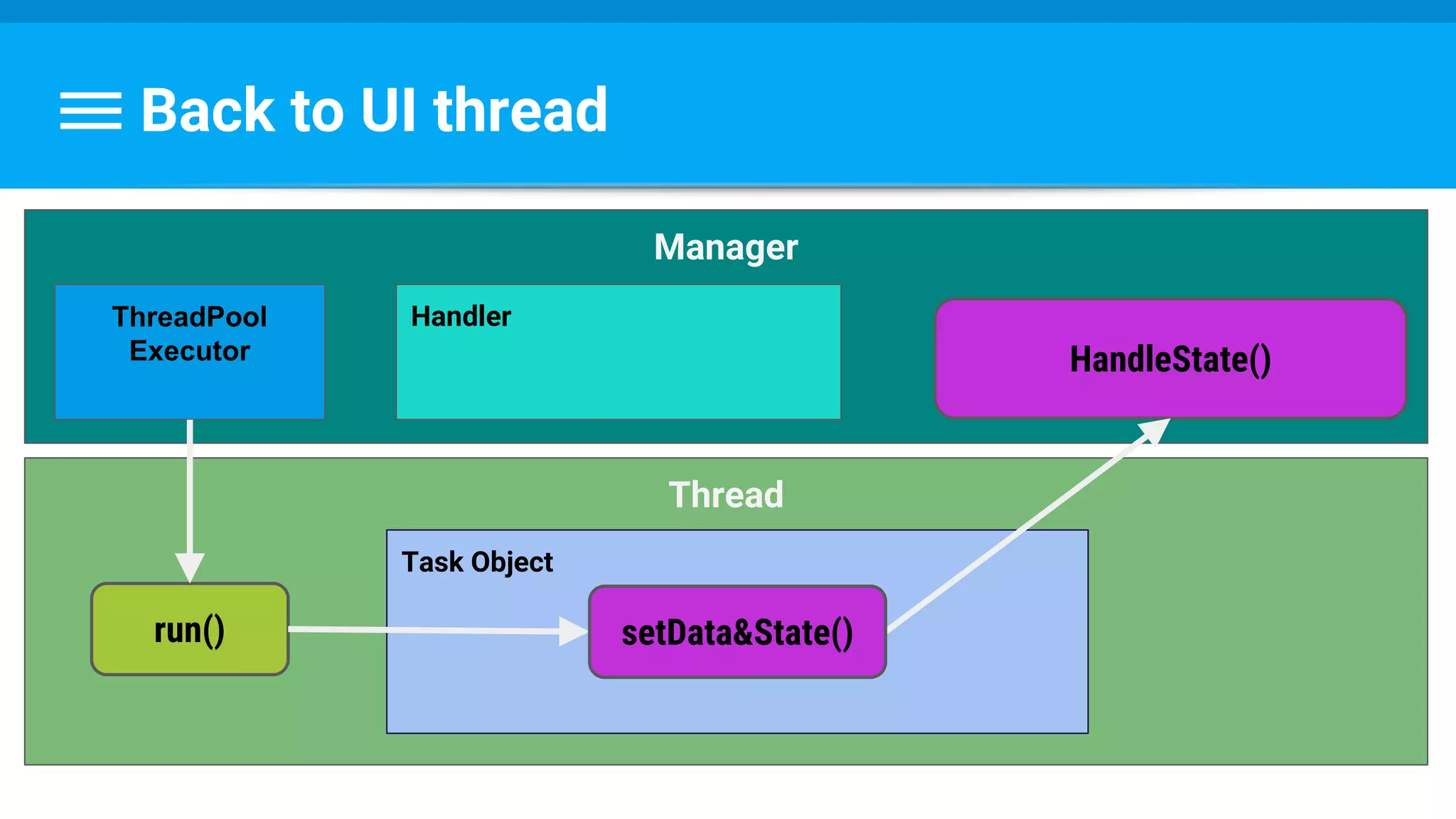
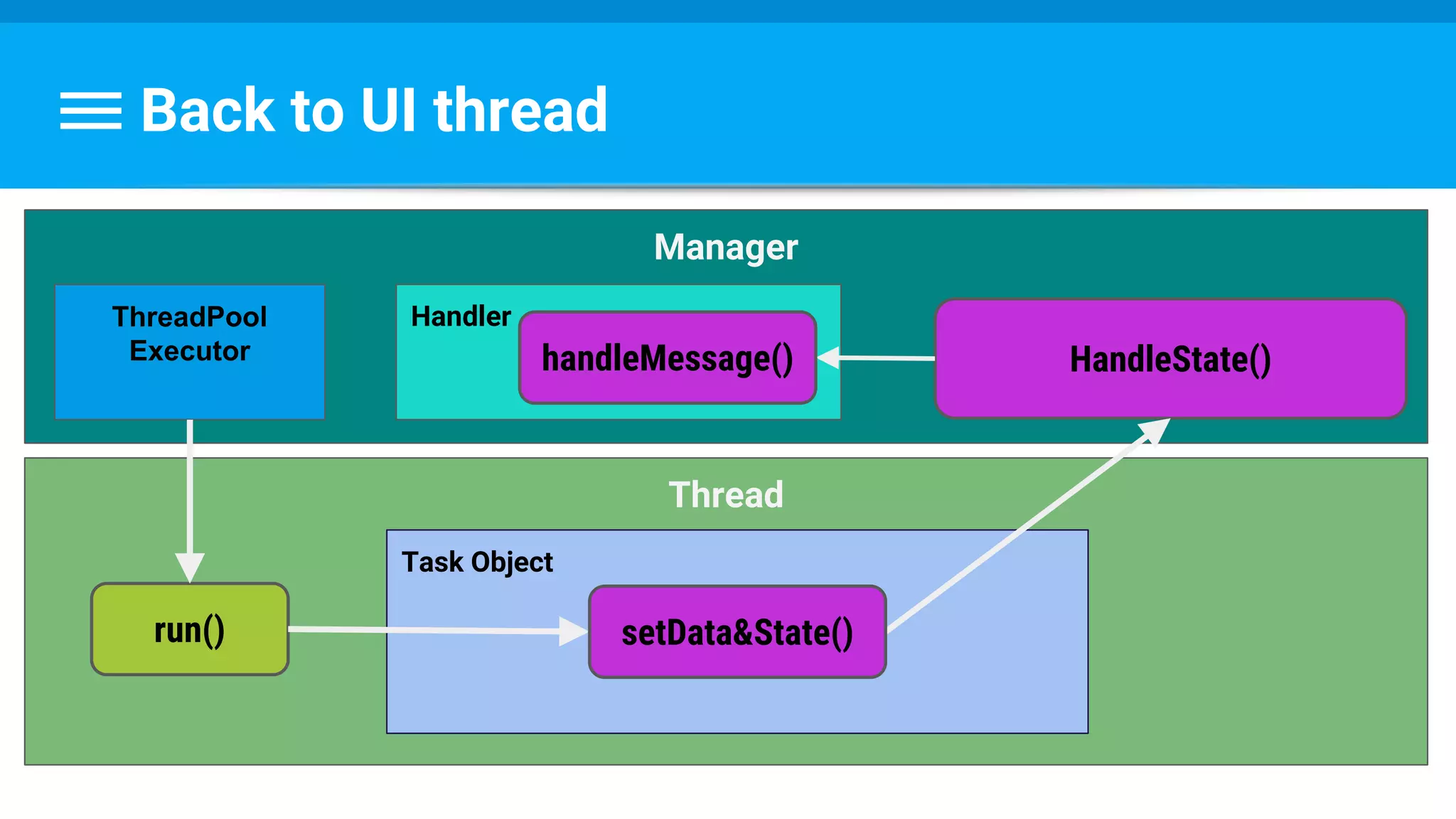
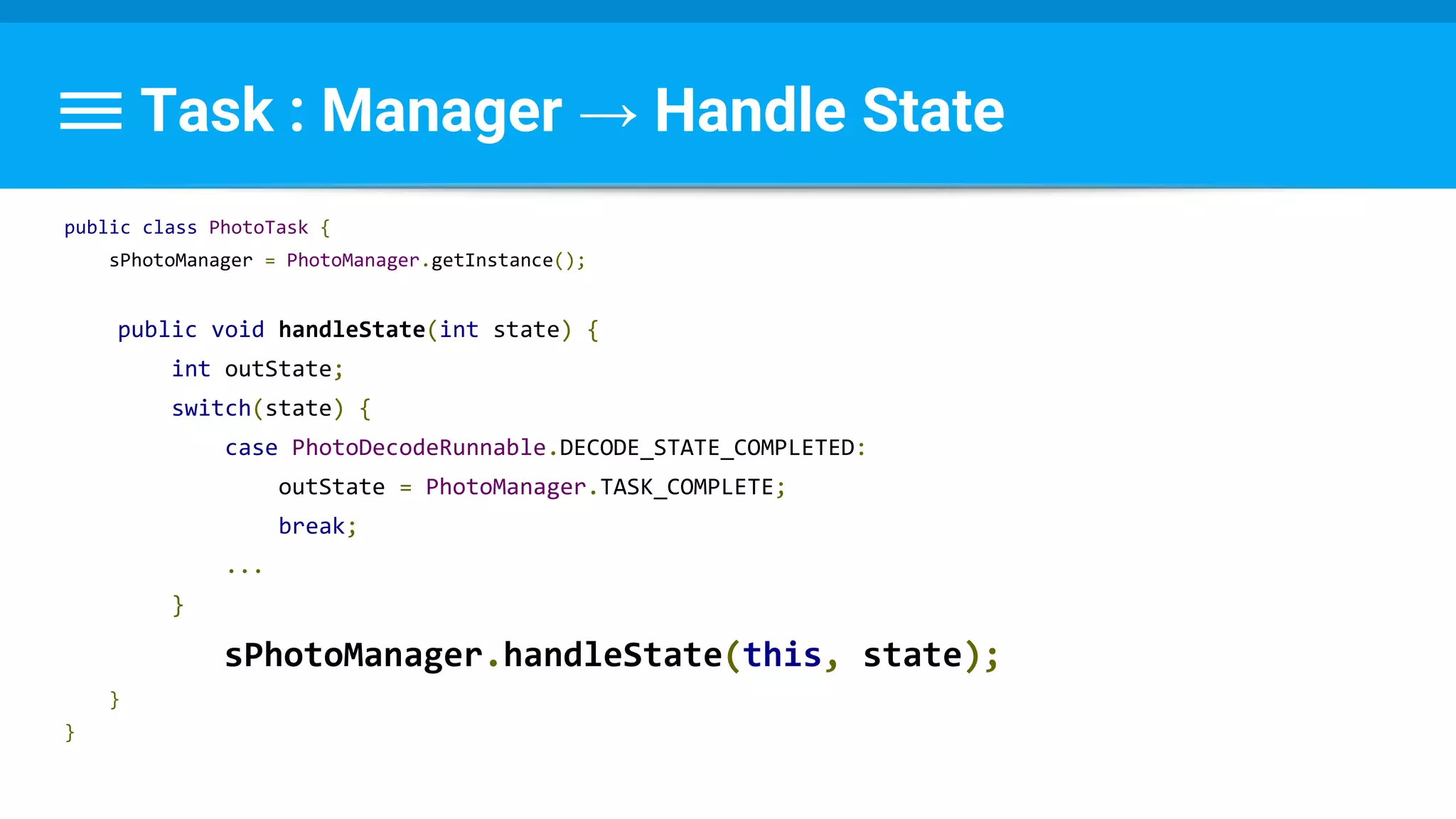
![Runnable : Task → Set Data & State
class PhotoDecodeRunnable implements Runnable {
PhotoDecodeRunnable(PhotoTask downloadTask) {
mPhotoTask = downloadTask;
}
byte[] imageBuffer = mPhotoTask.getByteBuffer();
...
public void run() {
returnBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(imageBuffer, 0,
imageBuffer.length, bitmapOptions);
mPhotoTask.setImage(returnBitmap);
mPhotoTask.handleState(DECODE_STATE_COMPLETED);
...
}
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/performance6-threading-160915191218/75/Performance-6-threading-176-2048.jpg)