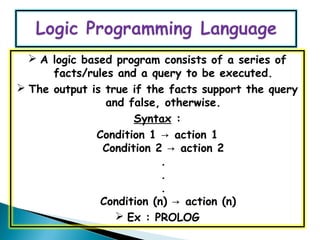
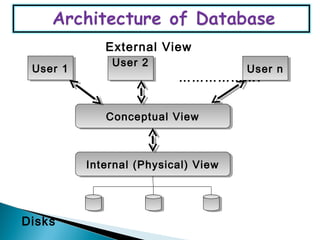
The document discusses different types of programming languages including declarative languages which are fact-oriented and do not consider sequence of execution, logic programming languages which use symbolic logic for programming, and functional languages which perform all computations through function applications. It also covers database languages which include DDL for data definition, DML for data manipulation like insertion and deletion, and DCL for data control through operations like commit and rollback.