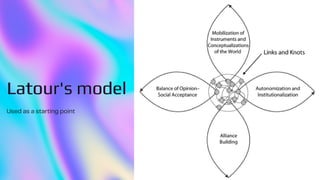
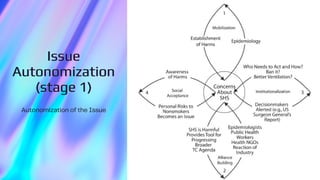
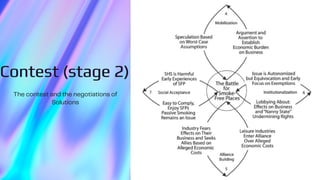
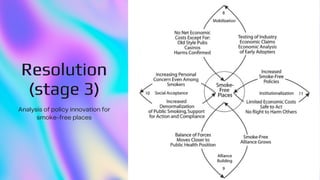
The document explores the application of actor-network theory in analyzing innovations for smoke-free indoor places, emphasizing the importance of various human and non-human actors in this process. It outlines three stages: autonomization of the issue, contest and negotiation of solutions, and resolution, highlighting how public engagement and institutional support are critical for success. Additionally, it suggests that collaborative networks can lead to effective solutions for complex public health issues.