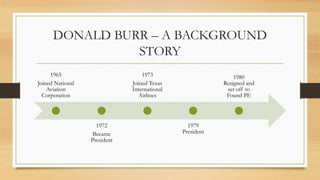
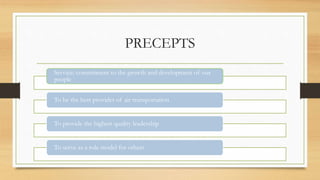
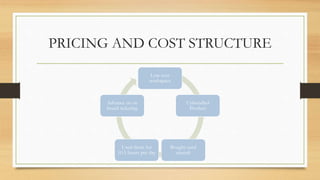
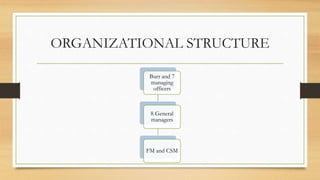
People Express Airlines was founded in 1980 by Donald Burr with a goal of providing superior customer service at very low prices. It grew rapidly through its differentiated approach but faced challenges as major carriers matched its low fares and People Express struggled with operational issues due to overbooking and understaffing. After several acquisitions that increased costs, People Express was unable to compete and declared bankruptcy in 1986.