The document discusses localizing XSL-FO style sheets for PDF output. It covers topics like locale formatting standards, handling static strings, character sets and fonts, and customizing index grouping. The presenter's company, Suite Solutions, provides services for content lifecycle implementation and maximizing the value of information assets for customers.



![Locale Formatting Standard The formatting standard for locale is [language]_[REGION]. Examples: en_US – English, as spoken in the US pt_PT – Portugese, as spoken in Portugal (“European Portugese”) pt_BR – Portugese, as spoken in Brazil (“Brazilian Portugese”) Other standards (e.g., “en”, “en-us”, “en_us”) may require adjustments to the DITA-OT infrastructure to work properly. A partial list can be found at DITA-OT\doc\installguide\sysreqs.html Languages supported by default for PDF output: en_US, de_DE, es_ES, fr_FR, it_IT, ja_JP, zh_CN](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-5-320.jpg)




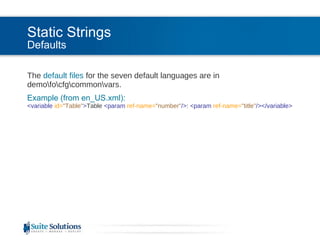
![Static Strings Usage Static strings are inserted using the insertVariable template. Example (from tables.xsl): <xsl:call-template name= "insertVariable" > <xsl:with-param name= "theVariableID" select= "'Table'" /> <xsl:with-param name= "theParameters" > <number> <xsl:number level= "any" count= "*[contains(@class, ' topic/table ')]/*[contains(@class, ' topic/title ')]" from= "/" /> </number> <title> <xsl:apply-templates/> </title> </xsl:with-param> </xsl:call-template>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-11-320.jpg)


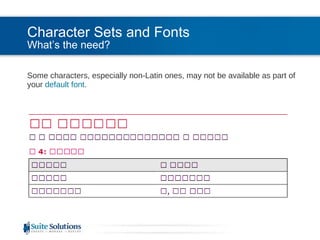
![Character Sets and Fonts What’s the need? Antenna House Warnings: [exec] XSLCmd :INFO: Error Level : 1 [exec] XSLCmd :INFO: Error Code : 24322 (5F02) [exec] XSLCmd :INFO: Missing glyph U+627E (->) in 'Verdana'. [exec] XSLCmd :INFO: Line 664, Col 370, C:\out\topic.fo Or: [exec] AHFCmd :INFO: Error Level : 1 [exec] AHFCmd :INFO: Error Code : 24323 (5F03) [exec] AHFCmd :INFO: Fallbacked glyph U+0161 (š) to 'Times New Roman'. [exec] AHFCmd :INFO: Line 619, Col 441, C:\out\topic.fo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-16-320.jpg)







![Index Grouping What’s the need? The stylesheets need to know how to group various similar but non-identical characters together in the index. [index-preprocess] [ERROR] Index entry '?' is dropped, because corresponding group is not found The transforms don’t know that “u” and “ù” are really the same letter and should both appear under the “U” heading.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-24-320.jpg)




![Miscellaneous Per-language Notation Goal The client wants <uicontrol> to be surrounded by brackets instead of bold in some languages Solution Use the variables file Example (from vars\ja_JP.xml and ui-domain-custom.xsl): <variable id= "UiControlBefore" > [ </variable> <variable id= "UiControlAfter" > ] </variable> <xsl:call-template name= "insertVariable" > <xsl:with-param name= "theVariableID" select= "'UiControlBefore'" /> </xsl:call-template> <xsl:apply-templates/> <xsl:call-template name= "insertVariable" > <xsl:with-param name= "theVariableID" select= "'UiControlAfter" /> </xsl:call-template>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-30-320.jpg)





![End of Localizing XSL-FO Style Sheets for PDF Be in touch! Reuven Weiser [email_address] Let us know how we can help you further… Stylesheet development One-on-one support and training CMS integration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/suite-webinar-pdflocalization-100818070042-phpapp01/85/PDF-Localization-37-320.jpg)