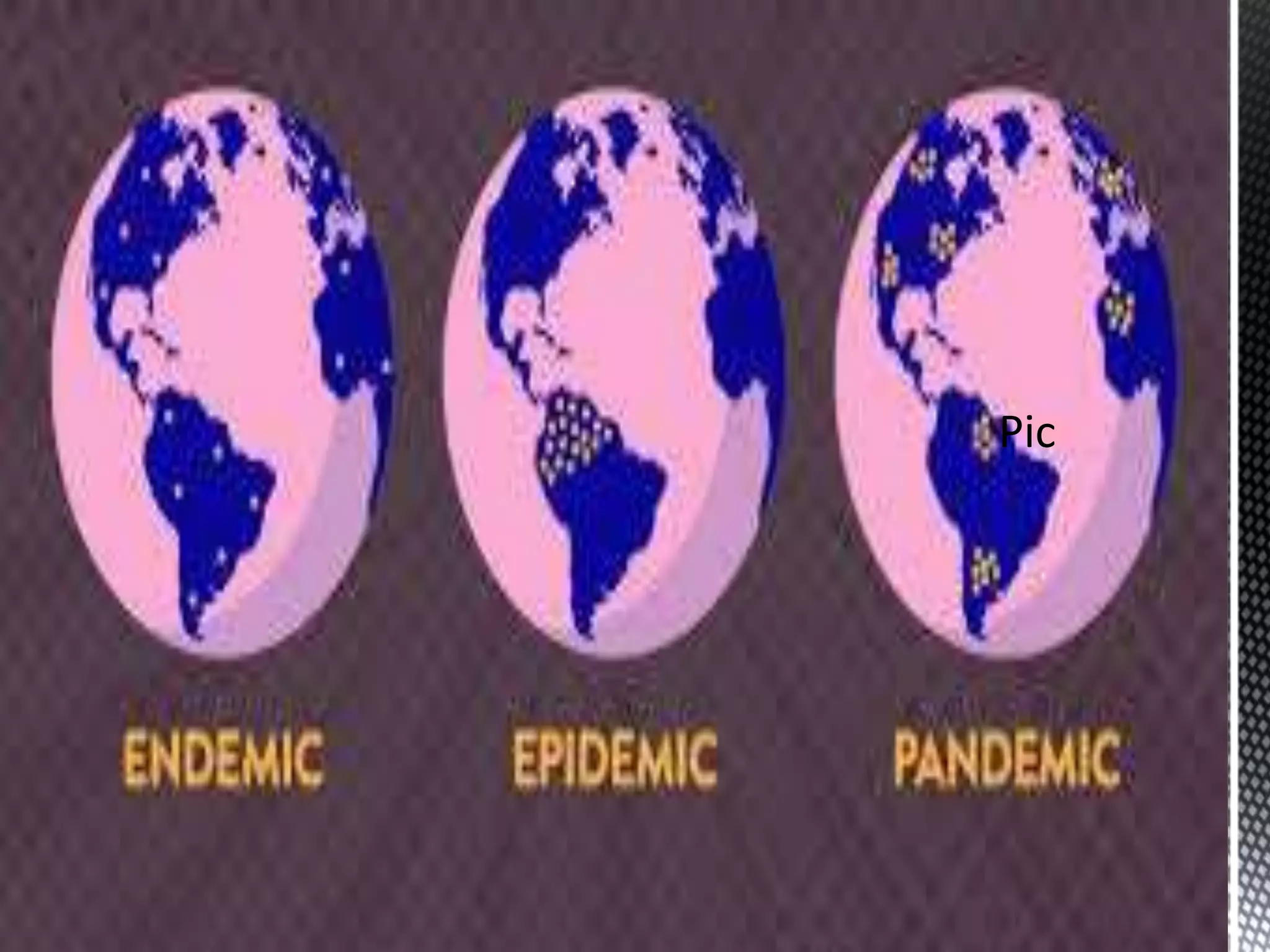
This document discusses the COVID-19 pandemic. It defines a pandemic as an epidemic that has spread over a large region, such as multiple countries or worldwide. The coronavirus pandemic originated as an epidemic but spread globally, infecting more people and areas. A pandemic crosses international borders and affects a larger population than an epidemic. The document provides details on viruses, viral infections, the uniqueness of coronaviruses, those most vulnerable, prevention methods like social distancing, and precautions against the virus.