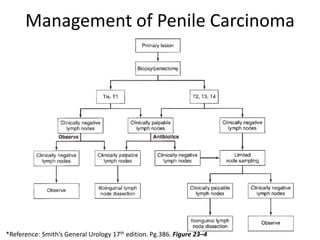
Tumors of the penis are rare, comprising less than 1% of cancers in males. Poor hygiene is a major risk factor. Precancerous conditions include carcinoma in situ and erythroplasia of Queyrat. Invasive squamous cell carcinoma is most common, usually originating on the glans or prepuce. Treatment depends on the size and extent of invasion but may include circumcision, partial or total penectomy, and lymph node dissection. Outcomes are best when the cancer is localized; lymph node involvement significantly worsens prognosis. Squamous cell carcinoma is also the most frequent malignant tumor of the scrotum, treated with wide local excision and lymph node management similar to penile cancer.