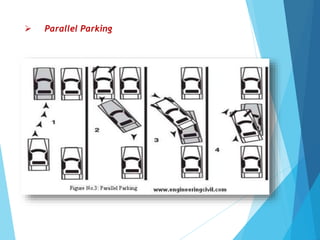
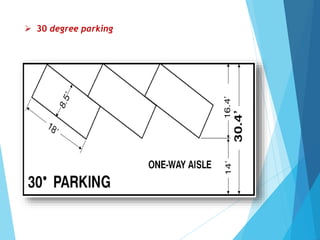
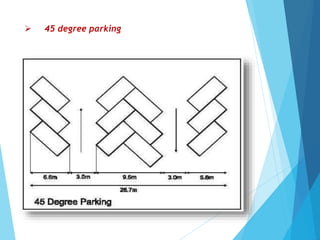
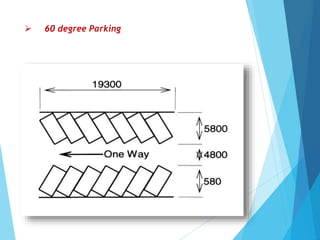
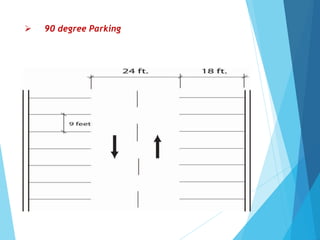
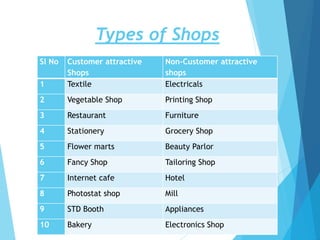
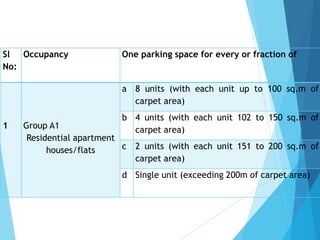
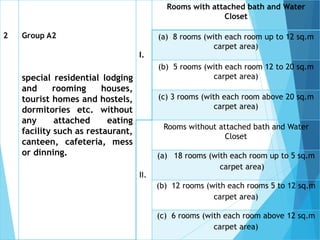
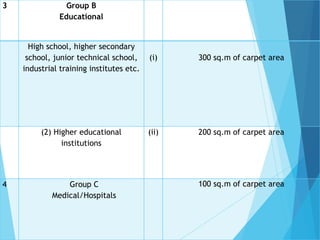
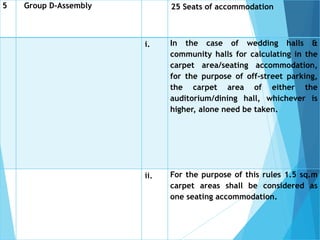
The document discusses the significant parking problems resulting from road traffic, particularly in the Pattambi-Cherpulassery area. It outlines objectives such as studying parking characteristics, identifying traffic and parking issues, and proposing improvements. The document also details different types of parking facilities and studies to assess current usage and demands, aiming to alleviate congestion and enhance parking availability.