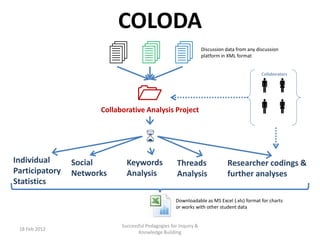
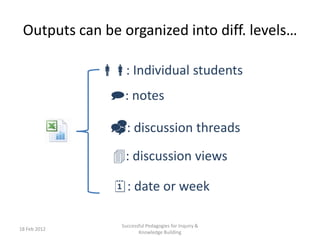
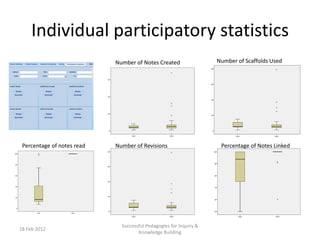
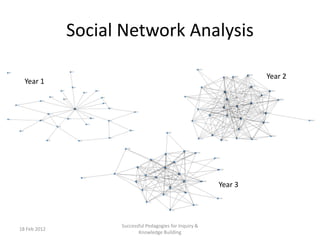
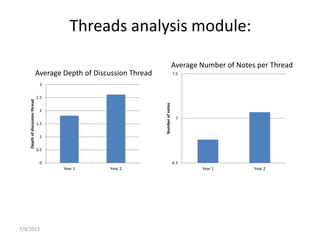
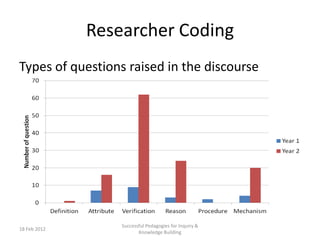
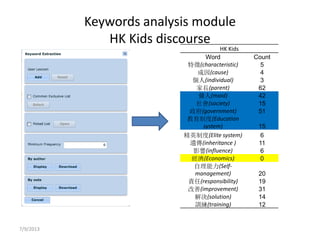
The document discusses the application of big data analytics in both sports and education, emphasizing differences in their settings and methodologies. It highlights various pedagogical approaches and frameworks for evaluating student participation and engagement in online discussions. Furthermore, it outlines the importance of tailored analysis to improve learning outcomes based on individual contributions and discourse quality over time.