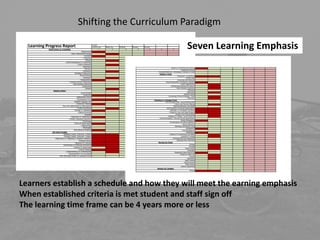
The document discusses the need for a paradigm shift in education, emphasizing a move from a one-size-fits-all model to a learner-centered approach that leverages current research on learning and available technology. It outlines a vision for a transformed educational environment that fosters individual growth, collaboration, creativity, and relevance while integrating various subjects and real-world applications. The shift aims to produce well-rounded citizens capable of thriving in a changing world, with a focus on personalized learning plans and community involvement.