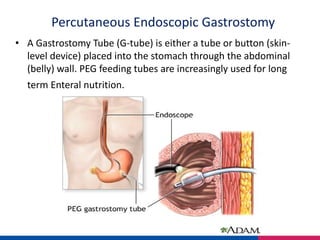
PEG tube care involves placing a feeding tube through the abdominal wall into the stomach. Formula can be given continuously via pump, or through bolus feeds using a syringe or gravity drip. When giving bolus feeds, the nurse washes hands, assembles supplies, flushes the tube with water, measures the formula, injects it slowly via syringe, flushes again with water, and documents the procedure. The site is cleaned daily to prevent infection while protecting the tube. Flushes and medication dilution are also needed to prevent blockages.