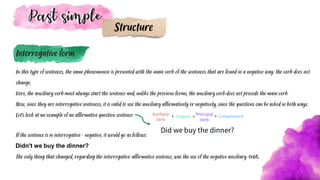
The document explains the use of the simple past tense in English, detailing its structure, conjugation of regular and irregular verbs, and how to form negative and interrogative sentences. It highlights the importance of understanding verb conjugation rules, including how some verbs change form completely in the past. The document also includes examples and exercises for better comprehension of the simple past tense.