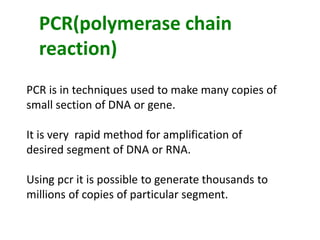
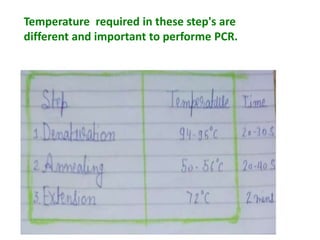
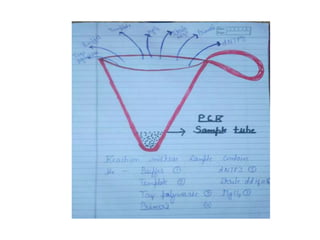
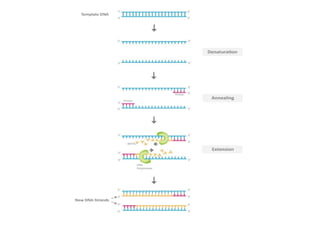
The document provides an overview of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), detailing its definition, materials, methods, advantages, and applications. It outlines the steps involved in PCR, including denaturation, annealing, and extension, along with the role of Taq polymerase and various other components. Additionally, it discusses the traditional limitations of PCR and introduces different types such as real-time PCR and multiplex PCR for various applications including forensic science and genetic testing.