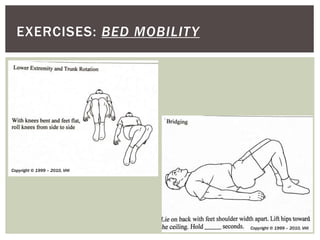
This document provides information on exercise for individuals with Parkinson's disease. It describes typical movement impairments in Parkinson's such as tremors, rigidity, and impaired mobility. It explains that regular exercise can help manage symptoms, possibly slow disease progression, and improve mobility and quality of life. The document recommends consistent, moderate to vigorous exercise 4-5 times per week and identifies specific programs such as PWR!Moves and exercises including bed mobility, balance, sit-to-stand, walking, and aerobic exercises. It emphasizes practicing exercises regularly with guidance from a physical or occupational therapist.