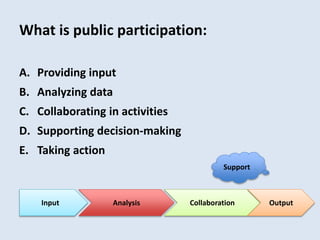
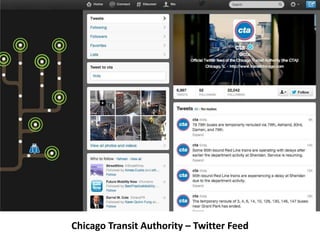
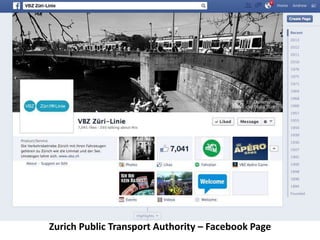
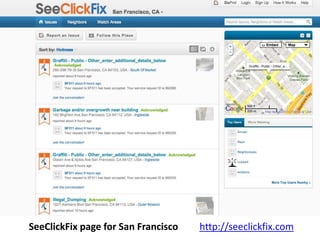
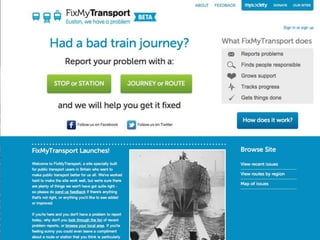
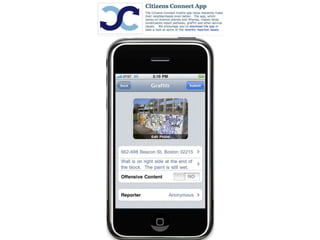
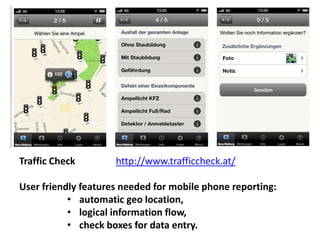
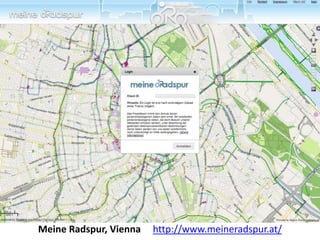
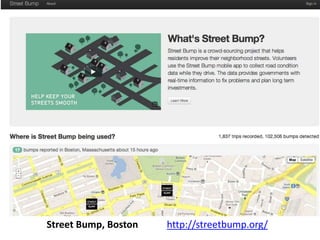
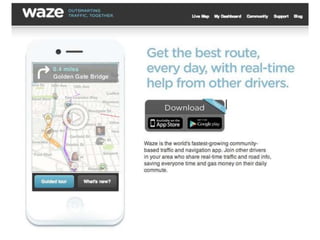
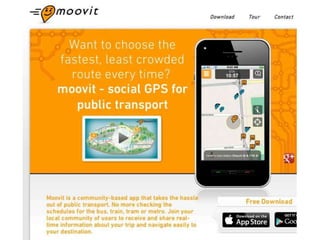
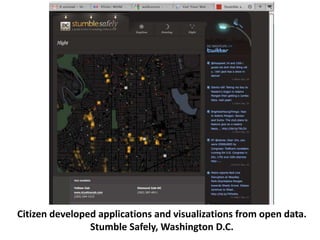
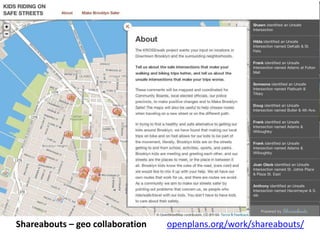
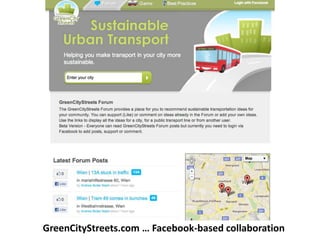
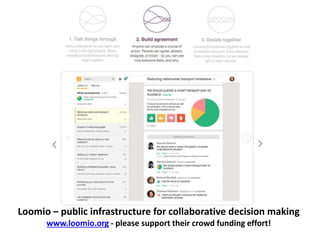
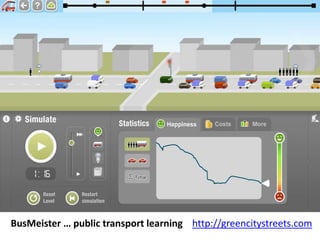
The document discusses how cities can become smart through public participation. It argues that cities are smart when they actively involve the public in management through (1) providing open data, (2) using apps to efficiently harness public input, and (3) recognizing that citizens will find their own solutions if opportunities for participation are not provided. The document provides many examples of apps and projects that facilitate public participation in city governance and management.