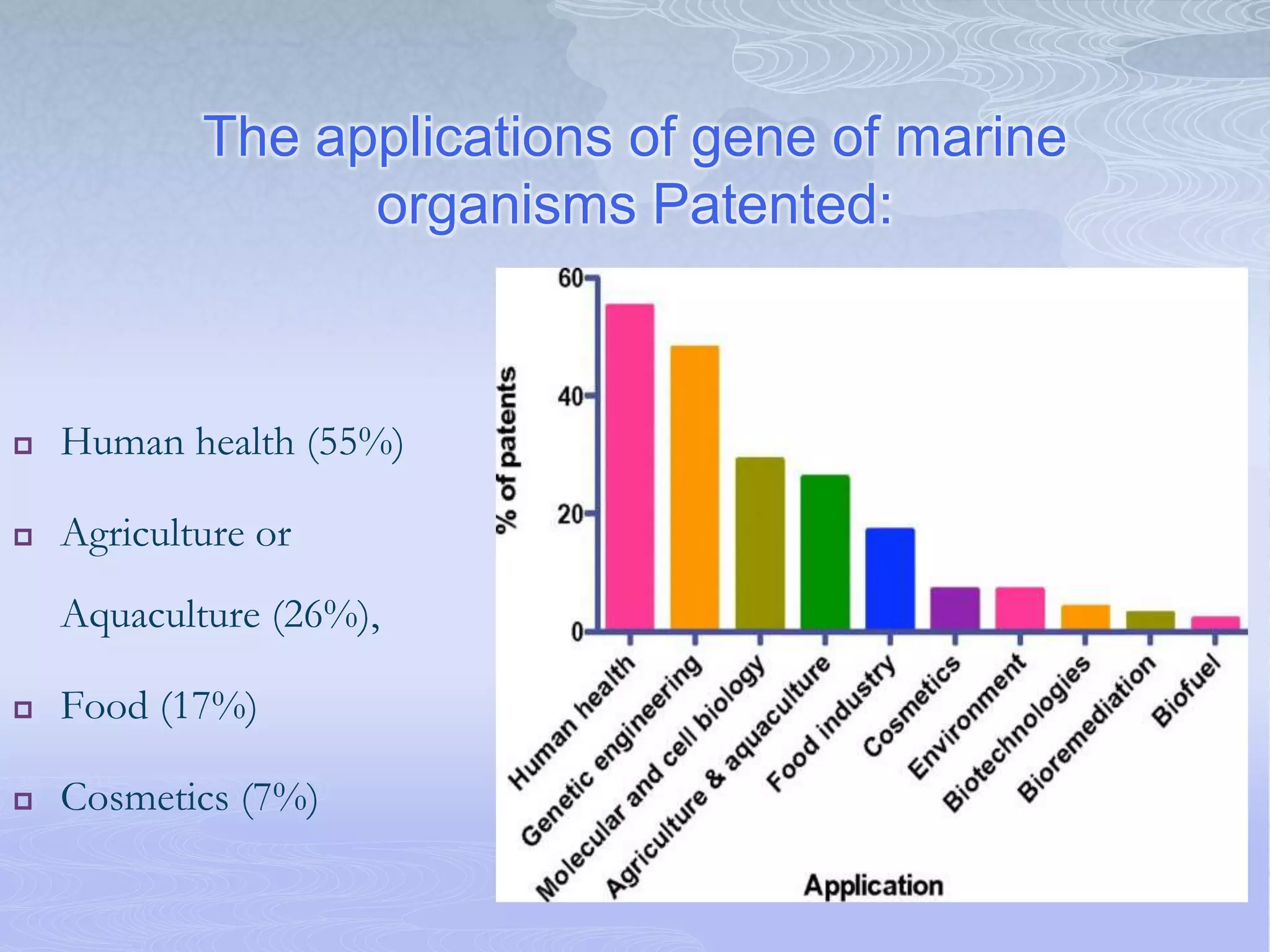
The document discusses patenting trends and challenges related to marine biodiversity, highlighting its significance for sustainable development and the legal frameworks governing it in India and globally. It presents statistics on marine species, patent applications, and the exploitation of marine genetic resources, along with recommendations for stronger international and national conservation laws. The authors emphasize the urgent need for policies that protect marine ecosystems to prevent biodiversity loss.