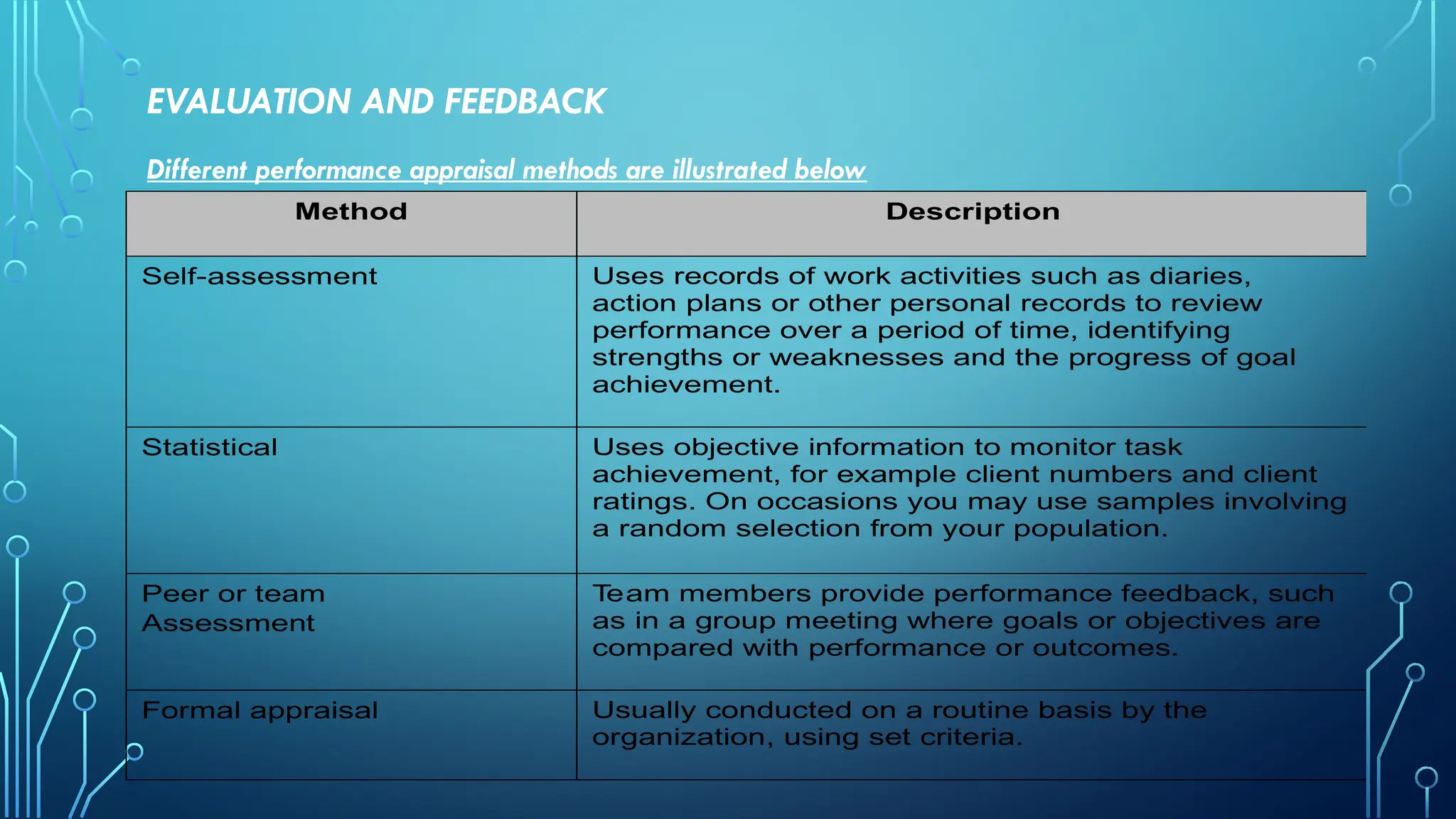
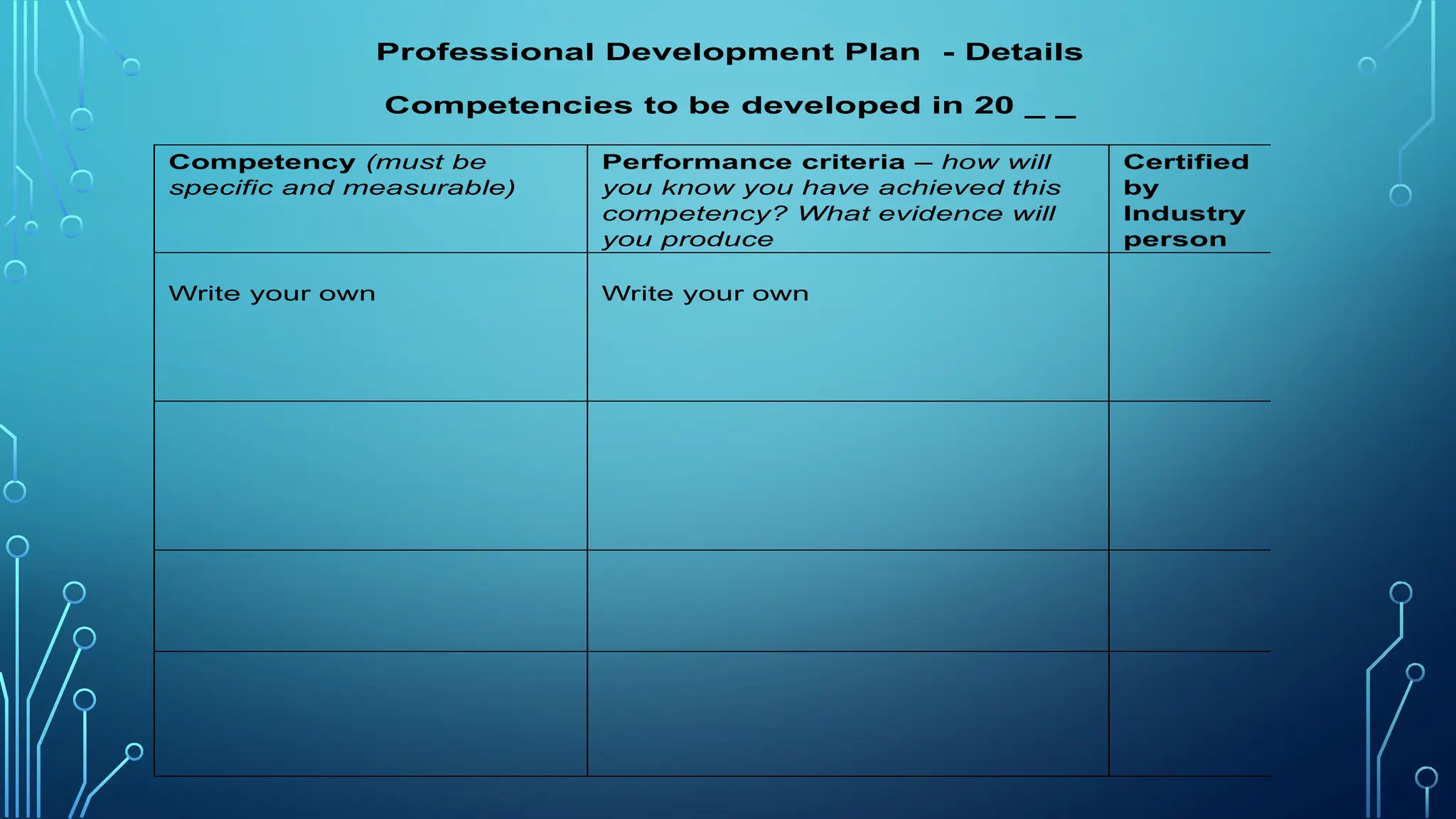
This document outlines the importance of maintaining and enhancing professional practices across various fields through continuous learning, ethical behavior, and reflection on personal performance. It details strategies for modeling high standards of performance, determining personal development needs, and engaging in professional development activities to ensure alignment with industry standards and ongoing professional growth. Additionally, it emphasizes assessing skill gaps, seeking feedback, and participating in professional networks to foster continuous learning.